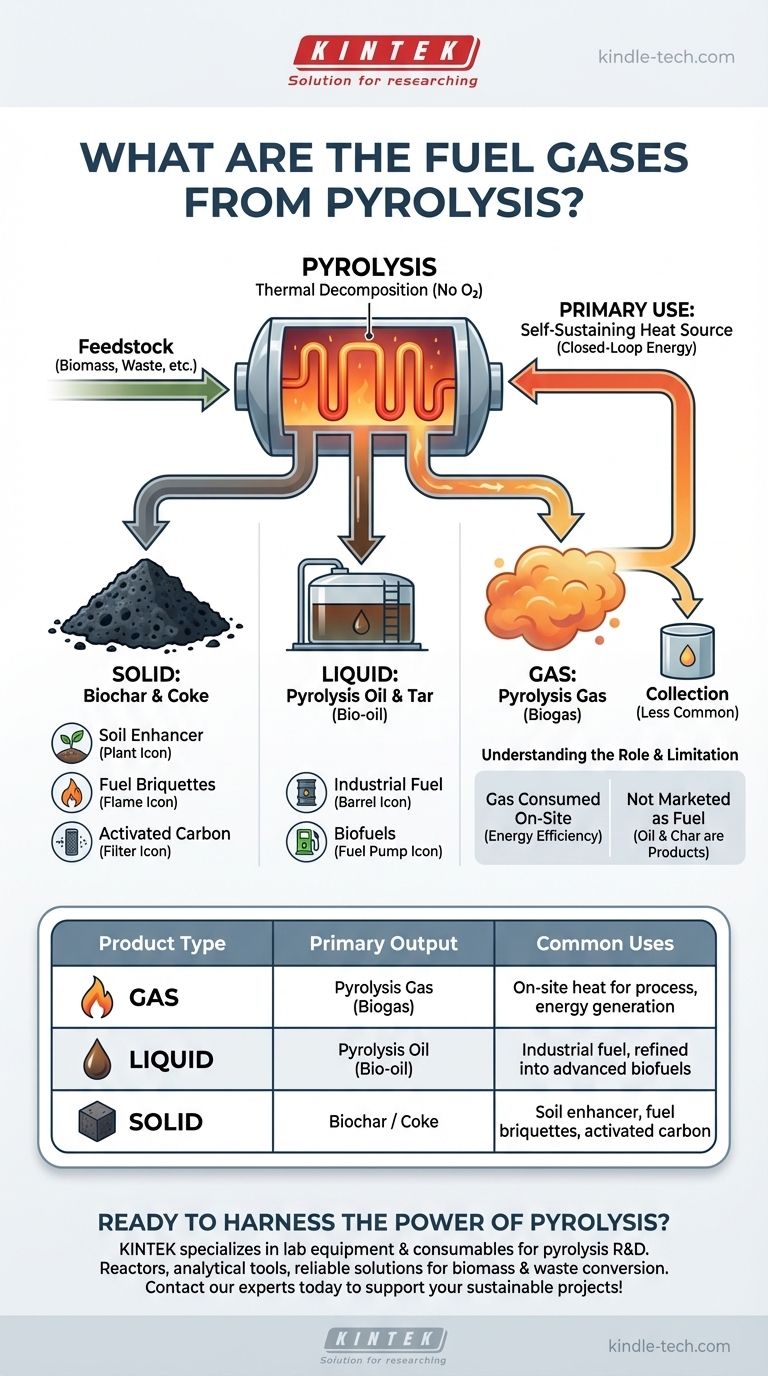
The primary fuel gas from pyrolysis is a non-condensable mixture commonly referred to as pyrolysis gas or biogas. This gas is one of three main products generated when organic material is heated in the absence of oxygen, alongside a liquid (pyrolysis oil) and a solid (coke or biochar). In most applications, this fuel gas is immediately recycled to provide the heat required to sustain the pyrolysis process itself.
Pyrolysis is best understood not as a gas production method, but as a thermal decomposition process that fractures organic material into three distinct product streams: a solid, a liquid, and a gas. The fuel gas is a valuable byproduct, but its most common role is to make the entire system more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.

The Three Core Products of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis doesn't create a single output; it separates a feedstock into a portfolio of useful materials. Understanding all three outputs is essential to grasping the value of the process.
The Solid Product: Biochar and Coke
The solid residue left after pyrolysis is a carbon-rich material. When derived from biomass, it's called biochar or biomass charcoal.
This solid product has several applications, including use as agricultural soil enhancers, for creating fuel briquettes, or as activated carbon sorbents.
The Liquid Product: Pyrolysis Oil and Tar
The condensable vapors from the process are cooled into a liquid known as pyrolysis oil, bio-oil, or tar.
This dark, viscous liquid can be used as an alternative industrial fuel or can be further refined into more advanced biofuels like biodiesel.
The Gaseous Product: Pyrolysis Gas
The remaining non-condensable vapors form the pyrolysis gas. This is the fuel gas you asked about.
It is a mixture of various flammable gases. Its primary and most immediate value comes from its high energy content, which is harnessed on-site.
How Pyrolysis Gas is Utilized
The gas stream is rarely the primary commercial product. Instead, its value is realized by integrating it back into the plant's operation.
A Self-Sustaining Heat Source
The most common use for pyrolysis gas is to route it directly back to the pyrolysis chamber's heating system.
By burning its own gaseous byproduct, a pyrolysis plant can significantly reduce its reliance on external energy sources, lowering operational costs and improving its overall energy balance.
Collection for Other Uses
While less common, the gas can also be collected and stored in a tank.
This allows it to be used for other on-site energy needs or potentially sold if produced in sufficient quantity and quality, though this is not the typical model.
Understanding the Key Limitation
While powerful, the role of pyrolysis gas is often misunderstood. The process is typically designed around the solid and liquid products, not gas generation.
On-site Consumption is the Norm
Most pyrolysis systems are designed as closed-loop energy systems. The goal is to use the gas to make the conversion process as efficient as possible.
This means the pyrolysis gas is almost always entirely consumed on-site and is not available as a separate, marketable fuel product. The real commercial outputs are the oil and char.
Yield Depends on Feedstock
The specific composition and volume of the gas, oil, and char will vary significantly depending on the initial material being processed.
Different types of biomass, plastics, or other waste will yield different proportions of the three core products, affecting the overall economics of the operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The value of pyrolysis comes from its ability to turn a single input into multiple outputs. Your primary goal will determine which output you prioritize.
- If your primary focus is energy self-sufficiency: The pyrolysis gas is the key, as it provides the fuel to run the entire conversion process with minimal external energy input.
- If your primary focus is creating marketable commodities: The value lies in the pyrolysis oil and biochar, which can be sold for use in agriculture, energy, or chemical production.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a versatile technology for converting waste and biomass into a spectrum of valuable energy and material products.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Primary Output | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Gas | Pyrolysis Gas (Biogas) | On-site heat for the process, energy generation |
| Liquid | Pyrolysis Oil (Bio-oil) | Industrial fuel, refined into advanced biofuels |
| Solid | Biochar / Coke | Soil enhancer, fuel briquettes, activated carbon |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your lab or pilot plant? KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for pyrolysis research and development. From reactors to analytical tools, we provide the reliable solutions that help you efficiently convert biomass and waste into valuable energy products. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sustainable technology projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere













