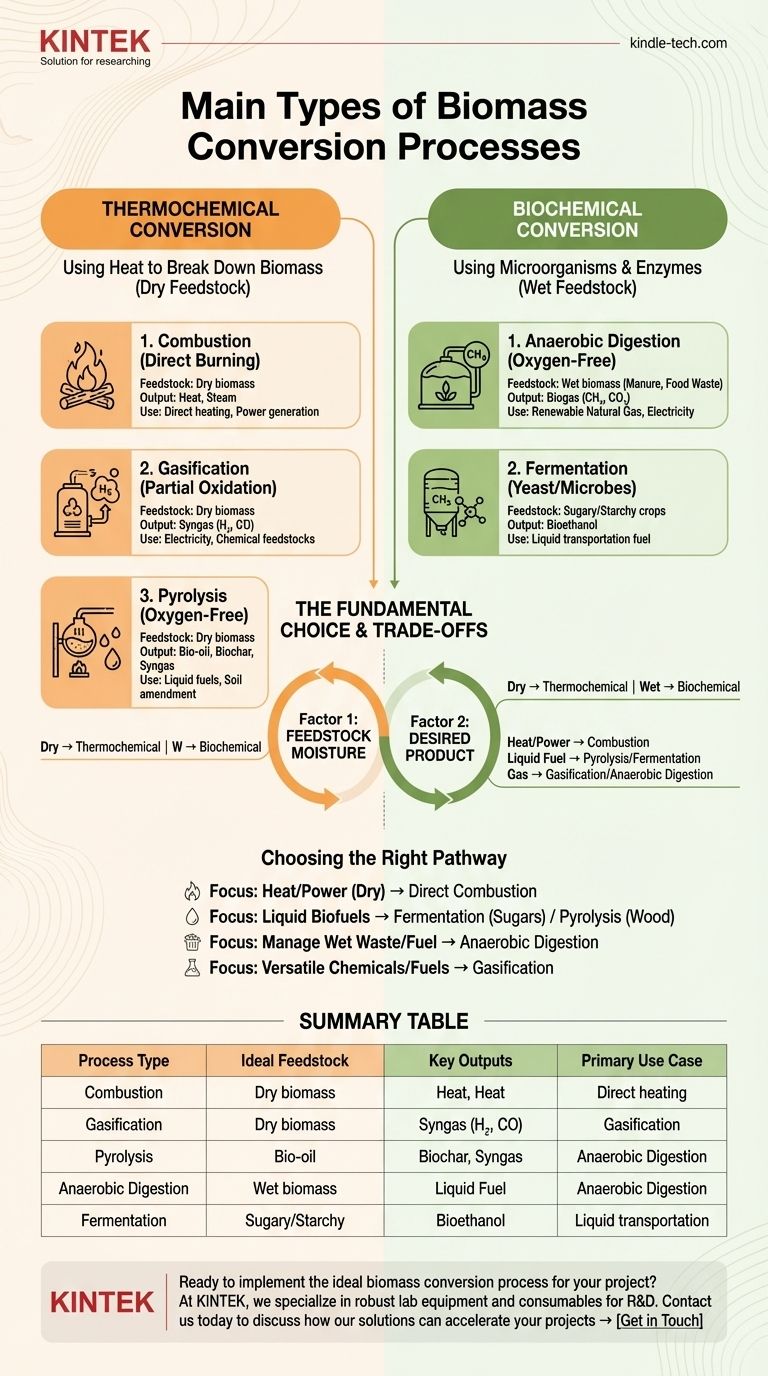
At its core, biomass conversion involves transforming organic matter into usable energy and products through two primary pathways: thermochemical and biochemical processes. Thermochemical methods use heat to break down dry biomass like wood, while biochemical methods use microorganisms to decompose wet biomass like food waste or manure.
The fundamental choice between conversion processes is dictated by two factors: the type of biomass feedstock (primarily its moisture content) and the desired final product (heat, liquid fuel, gaseous fuel, or chemicals).

Thermochemical Conversion: Using Heat to Break Down Biomass
Thermochemical conversion is best suited for biomass with low moisture content, such as wood, straw, and other dry agricultural residues. These processes use heat and controlled chemical reactions to deconstruct the material.
Combustion (Direct Burning)
Combustion is the most straightforward and common method. It involves the direct burning of biomass in the presence of excess oxygen to produce heat.
This heat can be used directly for heating applications or to produce steam that drives a turbine, generating electricity. It is a mature technology, but it is less efficient for producing anything other than heat and power.
Gasification: Creating a Fuel Gas (Syngas)
Gasification involves heating biomass with a limited amount of oxygen or steam, which prevents full combustion. This partial oxidation converts the solid material into a combustible gas mixture.
This product, known as syngas (synthesis gas), is primarily composed of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. Syngas is highly versatile and can be burned to generate electricity or used as a chemical feedstock to produce liquid fuels and other valuable chemicals.
Pyrolysis: Decomposing Biomass Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in a completely oxygen-free (inert) environment. Instead of burning, the heat breaks the material down into three distinct products.
These products are:
- Bio-oil: A dark, viscous liquid fuel that can be upgraded into transportation fuels. This is collected through the condensation of vapors produced during the process.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal that can be used as a soil amendment or as a solid fuel.
- Syngas: A non-condensable gas that can be used to provide heat for the pyrolysis process itself.
Biochemical Conversion: Using Microorganisms and Enzymes
Biochemical processes are ideal for high-moisture biomass, such as animal manure, sewage sludge, food waste, and specific energy crops. These methods leverage the natural metabolic processes of microorganisms.
Anaerobic Digestion: Producing Biogas
In anaerobic digestion, microorganisms break down organic matter in an oxygen-free environment, similar to what happens in a landfill or the digestive system of a cow.
The primary output is biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. This biogas can be burned to generate heat and electricity or purified to produce renewable natural gas (RNG) for pipeline injection or use as a vehicle fuel.
Fermentation: Converting Sugars into Bioethanol
Fermentation uses yeast and other microbes to convert the sugars and starches found in crops like corn, sugarcane, or wheat into alcohol.
The most common product is bioethanol, a liquid fuel that is widely blended with gasoline. Research is also advancing on cellulosic fermentation, which aims to produce ethanol from non-food biomass like wood and grasses.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right conversion pathway involves navigating a series of technical and economic trade-offs. The optimal choice is rarely universal and depends entirely on your specific resources and goals.
Feedstock Moisture Content is Key
This is the most critical factor. Trying to use a high-heat thermochemical process on wet biomass is extremely inefficient, as enormous energy is wasted simply boiling off water. Conversely, dry biomass is unsuitable for biochemical processes, which require water for the microbes to thrive.
End Product Determines the Process
Your target output dictates the technology. If you only need process heat, simple combustion is most cost-effective. If you need a liquid transportation fuel, pyrolysis or fermentation are the primary options. If you need a versatile gas, you would choose gasification or anaerobic digestion.
Process Complexity and Scale
Combustion is relatively simple and scalable. Pyrolysis and gasification require more sophisticated reactors and precise control over temperature and atmosphere, often making them more complex and capital-intensive. Anaerobic digestion can be implemented at scales ranging from small farm-based digesters to large municipal facilities.
Choosing the Right Pathway for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, align your primary objective with the most suitable conversion technology.
- If your primary focus is generating heat and power from dry waste: Direct combustion is the most mature and economically viable pathway.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid biofuels: Choose fermentation for sugary or starchy crops and pyrolysis for woody or fibrous biomass.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste and producing fuel: Anaerobic digestion is the ideal choice to create valuable biogas.
- If your primary focus is producing versatile chemical building blocks or advanced fuels: Gasification offers the most flexible platform by converting solid biomass into syngas.
Ultimately, effective biomass conversion is about intelligently matching the right technology to the available resource to achieve a specific outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Ideal Feedstock | Key Outputs | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Dry biomass (wood, straw) | Heat, Steam | Direct heating and power generation |
| Gasification | Dry biomass | Syngas (H₂, CO) | Electricity, chemical feedstocks |
| Pyrolysis | Dry biomass | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas | Liquid fuels, soil amendment |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Wet biomass (manure, food waste) | Biogas (CH₄, CO₂) | Renewable natural gas, electricity |
| Fermentation | Sugary/Starchy crops | Bioethanol | Liquid transportation fuel |
Ready to implement the ideal biomass conversion process for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for R&D in biomass conversion. Whether you're developing pyrolysis reactors, optimizing fermentation, or analyzing syngas, our tools help you achieve precise, scalable results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your biomass energy projects → Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the factors affecting the yield of bio-oil from the pyrolysis of coconut shell? Control 4 Key Parameters
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















