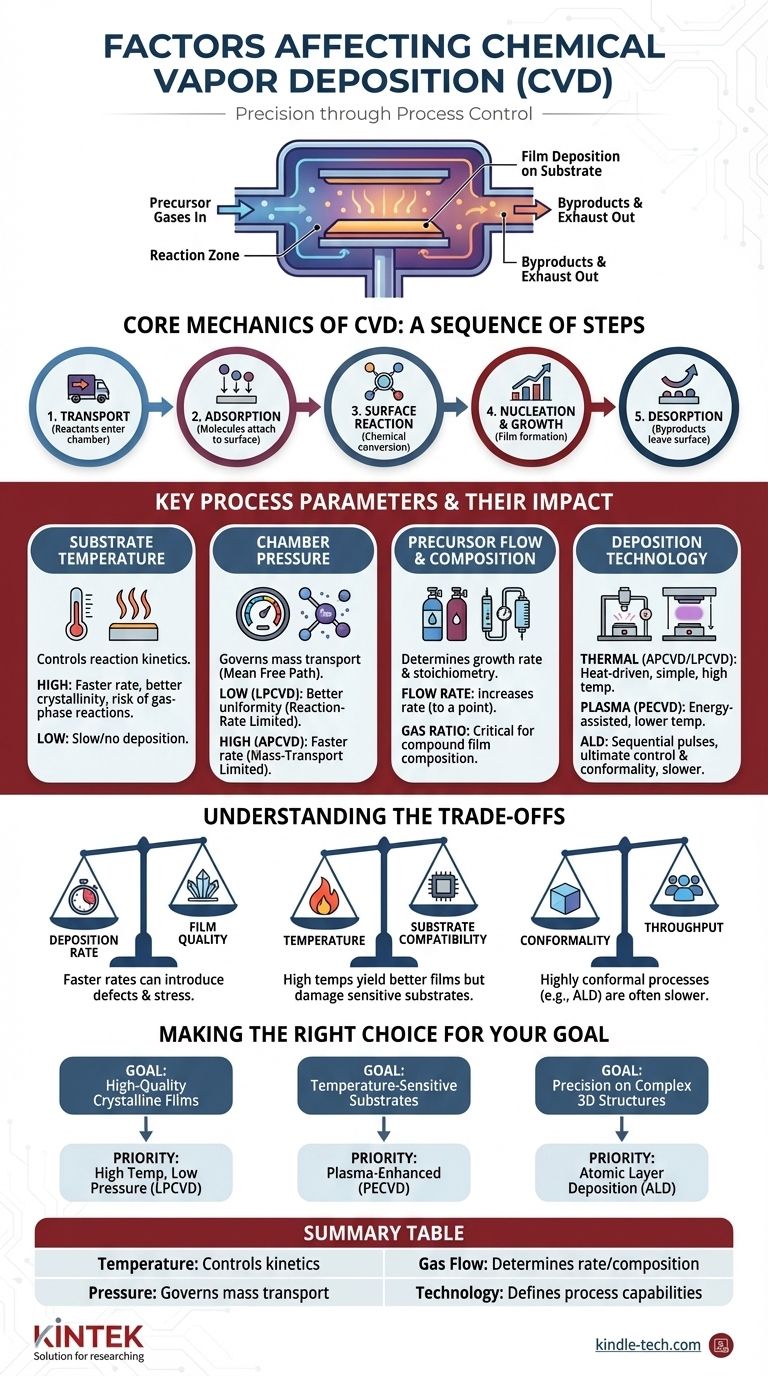
In short, the primary factors affecting Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are the substrate temperature, chamber pressure, the chemical composition and flow rate of the precursor gases, and the specific deposition technology used. These parameters collectively govern the rate of deposition, the chemical composition, the uniformity, and the physical properties of the resulting thin film.
The success of any CVD process hinges on a delicate balance between two competing phenomena: the rate at which reactant gases arrive at the substrate surface (mass transport) and the rate at which they react to form a film (surface reaction kinetics). Every factor you control is an attempt to manage this balance.
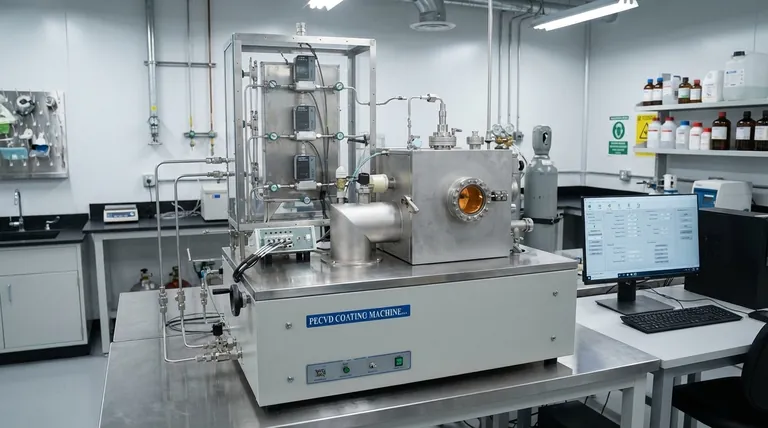

The Core Mechanics of CVD
To understand how different factors influence the outcome, you must first understand the fundamental steps of the process. CVD is not a single event, but a sequence of physical and chemical steps that must be carefully managed.
Step 1: Transport of Reactants
Reactant gases, known as precursors, are introduced into a reaction chamber. Their movement toward the substrate surface is governed by the chamber pressure and gas flow dynamics.
Step 2: Adsorption on the Surface
Once at the substrate, the precursor molecules must physically attach, or adsorb, onto the surface. This step is a prerequisite for any chemical reaction to occur.
Step 3: Surface Reaction
With sufficient thermal or plasma-induced energy, the adsorbed molecules undergo a chemical reaction. This can be decomposition or a reaction with other precursors, resulting in the desired solid material and volatile byproducts.
Step 4: Nucleation and Growth
The solid atoms or molecules produced by the reaction diffuse across the surface and bond together at stable sites, forming initial islands (nucleation). These islands then expand and coalesce to form a continuous thin film (growth).
Step 5: Desorption and Removal of Byproducts
The volatile byproducts from the surface reaction must detach from the surface (desorption) and be transported away by the gas flow. If byproducts are not removed efficiently, they can contaminate the film.
Key Process Parameters and Their Impact
Controlling the CVD process means deliberately manipulating the following parameters to favor specific steps in the sequence described above.
Substrate Temperature
Temperature is arguably the most critical factor in thermal CVD. It provides the activation energy required for the surface reactions to occur.
- Low temperatures result in very slow or no deposition because the precursor molecules lack the energy to react.
- High temperatures increase the reaction rate, but excessively high temperatures can cause unwanted gas-phase reactions before the precursors even reach the substrate, leading to particle formation and poor film quality.
Chamber Pressure
Pressure controls the concentration of precursor molecules and their mean free path—the average distance a molecule travels before colliding with another.
- Low pressure (vacuum conditions) increases the mean free path. This leads to more uniform deposition because gas transport is less hindered, a state known as being reaction-rate limited.
- High pressure (e.g., Atmospheric Pressure CVD) decreases the mean free path. This can increase the deposition rate but makes it harder for reactants to reach the entire surface uniformly, a state known as being mass-transport limited.
Precursor Gas Flow Rate & Composition
The choice of precursor chemicals determines the material being deposited. The flow rate and the ratio of different gases directly control the film's growth rate and stoichiometry.
- Flow Rate: Increasing the flow rate supplies more reactant to the surface, which can increase the deposition rate up to a point.
- Gas Ratio: For compound films (e.g., silicon nitride from silane and ammonia), the ratio of the precursor gases is critical for achieving the correct chemical composition in the final film.
Deposition Technology
Different CVD methods have been developed to manipulate these parameters, especially temperature, in unique ways.
- Thermal CVD (APCVD/LPCVD): Relies purely on heat to drive the reaction. Simple and effective, but the high temperatures limit the types of substrates that can be used.
- Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): Uses an electric field to generate a plasma. The energetic ions and electrons in the plasma provide the energy for the reaction, allowing deposition to occur at much lower temperatures.
- Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD): A specialized variant where precursors are introduced in sequential, self-limiting pulses. This provides unparalleled, atom-by-atom control over film thickness, but at the cost of being a much slower process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a CVD process always involves navigating a series of critical trade-offs. Understanding these is key to avoiding common pitfalls.
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
Pushing for a faster deposition rate, typically by increasing temperature or precursor flow, often comes at the expense of film quality. High rates can introduce stress, defects, and poor uniformity into the film structure.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
High temperatures often yield films with better crystallinity and fewer impurities. However, these temperatures will damage or destroy temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers or integrated circuits that have already undergone other processing steps. This is the primary reason for using lower-temperature methods like PECVD.
Conformality vs. Throughput
Conformality is the ability of a film to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional surface features. Processes like ALD offer nearly perfect conformality but are extremely slow. In contrast, high-rate processes are often limited by mass transport and may produce non-conformal coatings, with thicker films on top surfaces than on sidewalls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's goal will dictate how you prioritize and balance these factors.
- If your primary focus is high-quality, dense crystalline films: Prioritize a high substrate temperature and an optimized, reaction-rate-limited process in a low-pressure environment (LPCVD).
- If your primary focus is deposition on temperature-sensitive substrates: A plasma-enhanced (PECVD) or other energy-assisted method is essential to provide reaction energy without excessive heat.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and uniform coating on complex 3D structures: Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) is the superior choice, accepting its slower throughput in exchange for unparalleled control.
Mastering Chemical Vapor Deposition is the art of precisely controlling the process environment to guide a chemical reaction toward the desired film properties.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Primary Impact on CVD Process |
|---|---|
| Substrate Temperature | Controls reaction kinetics; high temp increases rate but can cause gas-phase reactions. |
| Chamber Pressure | Governs mass transport; low pressure (LPCVD) improves uniformity, high pressure (APCVD) increases rate. |
| Precursor Gas Flow & Composition | Determines growth rate and film stoichiometry (chemical composition). |
| Deposition Technology | Defines process capabilities (e.g., PECVD for low temps, ALD for ultimate conformality). |
Ready to Optimize Your CVD Process?
The right equipment is crucial for precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our expertise can help you achieve superior film quality and consistency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific CVD application goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods



















