At its core, a rotary kiln reactor is a large, rotating industrial furnace designed to process solid materials at extremely high temperatures. This controlled heating and tumbling motion induces a physical change or a chemical reaction, making it a versatile tool for applications ranging from waste recycling to mineral processing.
The fundamental purpose of a rotary kiln is to use continuous, gentle rotation to ensure every particle of a solid material is uniformly exposed to a controlled high-temperature environment, enabling efficient and consistent thermal processing.

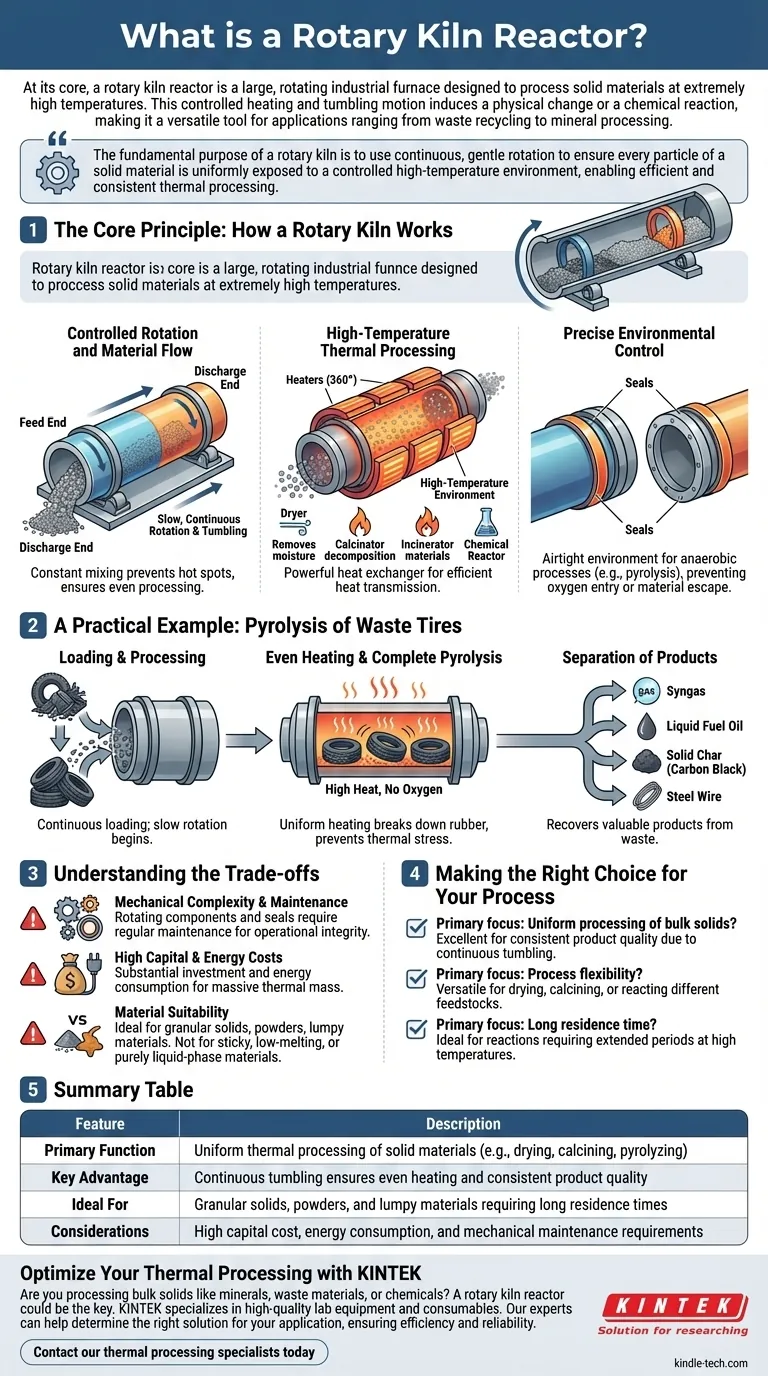
The Core Principle: How a Rotary Kiln Works
A rotary kiln's design is straightforward but highly effective. It combines three critical functions: material transport, high-temperature heating, and environmental control.
Controlled Rotation and Material Flow
The kiln is a long, cylindrical vessel mounted at a slight angle. As the cylinder slowly rotates, the solid material inside is gently lifted and tumbled, causing it to gradually move from the higher feed end to the lower discharge end.
This constant mixing is the key to its effectiveness, preventing hot spots and ensuring the entire batch of material is processed evenly.
High-Temperature Thermal Processing
The kiln acts as a powerful heat exchanger. External heaters, often placed in a 360° configuration, provide consistent and efficient heat transmission into the chamber.
Depending on the target temperature and material, the kiln can function as a dryer (to remove moisture), a calcinator (to cause thermal decomposition), an incinerator (to combust materials), or a chemical reactor.
Precise Environmental Control
For many chemical reactions, like pyrolysis, the atmosphere inside the reactor is critical. Rotary kilns use various sealing measures at the feed and discharge ends.
These seals ensure an airtight environment, preventing oxygen from entering or raw material from escaping. This allows for processes that must occur in an anaerobic (oxygen-free) setting.
A Practical Example: Pyrolysis of Waste Tires
To understand its application, consider its role as the core component in a waste tire pyrolysis plant.
Loading and Processing
Whole or shredded tires are loaded into the reactor. The slow rotation begins, and the kiln is heated. The process is continuous, allowing for easier loading compared to static batch reactors.
Even Heating and Complete Pyrolysis
Over a period of several hours, the constant tumbling ensures every part of the tire is exposed to the high heat without oxygen. This breaks down the rubber into valuable products.
This uniform heating prevents the reactor itself from developing thermal stress, which extends the machine's service life.
Separation of Products
The pyrolysis process separates the tire into three primary components: a synthetic gas (syngas), a liquid fuel oil, and a solid char (carbon black). The steel wire reinforcing the tires is also recovered.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary kilns are a significant piece of industrial machinery with inherent complexities.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotating nature of the kiln means components like drive gears, support rollers, and particularly the seals at either end are subject to wear. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure operational integrity and airtightness.
High Capital and Energy Costs
Rotary kilns are large, heavy, and require a substantial initial investment. Furthermore, bringing the massive thermal mass of the kiln up to operating temperature and keeping it there consumes a significant amount of energy.
Material Suitability
These reactors are ideal for processing granular solids, powders, or lumpy materials like shredded tires. They are not well-suited for processing sticky, low-melting-point materials that could coat the inner walls, or for purely liquid-phase reactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the strengths of a rotary kiln helps determine if it's the correct technology for a specific industrial goal.
- If your primary focus is uniform processing of bulk solids: The continuous tumbling action makes a rotary kiln an excellent choice for ensuring consistent product quality.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility: Its ability to function as a dryer, calcinator, or reactor for different feedstocks makes it a highly versatile asset.
- If your primary focus is a long residence time: The slow, controlled movement of material makes it ideal for reactions that require extended periods at high temperatures.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary kiln is a decision to invest in a robust and reliable system for high-volume, uniform thermal processing of solid materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Uniform thermal processing of solid materials (e.g., drying, calcining, pyrolyzing) |
| Key Advantage | Continuous tumbling ensures even heating and consistent product quality |
| Ideal For | Granular solids, powders, and lumpy materials requiring long residence times |
| Considerations | High capital cost, energy consumption, and mechanical maintenance requirements |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK
Are you processing bulk solids like minerals, waste materials, or chemicals? A rotary kiln reactor could be the key to achieving uniform, high-temperature results for your lab or pilot plant. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Our experts can help you determine if a rotary kiln is the right solution for your specific application, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover the right equipment for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment



















