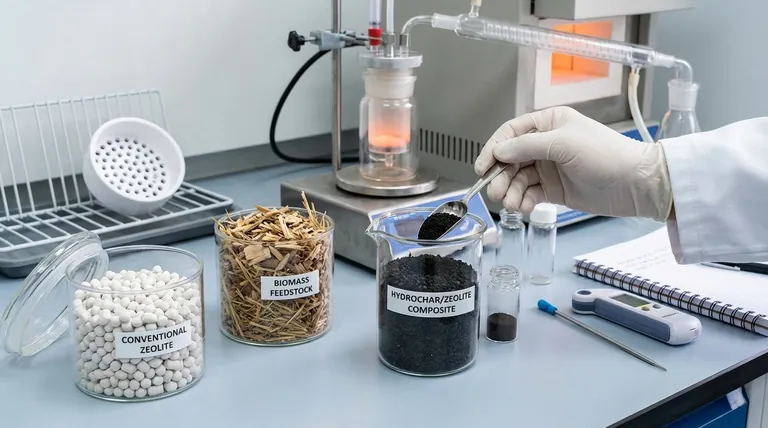
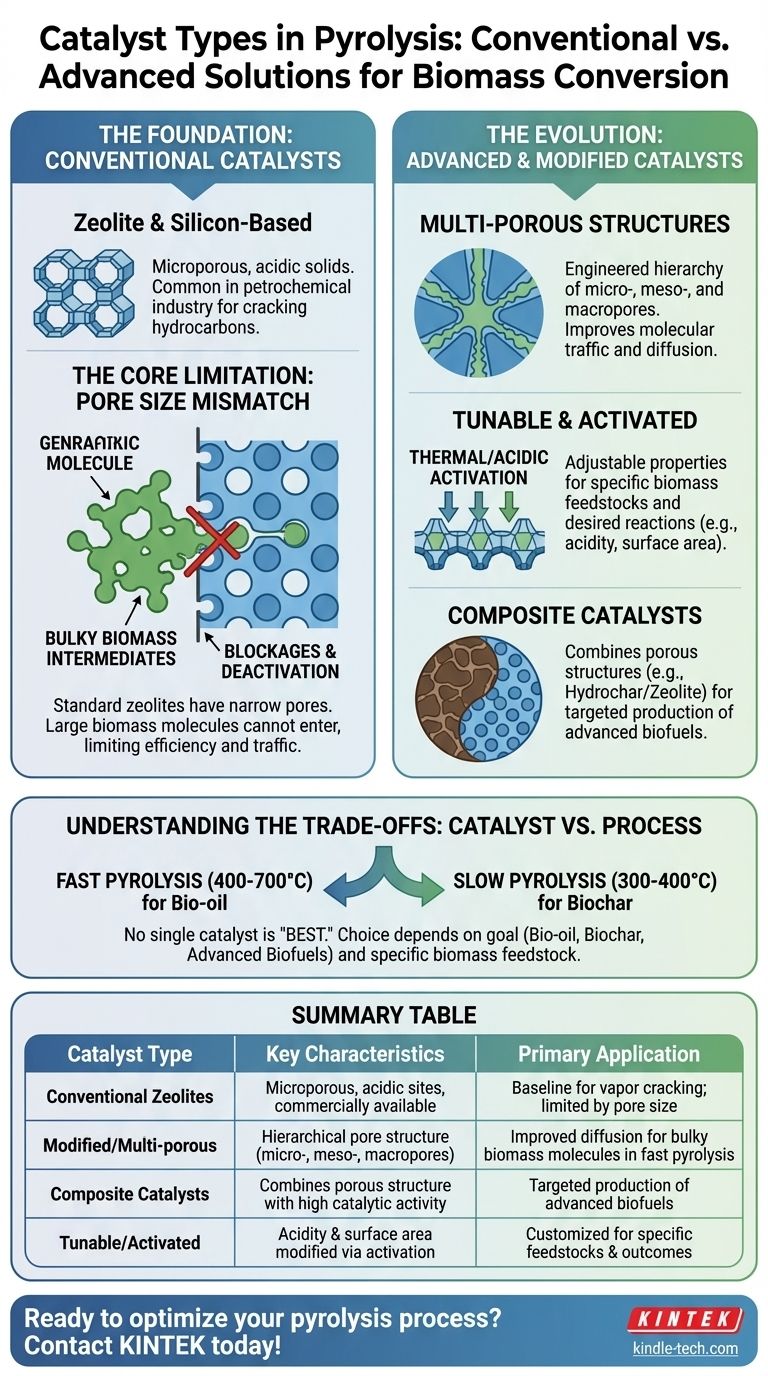
At its core, the catalysts used in biomass pyrolysis fall into two main categories: conventional catalysts borrowed from the petrochemical industry, such as zeolites, and advanced or modified catalysts specifically designed to handle the unique challenges of biomass. While commercial zeolites are common, their narrow pore structure is often inefficient for processing the large, complex molecules found in natural biomass.
The central challenge in catalytic pyrolysis is that standard catalysts are not designed for bulky biomass. The most effective strategies, therefore, involve modifying these catalysts or creating new composite materials to improve their structure and tune their chemical activity for specific outcomes like bio-oil or biochar.

The Foundation: Conventional Catalysts
Conventional catalysts serve as the baseline for pyrolysis but come with significant limitations when applied to biomass. Understanding these limitations is key to appreciating the need for more advanced solutions.
Zeolite and Silicon-Based Catalysts
Zeolites are microporous, crystalline solids commonly used in the petrochemical industry. Their well-defined pore structure and acidic sites make them effective for cracking long-chain hydrocarbons into smaller, more valuable molecules.
Due to their proven success and commercial availability, zeolites were a natural first choice for researchers exploring the catalytic upgrading of pyrolysis vapors.
The Core Limitation: Pore Size Mismatch
The primary issue with conventional catalysts is a physical one. The natural polymers in biomass, like cellulose and lignin, break down into bulky molecular intermediates.
These large molecules cannot easily enter the narrow pores of standard zeolites, leading to blockages and rapid deactivation of the catalyst. This "molecular traffic" problem severely limits their efficiency and suitability for large-scale biomass applications.
The Evolution: Advanced and Modified Catalysts
To overcome the shortfalls of conventional catalysts, researchers have developed innovative methods to redesign catalysts specifically for the demands of biomass pyrolysis.
Creating Multi-Porous Structures
The most direct solution is to engineer catalysts with a multidimensional structure. This involves creating a hierarchy of pore sizes: micropores for chemical reactions, and larger meso- and macropores that act as highways for bulky molecules to travel into the catalyst.
This improved structure enhances molecular traffic control, allowing for better diffusion and increasing the number of accessible active sites for reaction.
Tunable and Activated Catalysts
Biomass is not a uniform material; its properties vary significantly between sources like wood, straw, or agricultural waste. This necessitates tunable catalysts that can be adjusted to favor specific reactions.
Methods like thermal or acidic activation can modify a catalyst like natural zeolite, enhancing its surface area and acidity. This fine-tuning allows operators to target the production of more desirable compounds from a specific feedstock.
Composite Catalysts: The Next Frontier
A more advanced approach involves creating entirely new materials. Hydrochar/zeolite composite catalysts are an excellent example.
By combining the porous structure of hydrochar (a product of biomass treatment) with the catalytic activity of zeolites, these composites resolve diffusion limitations. They are particularly promising for producing advanced biofuels like biodiesel and bio-gasoline.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Catalyst vs. Process
The choice of a catalyst cannot be made in isolation. It is deeply intertwined with the pyrolysis process conditions and the specific type of biomass being used.
Why No Single Catalyst Is "Best"
The ideal catalyst depends entirely on your goal. Fast pyrolysis, which uses high temperatures (400-700°C) to maximize liquid bio-oil, requires a catalyst that can rapidly crack vapors.
In contrast, slow pyrolysis, which uses lower temperatures (300-400°C) to produce biochar, may use a catalyst to influence the char's final properties rather than to crack vapors. A catalyst optimized for one process is rarely optimal for the other.
The Challenge of Biomass Variability
The chemical makeup of the biomass feedstock dictates the types of molecules the catalyst will encounter. A catalyst that works well for low-lignin agricultural waste may perform poorly with high-lignin hardwood.
Therefore, a successful catalytic pyrolysis system requires a holistic approach, matching the catalyst not only to the process but also to the specific chemical nature of the input material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a catalytic strategy requires a clear understanding of your primary objective. Different goals demand different types of catalysts and process conditions.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil yield: Prioritize catalysts with multi-porous structures and high acidity, such as modified zeolites, used within a fast pyrolysis reactor.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: The catalyst's role is secondary to process control in slow pyrolysis, but additives can be used to functionalize the final char product.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced, specific biofuels: Investigate emerging composite catalysts, like hydrochar/zeolite, which offer greater control over the final chemical composition of the liquid product.
Ultimately, effective biomass pyrolysis depends on designing a catalytic system that harmonizes the feedstock, the process, and the desired end product.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst Type | Key Characteristics | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Zeolites | Microporous, acidic sites, commercially available | Baseline for vapor cracking; limited by pore size for biomass |
| Modified/Multi-porous Catalysts | Hierarchical pore structure (micro-, meso-, macropores) | Improved diffusion for bulky biomass molecules in fast pyrolysis |
| Composite Catalysts (e.g., Hydrochar/Zeolite) | Combines porous structure with high catalytic activity | Targeted production of advanced biofuels (biodiesel, bio-gasoline) |
| Tunable/Activated Catalysts | Acidity and surface area modified via thermal/acidic treatment | Customized for specific biomass feedstocks and desired outcomes |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process with the right catalyst?
The choice of catalyst is critical to achieving your specific goals, whether it's maximizing bio-oil yield, producing functionalized biochar, or creating advanced biofuels. KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your research and development needs in biomass conversion.
Our experts can help you select the right tools to test and evaluate catalyst performance for your unique feedstock and process conditions.
Contact KINTELK today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your pyrolysis efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized for POEGMA electrolyte conductivity? Ensure Precision in Electrochemical Measurements
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car



















