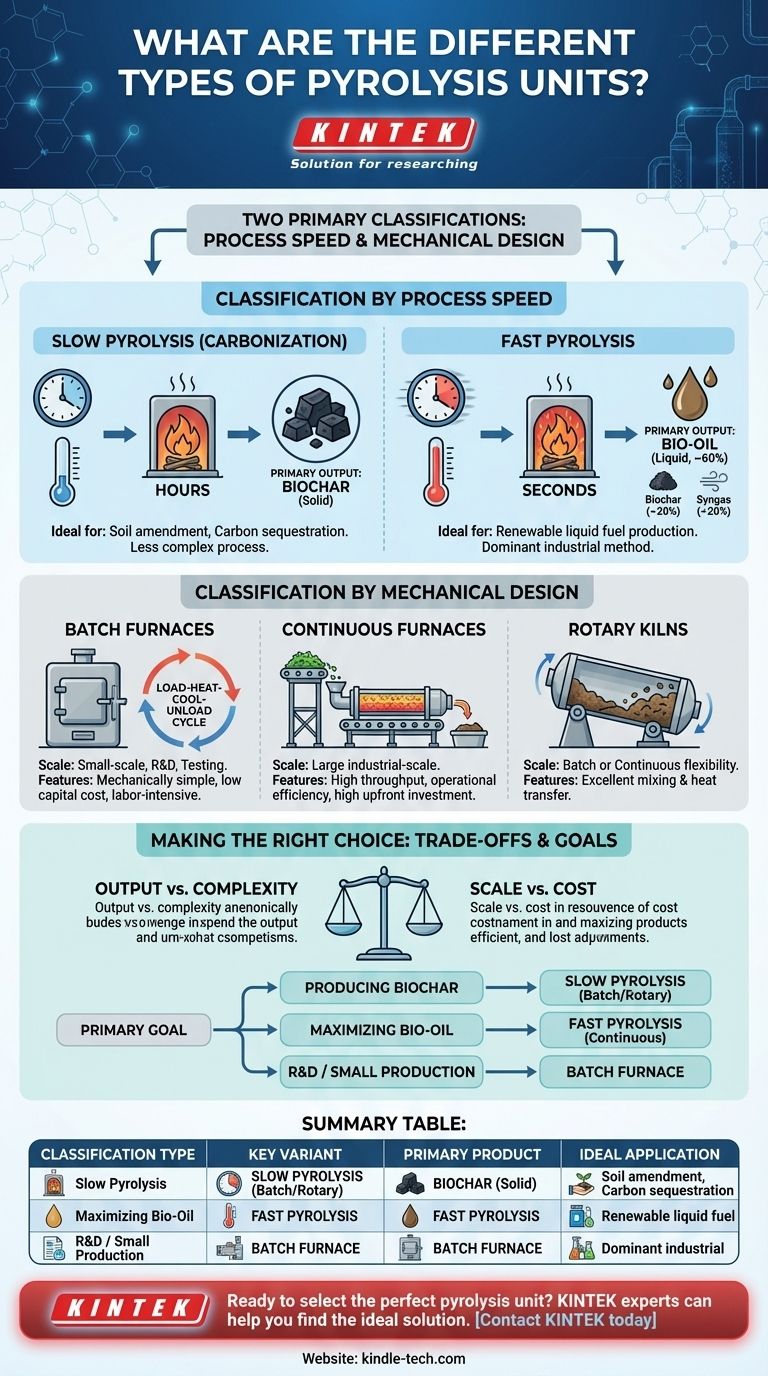
At its core, pyrolysis units are classified in two primary ways: by the speed of the chemical process and by the mechanical design of the furnace. The process speed—either slow or fast—determines the primary output product, while the mechanical design dictates the scale and method of operation.
The choice of a pyrolysis unit is not just about the hardware; it is a strategic decision driven entirely by your desired end product. Whether you aim to produce biochar, bio-oil, or syngas dictates the process you must use and, consequently, the type of reactor required.

Classification by Process Speed
The most fundamental distinction between pyrolysis systems is the rate at which biomass is heated. This single factor has the greatest impact on the final distribution of products.
Slow Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis, also known as carbonization, involves heating biomass slowly over several hours. This prolonged heating at lower temperatures maximizes the production of biochar.
The process is less complex than its faster counterpart, making it suitable for applications where soil amendment or carbon sequestration is the primary goal.
Fast Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis is the dominant method used in industrial applications. It involves heating biomass to high temperatures very rapidly, with the entire reaction completing in just a few seconds.
This rapid process is optimized to produce liquid bio-oil, typically yielding around 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% syngas. It is the preferred method for creating liquid fuels from biomass.
Classification by Mechanical Design
Beyond the process chemistry, pyrolysis units are also defined by their physical construction and mode of operation. This determines the system's throughput, scale, and operational efficiency.
Batch Furnaces
A batch furnace operates on a load-heat-cool-unload cycle. Feedstock is loaded into the chamber, the process is run to completion, and the products are removed before the next batch can begin.
These systems are mechanically simple and are best suited for small-scale production, laboratory testing, or situations where feedstock is not available continuously.
Continuous Furnaces
Continuous furnaces are designed for large, industrial-scale operations. Raw material is constantly fed into one end of the reactor, and the resulting products are continuously extracted from the other.
This design maximizes throughput and operational efficiency, making it the standard for commercial production of bio-oil and other pyrolysis products.
Rotary Kilns
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical vessel that is slightly inclined. The rotation causes the feedstock to tumble and mix as it passes through the kiln, ensuring uniform heating.
This design provides excellent mixing and heat transfer. Rotary kilns can be configured to operate in either batch or continuous modes, offering significant flexibility for various applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis technology involves balancing output goals with operational realities. There is no single "best" unit; there is only the best fit for a specific objective.
Output vs. Complexity
Fast pyrolysis yields high-value liquid bio-oil but requires sophisticated equipment and precise control over temperature and residence time. Slow pyrolysis is far simpler to engineer but primarily produces solid biochar.
Scale vs. Cost
Batch systems have a low initial capital cost but are labor-intensive and do not scale efficiently. Continuous systems require a significant upfront investment but offer lower operating costs per unit of output and are built for high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be guided by your primary objective and intended scale of operation.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for agriculture or carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis in a simpler batch or rotary kiln system is the most direct and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil for renewable fuel production: Fast pyrolysis, almost always implemented in a continuous furnace design, is the industry standard for high-volume output.
- If your primary focus is research, development, or small-scale specialized production: A batch furnace provides the operational flexibility and lower entry cost needed for testing and validation.
Ultimately, the right pyrolysis unit is the one that best aligns the process physics with your final product goal.
Summary Table:
| Classification Type | Key Variant | Primary Product | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| By Process Speed | Slow Pyrolysis | Biochar | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Bio-Oil | Renewable liquid fuel production | |
| By Mechanical Design | Batch Furnace | Varies (Batch) | Small-scale production, R&D, testing |
| Continuous Furnace | Varies (Continuous) | Large-scale, high-volume commercial production | |
| Rotary Kiln | Varies (Batch/Continuous) | Applications requiring excellent mixing & heat transfer |
Ready to select the perfect pyrolysis unit for your specific biofuel or biochar production goals?
The right equipment is critical to your project's success, balancing output, scale, and complexity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your research and production needs. Our experts can help you navigate the technical specifications to find the ideal solution for your laboratory or pilot plant.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can optimize your pyrolysis process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a PTFE-lined hydrothermal autoclave in cys-CDs synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Carbon Dots
- What is the advantage of using high-pressure hydrothermal reactors to treat biomass waste? Efficient Resource Recovery
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of bio-oil? Drive Deep Fuel Upgrading
- Why must SCWG reactors maintain a specific heating rate? Protect Your High-Pressure Vessels from Thermal Stress
- Why are high-strength alloy tube reactors critical for HHIP? Ensuring Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Environments



















