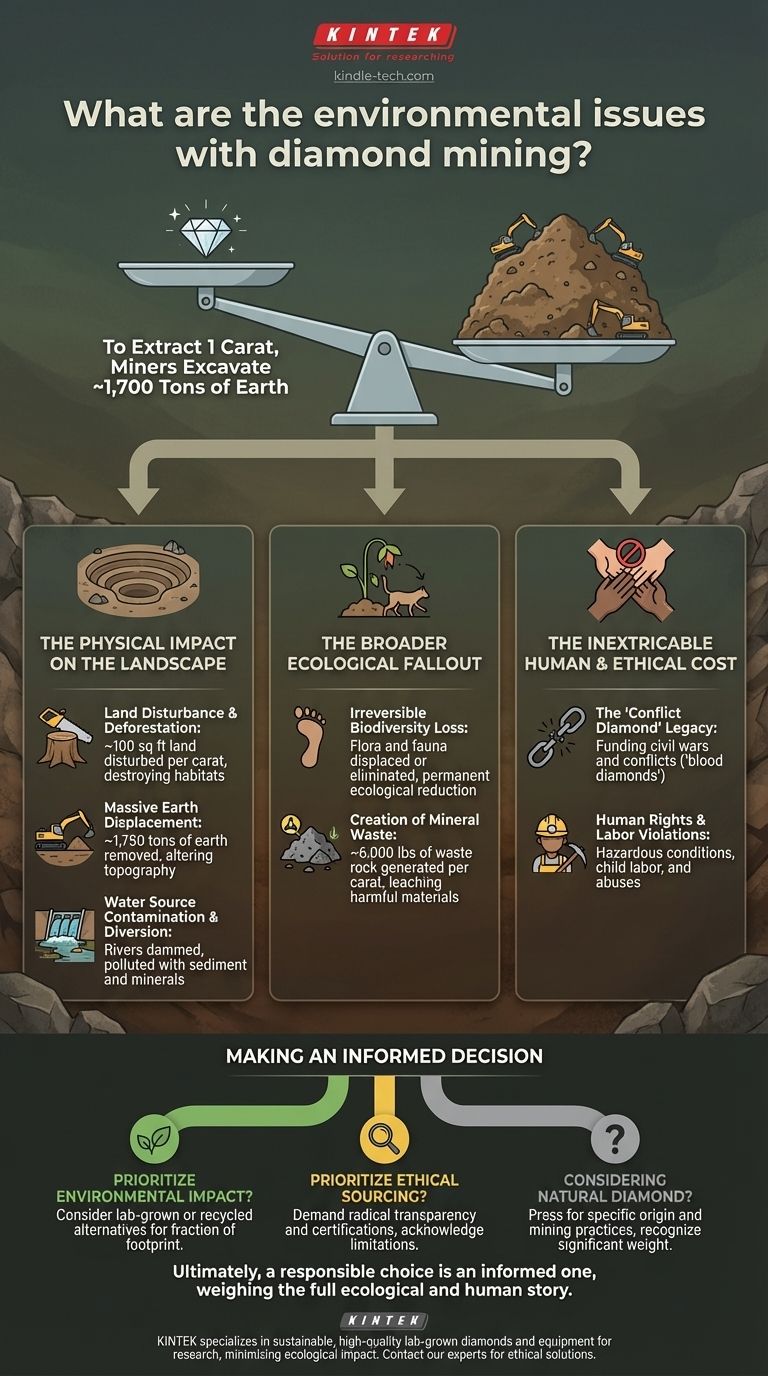
The environmental cost of a natural diamond is significant and multifaceted, stemming directly from the immense scale of the mining operations required. To extract a single carat of diamond, miners must excavate and process up to 1,700 tons of earth, profoundly disturbing local landscapes, waterways, and ecosystems.
The core issue extends beyond just digging a hole. The true cost of traditional diamond mining is its irreversible impact on entire ecosystems and the human communities that depend on them. The environmental and ethical issues are deeply intertwined, making it impossible to evaluate one without considering the other.
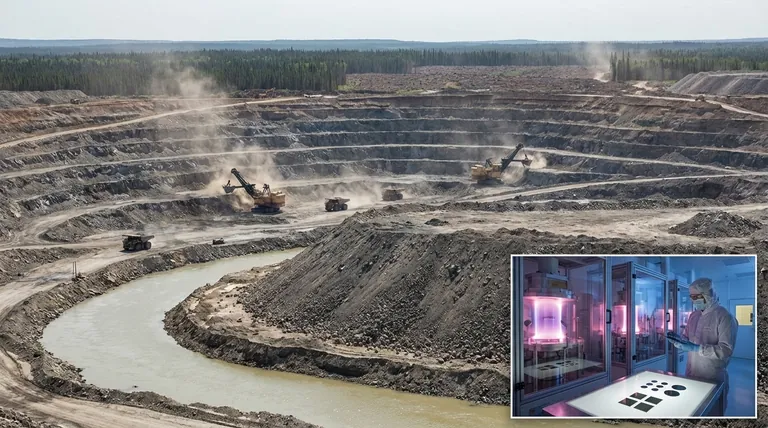

The Physical Impact on the Landscape
The most visible consequence of diamond mining is the permanent alteration of the land itself. These operations leave scars that the environment struggles to heal.
Massive Earth Displacement
To reach diamond deposits, enormous open-pit mines are created. For every carat of diamond found, it's estimated that nearly 1,750 tons of earth are removed. This process fundamentally changes the topography of a region.
Land Disturbance and Deforestation
The mining footprint is extensive. For each carat, nearly 100 square feet of land is directly disturbed. This often involves clear-cutting forests, which destroys vital habitats for wildlife and contributes to soil erosion.
Water Source Contamination and Diversion
Mining operations require vast amounts of water and can have a devastating effect on local hydrology. Rivers and streams are often dammed or diverted to access kimberlite pipes, depriving downstream communities and ecosystems of their water source. Runoff from mining sites can also pollute remaining water with sediment and minerals.
The Broader Ecological Fallout
The impact of a diamond mine radiates far beyond the site's perimeter, creating long-term and often permanent ecological damage.
Irreversible Biodiversity Loss
When habitats are completely removed, the loss of biodiversity is often irreversible. The flora and fauna that once thrived in the area are displaced or eliminated, leading to a permanent reduction in the region's ecological richness.
Creation of Mineral Waste
The extraction process generates immense quantities of waste rock. For a single carat, this can amount to nearly 6,000 pounds of mineral waste. These massive piles of refuse can leach harmful materials into the soil and water over time.
The Inextricable Human and Ethical Cost
It is impossible to discuss the environmental toll of diamond mining without addressing its profound human consequences. These issues are two sides of the same coin.
The 'Conflict Diamond' Legacy
Historically, the diamond trade has been notorious for funding brutal civil wars and conflicts, particularly in parts of Africa. These illegally traded gems, known as "blood diamonds" or "conflict diamonds," are mined in war zones and sold to finance insurgency or a warlord's activities.
Human Rights and Labor Violations
Even in areas without active conflict, the industry has been plagued by ethical problems. These include hazardous working conditions leading to frequent injuries, the use of child labor, and human rights abuses against local populations and mine workers.
Making an Informed Decision
Understanding these impacts allows you to make a choice that aligns with your values. Your decision depends on what factor you prioritize most.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact: Your clearest path is to consider alternatives to newly-mined diamonds, such as lab-grown or recycled stones, which have a fraction of the ecological footprint.
- If your primary focus is ensuring ethical sourcing: Demand radical transparency and certifications, but understand that even systems like the Kimberley Process have limitations and do not guarantee a stone is free from all human rights or environmental issues.
- If you are considering a natural diamond: Recognize that even a "conflict-free" stone carries a significant environmental weight and it's critical to press jewelers for information on a diamond's specific origin and mining practices.
Ultimately, a responsible choice is an informed one, weighing the full ecological and human story behind the stone.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Issue | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Land Disturbance | Up to 100 sq ft of land disturbed per carat; deforestation and topsoil loss. |
| Earth Displacement | Up to 1,700 tons of earth excavated per carat for open-pit mines. |
| Water Contamination | Diversion of rivers; pollution from sediment and mineral runoff. |
| Biodiversity Loss | Irreversible habitat destruction and species displacement. |
| Mineral Waste | Nearly 6,000 lbs of waste rock generated per carat. |
| Human & Ethical Cost | Links to conflict diamonds, child labor, and hazardous working conditions. |
Make an informed, ethical choice for your laboratory. The environmental and ethical challenges of traditional diamond mining highlight the importance of sustainable and transparent sourcing. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality, ethically sourced lab-grown diamonds and advanced lab equipment that minimize ecological impact. Whether you need diamonds for research, analysis, or industrial applications, our solutions ensure performance without compromise. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's commitment to sustainability and integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What are 5 negative impacts of diamond mines on the environment? The Hidden Environmental Cost of Diamond Mining
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are some ethical issues with diamond mining? Uncover the Hidden Costs of Your Gemstone
- Will CVD diamond change color? Discover the Science of Permanent, Stable Color
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods











