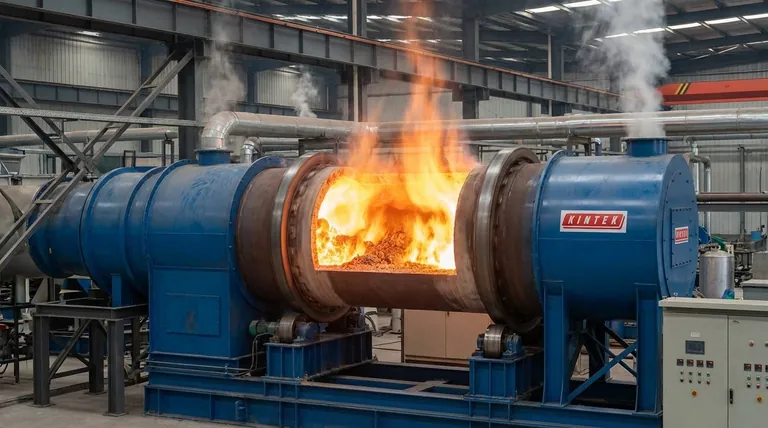
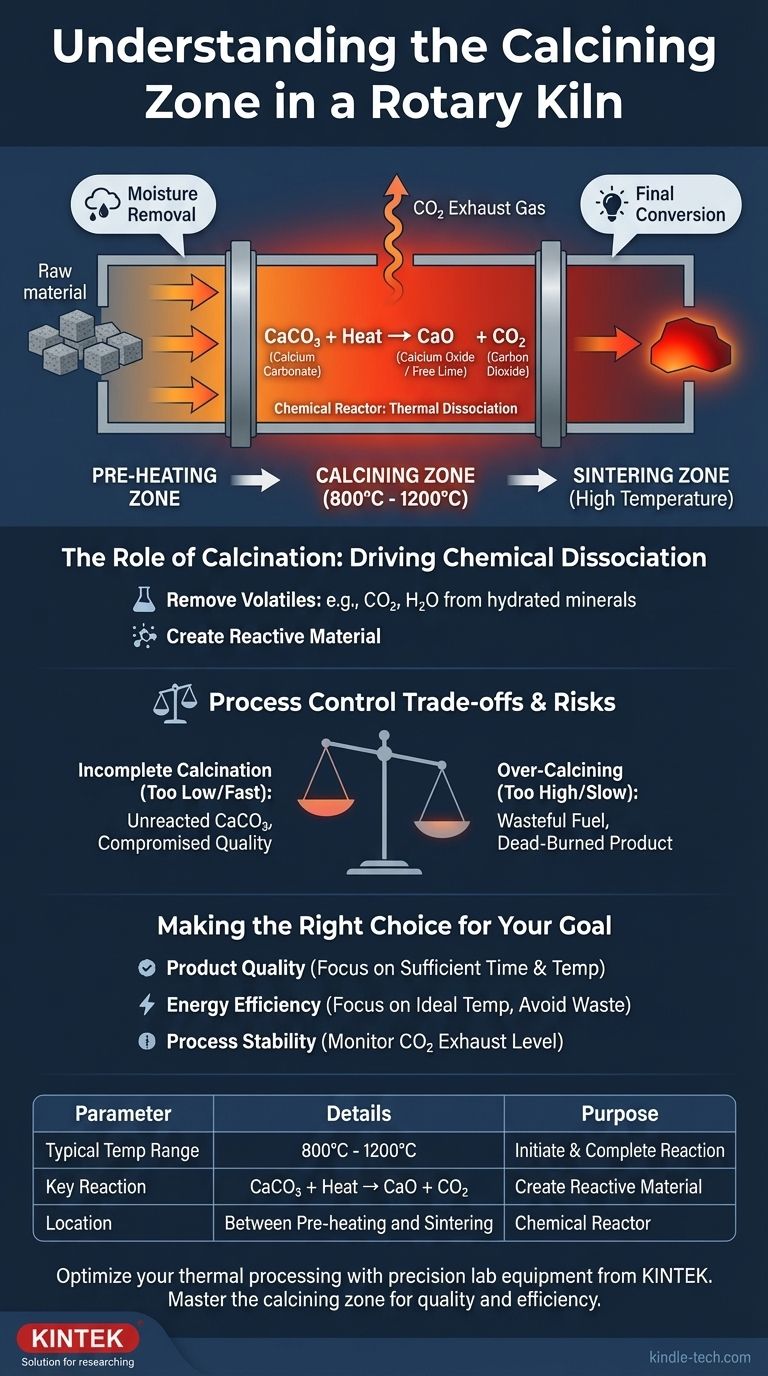
In a rotary kiln system, the calcining zone is the specific, high-temperature section where the raw material undergoes a fundamental chemical transformation. This process, known as calcination, uses temperatures between 800°C and 1200°C to break down materials like calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) into a more reactive substance like calcium oxide (CaO), or free lime, while driving off carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas.
The purpose of the calcining zone is not simply to heat material, but to act as a chemical reactor. It prepares the raw feed for the final, higher-temperature stage by initiating a chemical breakdown and removing volatile components, a critical step in manufacturing products like cement and lime.

The Role of the Calcining Zone in a Kiln System
A modern kiln is not a single, uniformly heated tube but a series of distinct thermal zones, each with a specific purpose. The calcining zone is a critical link in this chain.
A Step in a Larger Process
Material typically enters the calcining zone after passing through a pre-heating zone. In this preceding stage, the raw feed is heated and any free moisture is removed.
After the calcining zone, the now-transformed material moves into an even hotter section, often called the burning or sintering zone, for its final conversion.
The Core Chemical Reaction
The defining event in this zone is calcination, a form of thermal dissociation. For cement or lime production, this is the breakdown of calcium carbonate.
The reaction is: CaCO₃ (Calcium Carbonate) + Heat → CaO (Calcium Oxide) + CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide).
The CaO, or "free lime," is the primary reactive component needed for the final product, while the CO₂ is removed as an exhaust gas.
Key Operating Parameters
The temperature in this zone is precise, typically held between 800°C and 1200°C.
This range is hot enough to initiate and complete the chemical dissociation but is deliberately kept below the final sintering temperatures, which can exceed 1450°C.
What "Calcination" Actually Means
While often associated with cement, the term calcination applies to a broader set of industrial processes.
Driving Chemical Dissociation
At its core, calcination is the process of heating a solid material to a high temperature in the absence of air to cause a chemical breakdown.
The goal is to change the material's chemical structure by removing a volatile component.
Beyond Carbonates
This process is not limited to removing CO₂. It is also used to remove chemically bound water from hydrated minerals.
For example, heating borax or bauxite is also a form of calcination, driving off water molecules to create a more concentrated or reactive material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Control
Effective control of the calcining zone is a constant balance between ensuring product quality and maintaining operational efficiency. Mismanaging this stage has significant consequences.
The Risk of Incomplete Calcination
If the temperature is too low or the material passes through the zone too quickly, calcination will be incomplete.
This leaves unreacted CaCO₃ in the material, which compromises the quality and chemical soundness of the final product, such as cement.
The Problem of Over-Calcining
Conversely, applying excessive heat in this zone is wasteful and can be counterproductive. It consumes more fuel than necessary, increasing operational costs.
For some materials, like lime, overheating can produce a less reactive, "dead-burned" product, which is undesirable.
The Importance of Zone Separation
The existence of distinct temperature zones, which can be set separately, is crucial. It allows operators to optimize the calcination reaction without interfering with the conditions needed for the preceding pre-heating or subsequent sintering stages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving your desired outcome depends on how you manage the parameters of the calcining zone.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Ensure the material has sufficient residence time and the temperature is consistently above the minimum required for complete chemical dissociation (typically above 800°C).
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Avoid excessively high temperatures that waste fuel and instead focus on maintaining the ideal temperature needed for the reaction, and no more.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Continuously monitor the kiln's exhaust gas composition. The level of CO₂ provides a direct, real-time indicator of the rate and completeness of the calcination reaction.
Ultimately, mastering control over the calcining zone is fundamental to achieving both high-quality output and operational efficiency in any thermal processing system.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Chemical reactor for thermal dissociation (calcination) |
| Typical Temperature Range | 800°C - 1200°C |
| Key Reaction | CaCO₃ + Heat → CaO (Lime) + CO₂ |
| Primary Function | Remove volatile components (e.g., CO₂, H₂O) to create a reactive material |
| Location in Kiln | Between pre-heating and sintering zones |
Optimize your thermal processing with precision lab equipment from KINTEK.
Mastering the calcining zone is critical for product quality and energy efficiency. Whether you are in cement, lime, or advanced material production, KINTEK provides the durable furnaces, kilns, and temperature control systems you need to achieve complete and efficient calcination.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process stability and output.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















