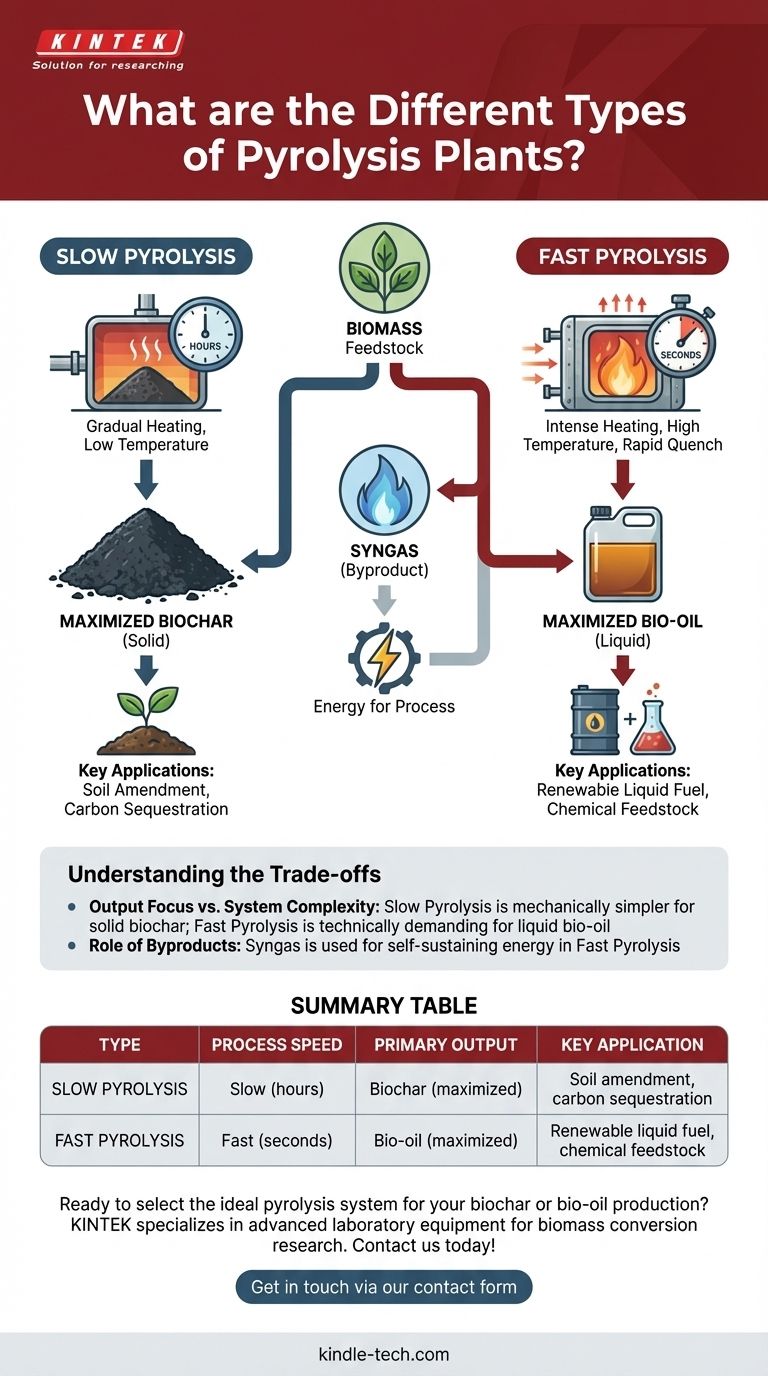
At its core, pyrolysis technology is divided into two primary categories. These types of plants are distinguished not by their size or complexity, but by the speed at which they process organic material. The main types are slow pyrolysis and fast pyrolysis, and the choice between them fundamentally dictates the primary output you will receive.
The decision between a slow or fast pyrolysis plant is not about which is superior, but about what you intend to produce. Slow pyrolysis is engineered to maximize solid biochar, while fast pyrolysis is optimized to create liquid bio-oil.

The Core Distinction: Process Speed and Heat
The fundamental difference between these systems is the heating rate and the residence time—how quickly biomass is heated and for how long it stays at temperature. This single factor creates a cascade of chemical reactions that result in vastly different end products.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Solid Biochar
Slow pyrolysis involves heating biomass at relatively low temperatures over a long period, often lasting several hours. This gradual, controlled "cooking" process allows most volatile components to escape as gases.
The primary result is a stable, carbon-rich solid known as biochar. Because the process is slow, the carbon structures have time to form and stabilize, maximizing the solid yield.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Liquid Bio-oil
Fast pyrolysis is the most common industrial method and operates on the opposite principle. It subjects biomass to very high temperatures for an extremely short duration, often less than two seconds.
This intense, rapid heating "cracks" the organic polymers into vapors. These vapors are then immediately cooled, or "quenched," to condense them into a liquid known as bio-oil. This process yields approximately 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis technology requires understanding the inherent compromises in process complexity and output priorities. Each approach is designed for a specific outcome.
Output Focus vs. System Complexity
Slow pyrolysis systems can be mechanically simpler, as they do not require the sophisticated reactors and rapid quenching systems needed for fast pyrolysis. Their goal is straightforward: produce a stable solid.
Fast pyrolysis plants are more technically demanding. They require precise control over temperature, pressure, and timing to ensure the vapors are created and condensed correctly. This complexity is the price for producing a transportable, liquid energy carrier.
The Role of Byproducts
In both processes, gaseous byproducts are created. In fast pyrolysis, this non-condensable gas is called syngas.
This syngas is not a waste product. It is often captured and combusted on-site to provide the energy required to heat the pyrolysis reactor, making the entire process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct pyrolysis plant is the one that aligns directly with your intended application and desired end product.
- If your primary focus is agriculture, soil amendment, or long-term carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the ideal choice because it is designed to maximize the yield of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing a renewable liquid fuel or a chemical feedstock: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary technology, as its entire process is optimized to capture and condense vapors into bio-oil.
Ultimately, your strategic goal—creating a solid or a liquid—is the single most important factor in selecting the right pyrolysis technology.
Summary Table:
| Type | Process Speed | Primary Output | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Slow (hours) | Biochar (maximized) | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Fast (seconds) | Bio-oil (maximized) | Renewable liquid fuel, chemical feedstock |
Ready to select the ideal pyrolysis system for your biochar or bio-oil production?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass conversion research and development. Whether you're focused on optimizing biochar for agricultural applications or developing efficient bio-oil production processes, our team can provide the precise, reliable pyrolysis reactors and systems you need to succeed.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and accelerate your research. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Jaw Crusher
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing




