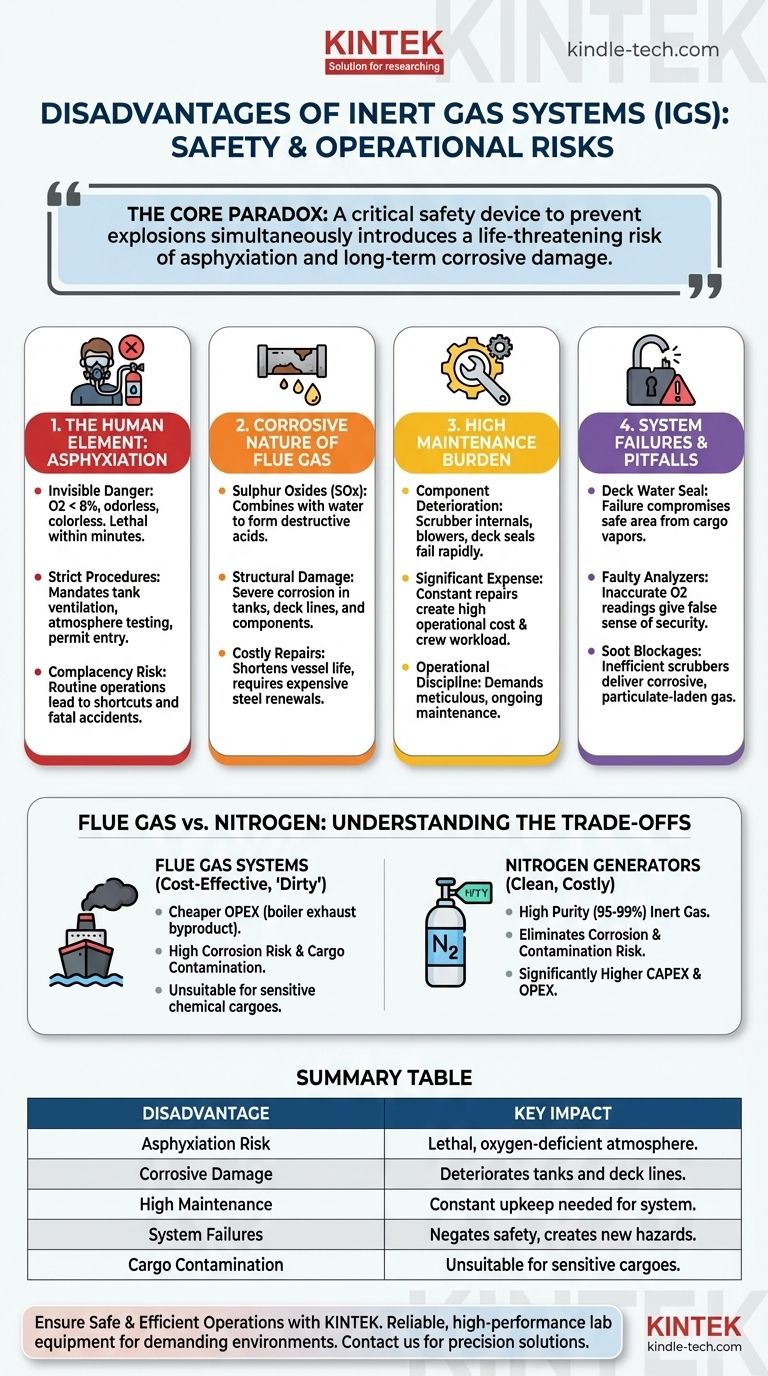
While essential for preventing explosions, an inert gas (IG) system's primary disadvantages stem from the very properties that make it effective. The system introduces a severe risk of asphyxiation to the crew, its operational byproducts can be highly corrosive to the vessel's structure, and it demands constant, meticulous maintenance and operational discipline to function safely and reliably.
The core disadvantage of an inert gas system is a paradox: a critical safety device designed to prevent catastrophic explosions simultaneously introduces a life-threatening risk of asphyxiation and long-term corrosive damage if not managed with absolute precision.

The Human Element: Asphyxiation and Operational Risk
The most immediate and severe disadvantage of an inert gas system is the danger it poses to human life. The system's entire purpose is to create an atmosphere where combustion cannot occur, which is also an atmosphere where life cannot be sustained.
The Invisible Danger of an Oxygen-Deficient Atmosphere
An inerted cargo tank contains less than 8% oxygen, and often as low as 5%. Unconsciousness occurs in seconds and death in minutes in such an environment. The gas mixture is odorless and colorless, providing no sensory warning to a crew member who might enter an unsafe space.
The Requirement for Strict Procedures
Because of this lethal risk, IG systems mandate rigorous and unwavering safety protocols. This includes tank ventilation, atmosphere testing with calibrated gas detectors, and strict "enclosed space entry" permit procedures. Any failure in these procedures can be fatal.
The Risk of Complacency
On vessels where the IG system is in constant use, there is a significant risk of crew complacency. The routine nature of operations can lead to shortcuts or a breakdown in procedural discipline, which is when accidents are most likely to occur.
The Corrosive Nature of Flue Gas
Most IG systems on oil tankers use treated flue gas from the ship's boilers. While cost-effective, this gas is "dirty" and introduces a significant long-term disadvantage: corrosion.
The Role of Sulphur Oxides (SOx)
Flue gas contains Sulphur Oxides (SOx) from the combustion of heavy fuel oil. When this gas is cooled and scrubbed with seawater, the SOx combines with water to form sulfurous and sulfuric acid. Even with an efficient scrubber, some acidic moisture remains.
The Impact on Tanks and Deck Lines
This acidic vapor causes severe corrosion in the cargo tanks, deck piping, and system components like valves and pressure/vacuum breakers. This damage shortens the vessel's service life and necessitates costly steel renewals and repairs.
The Long-Term Maintenance Burden
The corrosive environment means the IG system itself requires constant and expensive maintenance. Scrubber internals, demisters, blowers, and deck seals are all susceptible to rapid deterioration, creating a significant operational expense and workload for the crew.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Flue Gas vs. Nitrogen
Not all IG systems are the same. The choice between a standard flue gas system and a dedicated nitrogen generator highlights a key trade-off between cost and cargo purity.
Flue Gas Systems: Cost-Effective but "Dirty"
These systems are cheaper to install and operate on a per-volume basis because they use a readily available byproduct (boiler exhaust). However, they are unsuitable for cargoes that are sensitive to contamination from soot, acids, or other combustion products.
Nitrogen Generators: Clean but Costly
Nitrogen generators produce high-purity (95-99%) inert gas by separating nitrogen from the air. This eliminates the risk of corrosion and cargo contamination. The disadvantage is their significantly higher installation cost (CAPEX) and operational cost (OPEX), as they are complex machinery requiring their own power and maintenance.
The Impact on Cargo Quality
For chemical tankers carrying high-purity products, using a flue gas system is not an option. The inert gas itself would contaminate the cargo, rendering it off-spec. The choice of IG system is therefore dictated by the vessel's intended trade.
Common Pitfalls and System Failures
An IG system is a complex network of mechanical parts, and failures can negate its safety function or create new hazards.
Failure of the Deck Water Seal
The deck water seal is a critical non-return barrier that prevents flammable cargo tank vapors from flowing back into the engine room. If its water level drops due to neglect or malfunction, the vessel's entire safe area could be compromised.
Malfunctioning Oxygen Analyzers
The entire operation relies on accurate measurement of the oxygen content in the tanks. A faulty or poorly calibrated oxygen analyzer can give a false sense of security, leading the crew to believe a tank is safely inerted when it is actually in an explosive condition.
Soot and Scrubber Blockages
If the system's scrubber tower becomes inefficient or clogged with soot, corrosive and particulate-laden gas will be delivered to the tanks. This accelerates corrosion and can foul system components, leading to operational failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these disadvantages is key to managing the risks associated with inert gas systems. Your approach depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective operation of oil tankers: Accept that a flue gas IG system is standard, but you must budget aggressively for maintenance and steel replacement to combat its inherent corrosive effects.
- If your primary focus is preserving the purity of sensitive chemical cargoes: A nitrogen generator is a non-negotiable requirement, and its higher capital and operational costs must be factored into the vessel's commercial model.
- If your primary focus is crew safety and regulatory compliance: The type of system is secondary to the quality of your procedures. Rigorous training, unwavering adherence to enclosed space entry protocols, and a proactive maintenance culture are the most critical investments you can make.
Ultimately, managing the disadvantages of an inert gas system is a non-negotiable aspect of maritime safety, demanding constant vigilance and technical expertise.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Asphyxiation Risk | Lethal, oxygen-deficient atmosphere in cargo tanks |
| Corrosive Damage | Acidic flue gas deteriorates tanks and deck lines |
| High Maintenance | Constant upkeep needed for scrubbers, seals, and analyzers |
| System Failures | Malfunctions can negate safety and create new hazards |
| Cargo Contamination | Flue gas systems unsuitable for sensitive chemical cargoes |
Ensure your laboratory operations are safe and efficient with the right equipment. The challenges of managing complex systems like inert gas units highlight the need for reliable, high-performance lab equipment. KINTEK specializes in providing durable lab equipment and consumables tailored to meet stringent safety and purity standards. Whether you're handling sensitive materials or require robust systems for demanding environments, we have the solutions to enhance your lab's safety and productivity. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory needs with precision and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
















