When classifying coatings, the most common and practical framework is to categorize them by their end-use or market application. The three primary types are Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose. While you may encounter other classifications based on the specific application process, such as those for PVD, understanding these three high-level categories provides the clearest strategic overview.
The most effective way to understand coatings is to first define the problem you are trying to solve. Classifying by application—Architectural, Industrial, or Special Purpose—aligns the coating's characteristics directly with the demands of the environment it will serve.
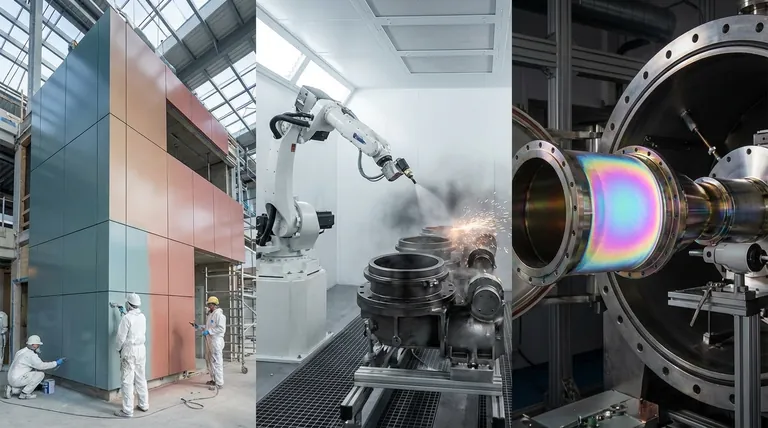
The Primary Framework: Classification by Application
Thinking about coatings by their end-use is the industry standard. This approach immediately clarifies the performance requirements, cost expectations, and typical chemistries involved in any given project.
Architectural Coatings
Architectural coatings are what most people think of as "paint." They are designed for use on residential, commercial, and institutional buildings.
Their primary purpose is decorative, but they also provide surface protection against weather, moisture, and general wear. These coatings are typically applied on-site to stationary structures.
Industrial Coatings
Industrial coatings are engineered for performance and protection in manufacturing and industrial settings. They are applied to a wide range of products, including machinery, automotive parts, pipelines, and appliances.
The key drivers for this category are durability, corrosion resistance, and chemical resistance. Unlike architectural coatings, these are often applied in a factory setting as part of the production process.
Special Purpose Coatings
This is a high-performance category for applications with unique or extreme requirements. These coatings are designed to perform a specific function that commodity paints cannot.
Examples include marine coatings that prevent biofouling on ship hulls, aerospace coatings that withstand extreme temperatures, or coatings that provide electrical insulation. They are defined by their highly specific and demanding performance criteria.
Understanding an Alternate Framework: Classification by Process
It is important to recognize that coatings can also be categorized by the technology used to apply them. This often causes confusion, as a specific process is a method for achieving an end-use, not a market category in itself.
The Example of PVD Coatings
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is an advanced coating process, not an end-use category. PVD coatings are applied in a vacuum environment and are known for being extremely thin yet durable.
The three main types of PVD processes are thermal evaporation, sputter deposition, and arc vapor deposition. Each method has unique characteristics, but they all fall under the PVD umbrella.
A PVD coating applied to a drill bit for hardness would be classified as an Industrial coating. If applied to a satellite component for thermal control, it would be a Special Purpose coating. The process serves the application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right coating requires understanding the fundamental trade-offs between these categories. Focusing on the wrong criteria can lead to project failure or unnecessary expense.
Performance vs. Cost
Architectural coatings are generally optimized for aesthetic appeal and low cost. Industrial and Special Purpose coatings, however, prioritize performance far above cost. The price per gallon can differ by orders of magnitude.
Application Complexity
Architectural coatings are designed for simple on-site application by brush, roller, or spray. Industrial and Special Purpose coatings often require specialized equipment, factory conditions, and complex surface preparation.
Generality vs. Specificity
The categories move from broad to narrow. Architectural coatings are general-purpose. Industrial coatings are designed for specific industries or products. Special Purpose coatings are engineered for a single, highly specific function.
How to Select the Right Coating Category
To determine the correct path, start by defining your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and general protection for structures: You are in the realm of Architectural coatings.
- If your primary focus is durability and protection for manufactured goods or equipment: Your needs fall under the category of Industrial coatings.
- If your primary focus is a unique performance characteristic for a high-stakes application: You will need to investigate Special Purpose coatings.
Ultimately, defining your goal is the first and most critical step in navigating the world of coatings.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Primary Purpose | Typical Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architectural | Decoration & Weather Protection | Buildings, Houses | Aesthetic appeal, cost-effective, easy on-site application |
| Industrial | Durability & Corrosion Resistance | Machinery, Automotive Parts, Appliances | High performance, factory-applied, chemical resistance |
| Special Purpose | Extreme Performance for Specific Needs | Marine, Aerospace, Electronics | Highly specialized, unique functions, high-stakes applications |
Struggling to select the right coating for your lab equipment or industrial application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance coatings and lab equipment solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our expertise ensures you get the durability, corrosion resistance, and precision required for demanding environments. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- 400-700nm Wavelength Anti Reflective AR Coating Glass
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Nickel Foam for Industrial and Laboratory Applications
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer



















