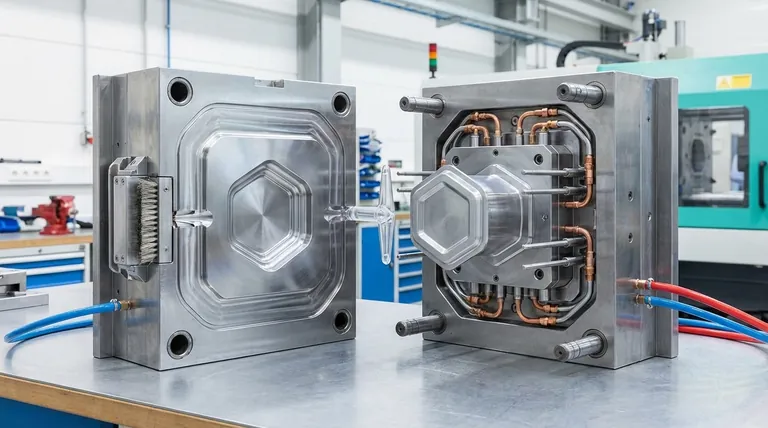
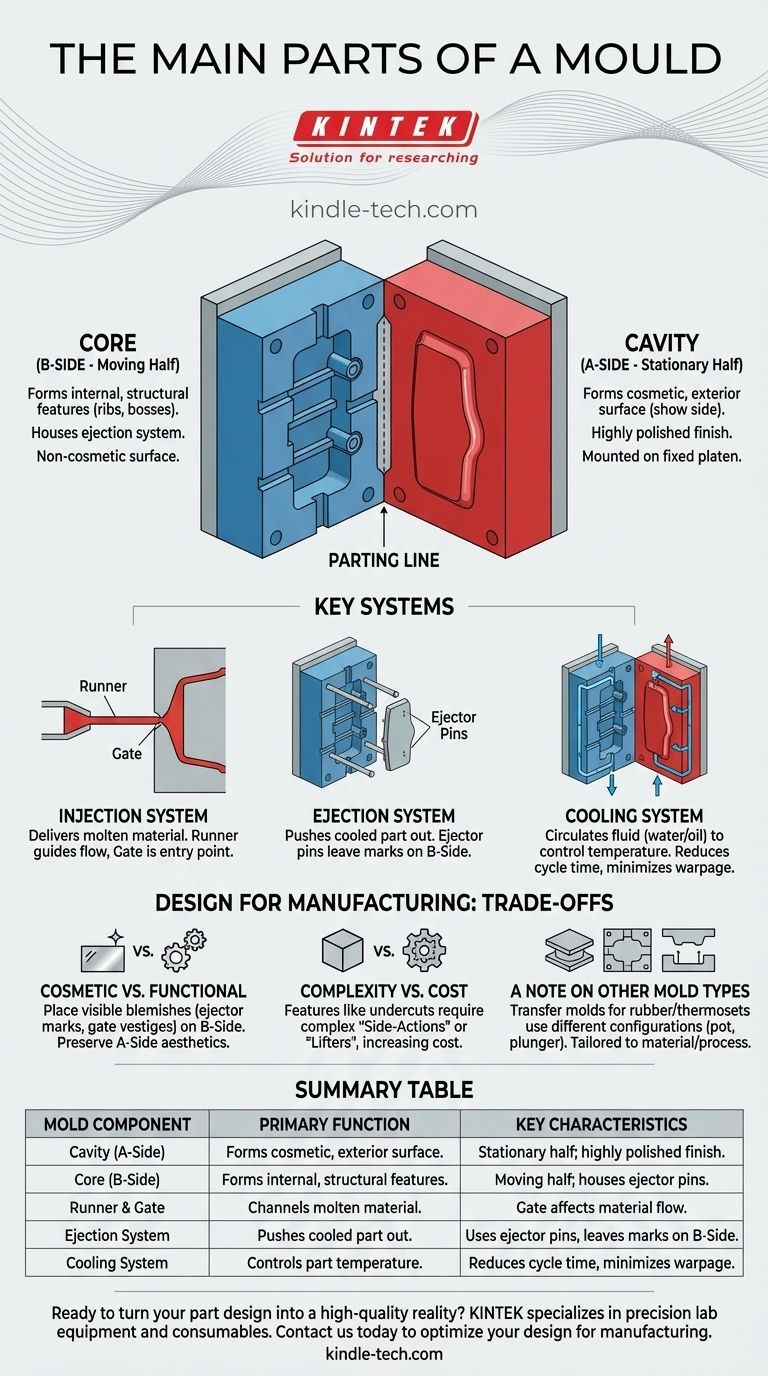
At its most fundamental level, a mold is comprised of two primary halves: the core and the cavity. When brought together, these halves form a negative space that shapes the molten material into a finished part. The cavity half typically forms the cosmetic, exterior surface of the component (the "A-Side"), while the core half forms the internal, structural features (the "B-Side").
While a mold appears to be a simple two-part tool, its design is a sophisticated balance of form and function. Understanding how the core, cavity, and their supporting systems interact is the key to designing parts that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also manufacturable and robust.
The Core and Cavity: The Two Halves of a Mold
The core and cavity are the heart of the mold, directly defining the geometry of the final product. Their design dictates everything from the part's appearance to its structural features.
The Cavity (The 'A' Side)
The cavity is the stationary half of the mold, often mounted on the fixed platen of the molding machine. It forms what is known as the "A-Side" of the molded part.
This is typically the cosmetic or "show" side—the surface users will see and interact with. It is polished to a high finish to ensure the final part has a smooth, unblemished appearance.
The Core (The 'B' Side)
The core is the moving half of the mold. It forms the "B-Side" of the part, which is usually the non-cosmetic, internal, or back-facing surface.
The core is where most of the part's functional geometry, such as ribs for strength, bosses for screws, and other mounting features, are located. The part shrinks onto and is held by the core as it cools, which is crucial for the ejection phase.
The Parting Line
The parting line is the precise seam where the core and cavity meet. This line will be visible on the final product, and its placement is a critical design consideration to minimize its aesthetic impact.
Key Systems That Make the Mold Function
A modern mold is more than just two blocks of steel. It is an intricate machine with several critical systems working in concert to produce a part efficiently and repeatedly.
The Injection System
This system delivers the molten material into the mold. It consists of a runner, which is a channel that guides the material from the machine's nozzle, and a gate, which is the specific entry point where the material flows into the cavity itself.
The Ejection System
Once the part has cooled and solidified, it must be removed from the mold. The ejection system, typically a series of ejector pins housed in the core half, pushes the finished part out of the mold. These pins often leave small, circular marks on the B-Side of the part.
The Cooling System
Controlling temperature is vital for quality and speed. Channels are machined into both the core and cavity halves to circulate a fluid, like water or oil. This system removes heat from the part, allowing it to solidify at a controlled rate, which minimizes warpage and reduces the overall cycle time.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Design for Manufacturing
The design of a mold's parts directly influences the quality, cost, and functionality of the final component.
Cosmetic vs. Functional Surfaces
The A-Side/B-Side distinction is fundamental. All visible blemishes, such as ejector pin marks or gate vestiges, should be designed to be on the non-cosmetic B-Side whenever possible. This preserves the clean appearance of the A-Side.
Complexity vs. Cost
Parts with features like deep holes or side-facing details (undercuts) cannot be made with a simple core and cavity alone. They require additional moving parts in the mold, called side-actions or lifters, which dramatically increase the mold's complexity and cost.
A Note on Other Mold Types
While injection molding is common, other processes use different mold configurations. A transfer mold, often used for rubber or thermoset plastics, uses a pot to hold the material, a plunger to pressurize it, and a mold cavity to form the final shape. This highlights that the mold's parts are always tailored to the specific material and manufacturing process.
Applying This to Your Design
Understanding these components allows you to make better decisions when designing a part for manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics: Pay close attention to the parting line location and ensure all non-cosmetic features are on the B-Side, away from the cosmetic A-Side.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Design functional features like ribs and bosses into the core (B-Side) and consider how the material flow from the gate will affect part strength.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Design the part to be easily released from a simple core and cavity to avoid the need for expensive side-actions or complex ejection systems.
By designing a part with the mold's function in mind, you move from simply creating a shape to engineering a successful product.
Summary Table:
| Mold Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cavity (A-Side) | Forms the cosmetic, exterior surface of the part. | Stationary half; highly polished finish. |
| Core (B-Side) | Forms the internal, structural features of the part. | Moving half; houses ejector pins and functional details. |
| Runner & Gate | Channels molten material from the machine nozzle into the cavity. | Gate is the specific entry point; affects material flow. |
| Ejection System | Pushes the cooled part out of the mold. | Typically uses ejector pins, which leave marks on the B-Side. |
| Cooling System | Circulates fluid to control part temperature and solidification. | Reduces cycle time and minimizes warpage. |
Ready to turn your part design into a high-quality, manufacturable reality? The right mold is critical for achieving the perfect balance of aesthetics, structural integrity, and cost-efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise to support your entire manufacturing process—from prototyping to production.
Let our team help you optimize your design for manufacturing. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can be your partner in innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region















