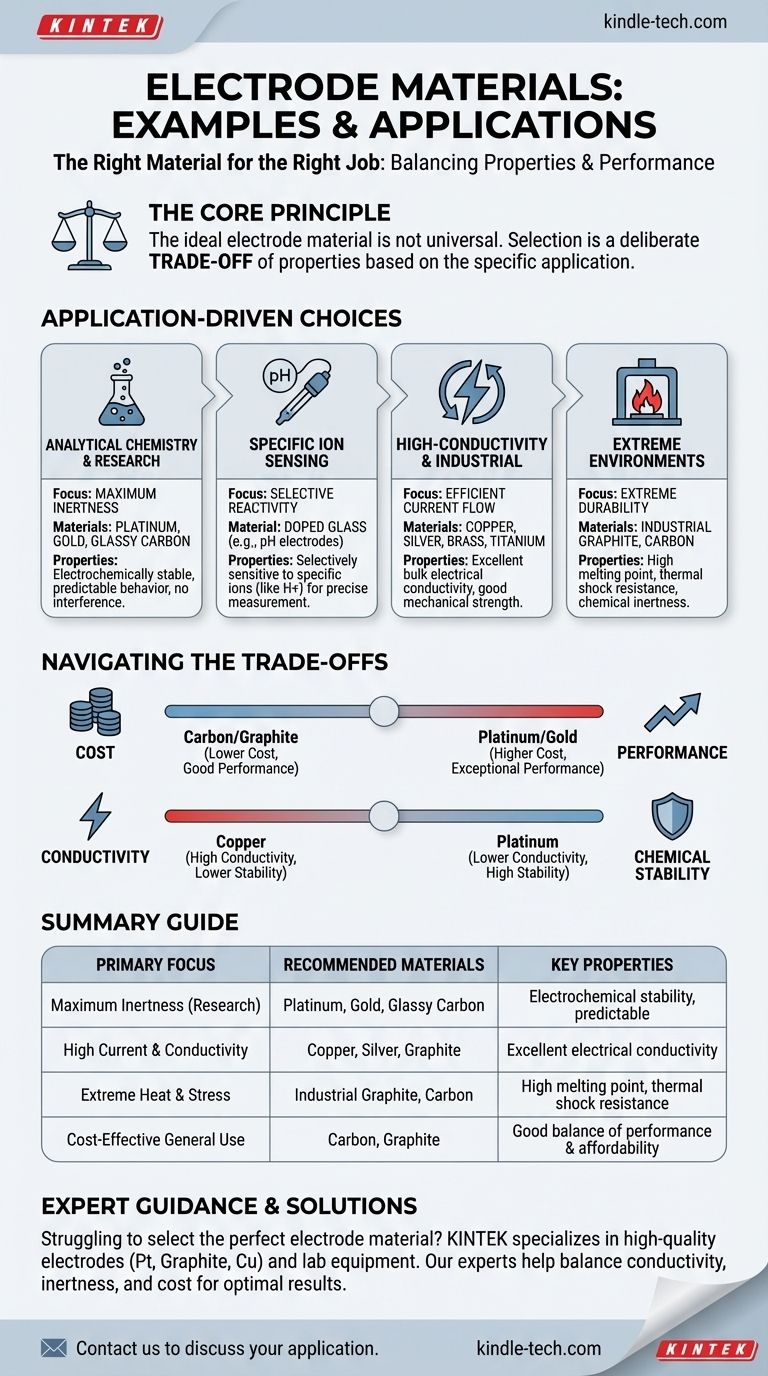
In short, common electrode materials range from highly conductive metals like copper and silver to inert elements like platinum and gold, and various forms of carbon such as graphite and glassy carbon. The specific material chosen is dictated entirely by the electrode's intended application.
The ideal electrode material is not a universal constant. The choice is always a deliberate trade-off, balancing critical properties like electrical conductivity, chemical inertness, mechanical strength, and cost against the specific demands of the electrochemical environment.

The Role of the Electrode Dictates the Material
The function of an electrode determines which material properties are most important. An electrode for a high-power furnace has vastly different requirements than one used for sensitive chemical analysis.
For Analytical Chemistry and Research
In research settings, the primary goal is to study a chemical reaction without interference from the electrode itself.
This demands a material that is electrochemically inert, meaning it won't react with the solution or influence the results. The most common choices are platinum, gold, and various forms of carbon (like glassy carbon).
These materials are frequently used for working, counter, and auxiliary electrodes because of their stability and the predictable speed of reactions on their surfaces.
For Specific Ion Sensing
Some applications require an electrode that is intentionally reactive in a highly specific way.
The classic example is the glass electrode used in pH meters. This electrode is made from glass that has been chemically doped to be selectively sensitive to hydrogen ions, allowing for precise pH measurement.
For High-Conductivity and Industrial Use
In applications where moving large amounts of current efficiently is the goal, bulk electrical conductivity is the most critical factor.
Copper is a primary choice here due to its excellent conductivity, second only to silver, and its superior mechanical strength. Materials like brass and titanium are also used.
For Extreme Industrial Environments
Electrodes used in processes like arc melting furnaces must withstand incredibly harsh conditions.
For these, carbon and graphite are standard. They are selected for a combination of properties: high electrical conductivity, insolubility, high melting point, chemical inertness, mechanical strength, and resistance to extreme thermal shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an electrode material is never about finding one "best" option, but about navigating a series of compromises based on the application's priorities.
Cost vs. Performance
Platinum and gold offer exceptional chemical inertness and performance for sensitive analysis, but they are very expensive.
Carbon and graphite often provide a cost-effective alternative, offering good inertness and conductivity for a fraction of the price, making them suitable for a wide range of uses, from disposable sensors to large-scale industrial processes.
Conductivity vs. Chemical Stability
There is often a trade-off between how well a material conducts electricity and how stable it is.
Copper is an excellent conductor but has inferior oxidation resistance, meaning it can corrode or react in certain environments. Platinum, while less conductive than copper, is far more chemically stable and resistant to corrosion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your primary objective dictates which material is the most logical choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum inertness for research: Choose platinum, gold, or glassy carbon for their stability and predictable behavior.
- If your primary focus is high current and conductivity: Look to materials like copper, silver, or specialized graphite formulations.
- If your primary focus is surviving extreme heat and physical stress: Industrial-grade graphite and carbon are designed for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective general use: Carbon and graphite electrodes offer a robust balance of performance and affordability.
Ultimately, selecting the right electrode material is about precisely matching its intrinsic properties to the demands of its environment and function.
Summary Table:
| Primary Focus | Recommended Materials | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Inertness (Research) | Platinum, Gold, Glassy Carbon | Electrochemical stability, predictable behavior |
| High Current & Conductivity | Copper, Silver, Graphite | Excellent electrical conductivity |
| Extreme Heat & Stress | Industrial Graphite, Carbon | High melting point, thermal shock resistance |
| Cost-Effective General Use | Carbon, Graphite | Good balance of performance and affordability |
Struggling to select the perfect electrode material for your lab's specific needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-quality electrodes made from materials like platinum, graphite, and copper. We help you balance critical properties like conductivity, inertness, and cost to achieve optimal results in your research or industrial process. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your application and let our experts match you with the ideal solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Nickel Aluminum Tabs for Soft Pack Lithium Batteries
- Li-Air Battery Case for Battery Lab Applications
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
People Also Ask
- How should a platinum wire/rod electrode be cleaned before use? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- What is the RRDE in electrochemistry? Unlock Detailed Reaction Pathways with Dual-Electrode Analysis
- What is the difference between ring disk electrode and rotating disk electrode? Unlock Deeper Electrochemical Insights
- What is the common role of a platinum disk electrode? A Guide to Its Primary Use as a Working Electrode


















