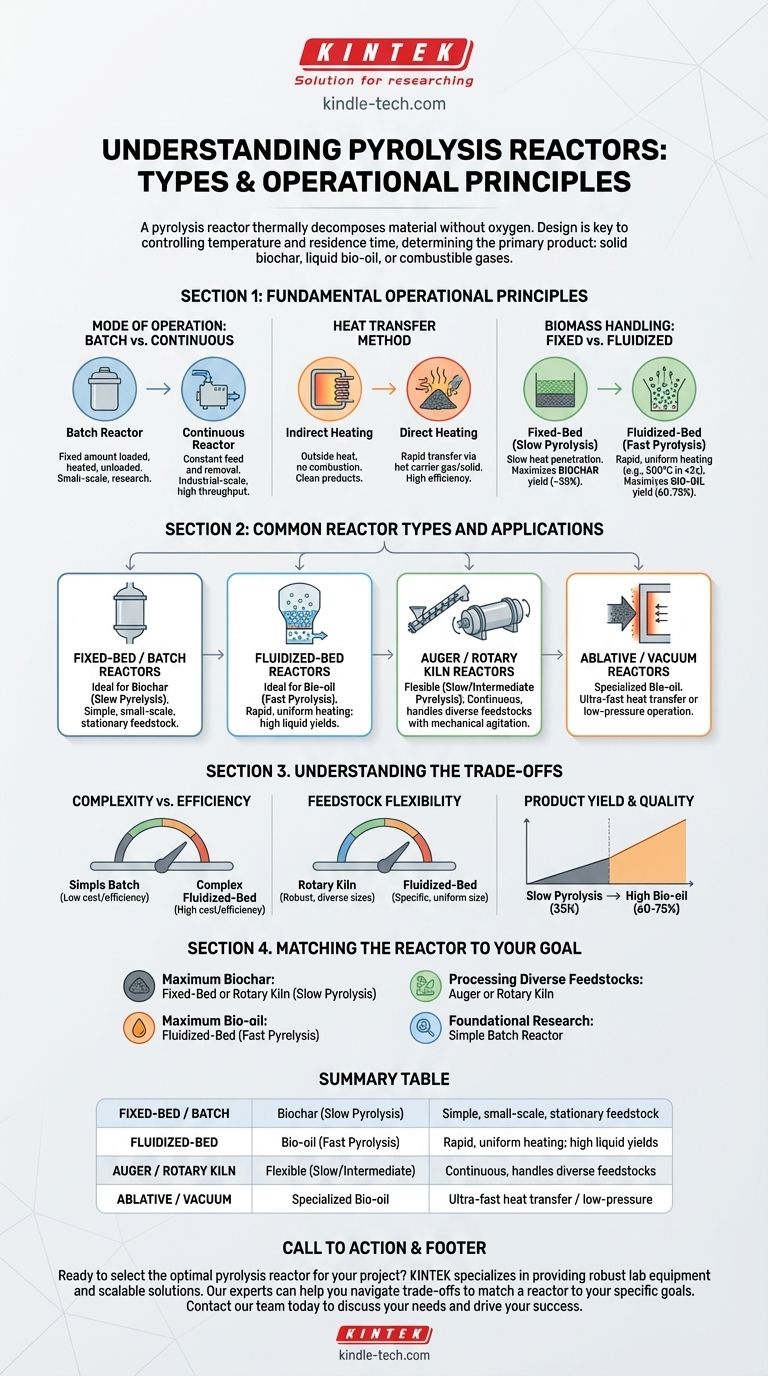
At its core, a pyrolysis reactor is a specialized furnace designed to thermally decompose material in the absence of oxygen. While many designs exist, they are primarily categorized not by name, but by three key operational principles: how they are loaded (batch or continuous), how they transfer heat, and how they handle the material during the process (e.g., fixed, moving, or fluidized). The most common types you will encounter are fixed-bed, fluidized-bed, and rotary kiln reactors.
The specific type of pyrolysis reactor is not chosen at random; it is a direct consequence of the desired outcome. The reactor's design is engineered to control temperature and residence time, which in turn determines whether the primary product will be solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible gases.

The Fundamental Principles of Reactor Design
To understand the different "types" of reactors, you must first understand the engineering principles that differentiate them. A reactor's name is simply a label for its unique combination of these principles.
Mode of Operation: Batch vs. Continuous
Batch reactors are the simplest form. A fixed amount of feedstock is loaded into a sealed vessel, heated for a set duration, and then the products are removed before the next batch begins. This is common for lab-scale research and smaller operations.
Continuous reactors are designed for industrial-scale production. Feedstock is constantly fed into the system, and products are continuously removed, allowing for uninterrupted operation and higher throughput.
Heat Transfer Method
The efficiency and speed of pyrolysis are dictated by how quickly and evenly heat is transferred to the feedstock.
Indirect heating is most common. The reactor chamber is heated from the outside, and heat transfers to the material through conduction and convection. This prevents combustion and keeps the resulting products "clean."
Direct heating involves using a hot carrier gas or solid (like sand) that is mixed directly with the feedstock. This allows for extremely rapid heat transfer, which is essential for certain types of pyrolysis.
Biomass Handling: Fixed vs. Fluidized
This is arguably the most critical distinction, as it directly impacts the process speed and resulting product.
Fixed-bed reactors, like a simple batch system, keep the feedstock stationary. Heat slowly penetrates the material, making this design ideal for slow pyrolysis, where the goal is maximizing the production of biochar.
Fluidized-bed reactors suspend the feedstock particles in a high-velocity stream of hot gas. This "fluidization" ensures every particle is surrounded by heat, leading to extremely rapid and uniform temperature increases. This design is the standard for fast pyrolysis, which aims to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
Common Reactor Types and Their Applications
With these principles in mind, the specific reactor types become much clearer. They are simply practical applications of these concepts.
Fixed-Bed and Batch Reactors
These are simple, sealed vessels often used for slow pyrolysis. Their straightforward design and operation make them ideal for small-scale applications or when the primary goal is producing high-quality biochar.
Fluidized-Bed Reactors
These systems are the workhorses of fast pyrolysis for bio-oil production. By forcing a hot gas through a bed of sand and feedstock, they achieve the rapid heat transfer (e.g., heating to 500°C in under 2 seconds) necessary to crack organic vapors into liquids before they can further decompose into gas.
Auger and Rotary Kiln Reactors
These are continuous, mechanically agitated reactors. An auger reactor uses a large screw to push material through a heated tube, while a rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylinder. The constant mixing ensures even heating and makes them highly effective at processing diverse or difficult feedstocks. They can be tuned for either slow or intermediate pyrolysis.
Ablative and Vacuum Reactors
These are more specialized designs. Ablative pyrolysis presses feedstock against a hot, moving surface, achieving ultra-fast heat transfer through mechanical force. Vacuum pyrolysis operates at low pressure, which lowers the boiling point of the pyrolysis vapors, allowing them to be removed quickly to preserve their quality as bio-oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reactor involves balancing cost, complexity, and the desired output. There is no single "best" type.
Complexity vs. Efficiency
Simple batch reactors are inexpensive to build and operate but are less efficient and have low throughput. Complex systems like circulating fluidized-bed reactors offer superior heat transfer and product control but come with significantly higher capital and operational costs.
Feedstock Flexibility
Reactors like rotary kilns are robust and can handle a wide variety of feedstock sizes and moisture contents. In contrast, fluidized-bed reactors demand very specific, uniform particle sizes to function correctly, often requiring extensive pre-processing of the raw material.
Product Yield and Quality
The reactor design is the primary control for product distribution. Fast pyrolysis reactors (fluidized-bed, ablative) are engineered to maximize liquid bio-oil, often at yields of 60-75% by weight. Slow pyrolysis reactors (fixed-bed) are designed to maximize solid biochar, typically yielding around 35%.
Matching the Reactor to Your Goal
Your choice of reactor should be guided entirely by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum biochar production: A slow pyrolysis process in a simple fixed-bed or rotary kiln reactor is your most direct path.
- If your primary focus is maximum bio-oil yield: You must use a fast pyrolysis reactor, with fluidized-bed systems being the most proven and common technology.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or non-uniform feedstocks: Mechanically agitated systems like auger or rotary kiln reactors offer the most operational flexibility.
- If your primary focus is foundational research or small-scale testing: A simple, low-cost batch reactor provides the necessary control without the industrial-scale complexity.
Understanding these core principles moves you from simply listing reactor names to making an informed engineering decision based on your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Ideal For (Primary Product) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Bed / Batch | Biochar (Slow Pyrolysis) | Simple, small-scale, stationary feedstock |
| Fluidized-Bed | Bio-oil (Fast Pyrolysis) | Rapid, uniform heating; high liquid yields |
| Auger / Rotary Kiln | Flexible (Slow/Intermediate) | Continuous, handles diverse feedstocks |
| Ablative / Vacuum | Specialized Bio-oil | Ultra-fast heat transfer or low-pressure operation |
Ready to select the optimal pyrolysis reactor for your project? The right reactor is critical to achieving your target yields of biochar, bio-oil, or gas. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and scalable solutions for pyrolysis research and development. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs in complexity, efficiency, and feedstock flexibility to match a reactor to your specific goal. Contact our team today to discuss your pyrolysis process needs and how our equipment can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















