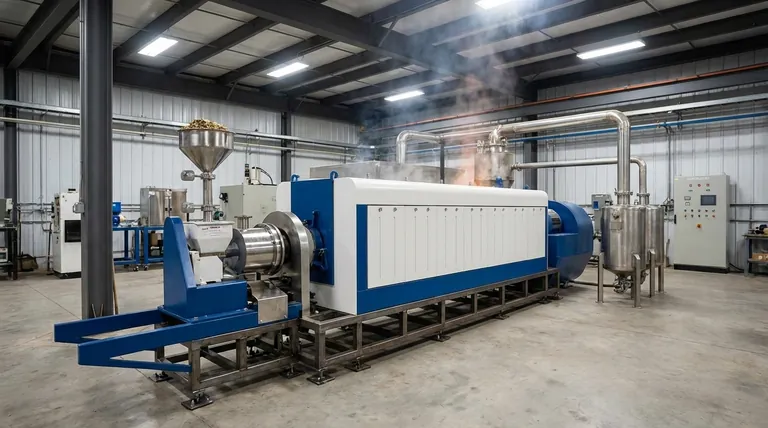
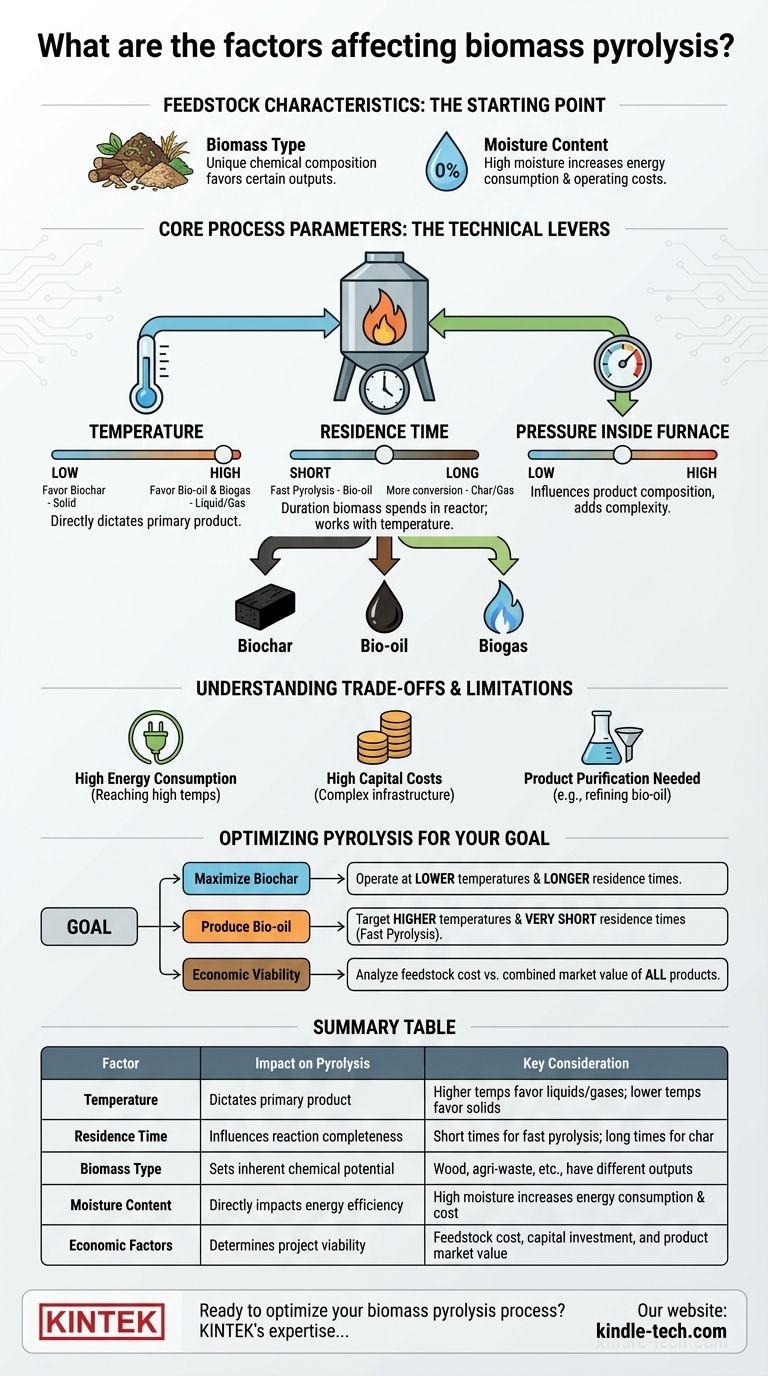
The success of biomass pyrolysis hinges on a precise balance of several key factors. The efficiency and final output of the process are directly controlled by the physical characteristics of the biomass feedstock, such as its type and moisture content, and the operational parameters of the reactor, including temperature, pressure, and residence time.
The technical parameters of pyrolysis determine the product yields, but the overall economic feasibility of a project depends just as heavily on factors outside the reactor, such as feedstock cost, capital investment, and the market value of the resulting bio-oil, biochar, and biogas.

Core Process Parameters: The Technical Levers
Controlling the conditions inside the pyrolysis furnace is the most direct way to influence the outcome. Each parameter acts as a lever to shift the balance between the different end products.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is arguably the most critical factor in pyrolysis. It directly dictates the primary product you will get.
Lower temperatures tend to favor the production of solid biochar. Higher temperatures crack the complex organic molecules more thoroughly, increasing the yield of liquid bio-oil and biogas.
Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the biomass spends inside the hot reactor. It works in tandem with temperature.
Longer residence times allow the thermal reactions to proceed further, converting more of the solid mass into liquids and gases. Shorter times are often used in "fast pyrolysis" to maximize the output of liquid bio-oil before it can break down further.
Pressure Inside the Furnace
While temperature and residence time are the primary controls, pressure also plays a role. Operating at higher pressures can influence the composition of the resulting products, although it adds complexity and cost to the system design.
Feedstock Characteristics: The Starting Point
The process begins long before the biomass enters the reactor. The nature of your input material sets the foundation for everything that follows.
Biomass Type
Different types of biomass (e.g., wood chips, agricultural waste, manure) have unique chemical compositions. This inherent makeup will naturally favor the production of certain outputs over others.
Moisture Content
High moisture content is a significant drain on efficiency. A large portion of the process energy must be spent simply to boil off water before pyrolysis can even begin, increasing energy consumption and operating costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Biomass pyrolysis is a powerful technology, but it is not without its challenges. A realistic assessment requires understanding its inherent weaknesses.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for pyrolysis demands a substantial energy input. Some of the biogas produced is often used to help heat the chamber, but there is still a significant net energy cost.
High Capital Costs
A biomass pyrolysis plant is a complex system composed of feeding, pyrolysis, discharging, and emission cleaning lines. This infrastructure requires a high initial capital investment.
The Need for Product Purification
The outputs of pyrolysis are not always ready for immediate use. The liquid bio-oil, for example, is often acidic and unstable, requiring further costly refining before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Optimizing Pyrolysis for Your Goal
The "best" way to run a pyrolysis process is entirely dependent on your desired outcome. Balancing the technical and economic factors is the key to a successful project.
- If your primary focus is maximizing biochar production: Operate at lower temperatures and potentially longer residence times to favor solid-phase carbonization.
- If your primary focus is producing bio-oil for fuel: Target higher temperatures and very short residence times (fast pyrolysis), but budget for the significant costs of downstream refining.
- If your primary focus is economic viability: Conduct a thorough analysis of feedstock sourcing costs against the combined market value of all potential products—biochar, bio-oil, and biogas.
Mastering the interplay of these factors is what transforms biomass from a simple raw material into a valuable source of energy and products.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Pyrolysis | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Dictates primary product (biochar, bio-oil, or biogas) | Higher temps favor liquids/gases; lower temps favor solids |
| Residence Time | Influences reaction completeness | Short times for fast pyrolysis (bio-oil); long times for char |
| Biomass Type | Sets inherent chemical potential | Wood, agricultural waste, etc., have different outputs |
| Moisture Content | Directly impacts energy efficiency | High moisture increases energy consumption and cost |
| Economic Factors | Determines project viability | Feedstock cost, capital investment, and product market value |
Ready to optimize your biomass pyrolysis process? KINTEK's expertise in laboratory equipment and consumables can help you precisely control the key factors—from temperature management to feedstock analysis—to maximize your yields of bio-oil, biochar, and biogas. Contact our lab experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and improve your project's economic viability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds

















