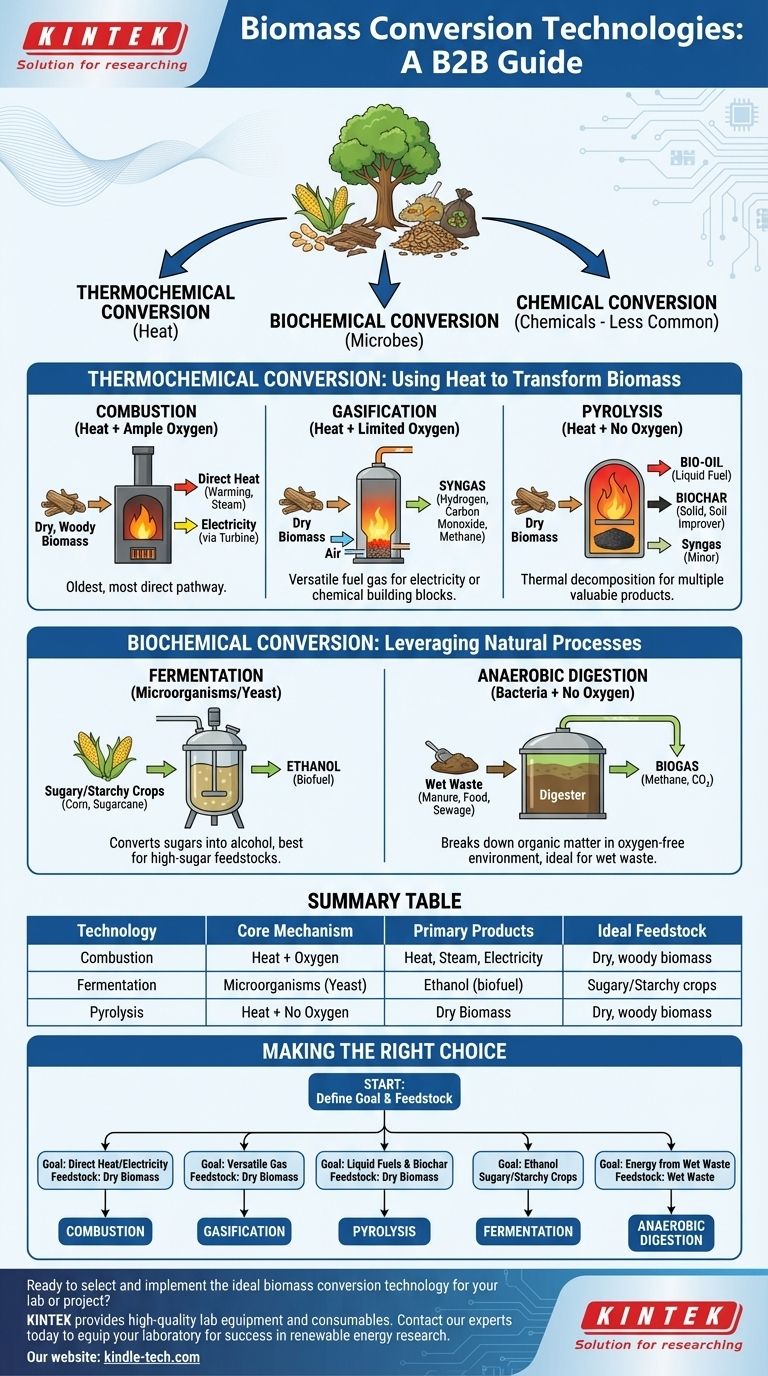
At its core, biomass conversion involves transforming organic matter into usable energy and products through three primary pathways: thermochemical, biochemical, and chemical processes. Thermochemical methods use heat, while biochemical methods use microorganisms to achieve this transformation.
The fundamental difference between biomass conversion technologies lies in their core mechanism—heat, microbes, or chemicals—which dictates the final product you can create, whether it's direct heat, a liquid biofuel, a combustible gas, or valuable solids like biochar.

Thermochemical Conversion: Using Heat to Transform Biomass
This is the most common category of biomass conversion. These processes use heat and controlled chemical reactions to break down the complex structure of organic material. The specific conditions, particularly the levels of heat and oxygen, determine the outcome.
Combustion: The Direct Path to Heat
Combustion is simply the direct burning of biomass in the presence of ample oxygen. It is the oldest and most straightforward energy conversion technology known.
The primary and often sole goal of combustion is to release the stored chemical energy as heat. This heat can be used directly for warming spaces, producing industrial steam, or turning a turbine to generate electricity.
Gasification: Creating a Versatile Fuel Gas
Gasification involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen, not enough for full combustion. This process doesn't primarily produce heat; it produces a combustible gas mixture.
This mixture, known as syngas (synthesis gas), is rich in hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. Syngas is highly versatile and can be burned to generate electricity or used as a chemical building block to produce liquid fuels and other valuable chemicals.
Pyrolysis: Decomposing Biomass Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass at high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen. This process breaks down organic materials into a mix of solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
The main products are bio-oil (a liquid that can be upgraded to transportation fuel), biochar (a charcoal-like solid that improves soil and sequesters carbon), and a smaller amount of syngas. The lack of oxygen prevents the biomass from burning, allowing these valuable components to be captured.
Biochemical Conversion: Leveraging Natural Processes
Unlike thermochemical methods, biochemical conversion operates at much lower temperatures and uses bacteria, yeasts, and other microorganisms to break down biomass. These are essentially harnessed and accelerated versions of natural decomposition.
Fermentation: Producing Biofuels like Ethanol
Fermentation uses microorganisms, typically yeast, to convert the sugars in biomass into alcohol, most commonly ethanol. This is the same fundamental process used to make alcoholic beverages.
This pathway is best suited for feedstocks with high sugar or starch content, such as corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic materials that have been pre-treated to release their sugars. The resulting ethanol is a high-value liquid fuel often used as a gasoline additive.
Anaerobic Digestion: Generating Biogas from Wet Waste
Anaerobic digestion uses bacteria to break down organic matter in an oxygen-free environment. This process is ideal for wet, high-moisture feedstocks like animal manure, sewage sludge, and food waste.
The primary output is biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. This biogas can be captured and burned to produce heat and electricity or purified to create renewable natural gas (RNG).
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a conversion technology is not about finding the "best" one, but the right one for your specific feedstock and desired outcome. Each pathway comes with distinct advantages and limitations.
Feedstock Flexibility vs. Specificity
Combustion and gasification are generally more flexible and can process a wide range of dry, woody biomass. In contrast, fermentation requires specific sugar or starch inputs, and anaerobic digestion works best with very wet organic waste.
End-Product Value and Complexity
Combustion produces heat, the lowest-value end product, but through the simplest and cheapest process. Pyrolysis and fermentation can create high-value liquid fuels and chemicals, but the technology required is more complex and expensive.
Process Speed and Efficiency
Thermochemical processes like combustion and gasification are very fast, converting biomass in seconds or minutes. Biochemical processes like fermentation and anaerobic digestion are much slower, often taking days or weeks to complete.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your starting material and your desired final product are the two factors that determine the optimal conversion technology.
- If your primary focus is direct heat or electricity from dry biomass: Combustion is the most direct and established technology.
- If your primary focus is creating a versatile gaseous fuel from dry biomass: Gasification is the ideal choice for producing syngas.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuels and biochar for soil improvement: Pyrolysis offers a balanced output of both valuable products.
- If your primary focus is producing ethanol from sugary or starchy crops: Fermentation is the specific and highly effective pathway.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste while producing energy: Anaerobic digestion is the most suitable and efficient method.
Understanding these distinct conversion pathways is the first step in harnessing the immense potential of biomass as a renewable resource.
Summary Table:
| Technology Type | Core Mechanism | Primary Products | Ideal Feedstock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Heat + Oxygen | Heat, Steam, Electricity | Dry, woody biomass |
| Gasification | Heat + Limited Oxygen | Syngas (for fuel/chemicals) | Dry biomass |
| Pyrolysis | Heat + No Oxygen | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas | Dry biomass |
| Fermentation | Microorganisms (Yeast) | Ethanol (biofuel) | Sugary/Starchy crops |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Bacteria (No Oxygen) | Biogas (Methane/CO₂) | Wet waste (manure, food) |
Ready to select and implement the ideal biomass conversion technology for your lab or project? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your research and development in renewable energy. Whether you need precise reactors for pyrolysis studies, fermenters for biofuel production, or analytical tools to monitor your processes, our solutions are designed for accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your laboratory for success in biomass conversion.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How big is the hot isostatic pressing market? Growth Drivers in Aerospace, Medical & 3D Printing
- What does HIP process do? Eliminate Porosity for Superior Material Performance
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What is the temperature of a warm isostatic press? Achieve Optimal Densification for Your Materials
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process



















