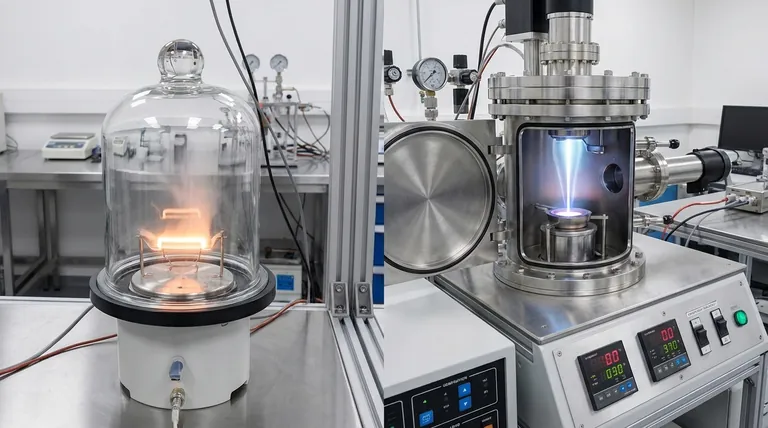
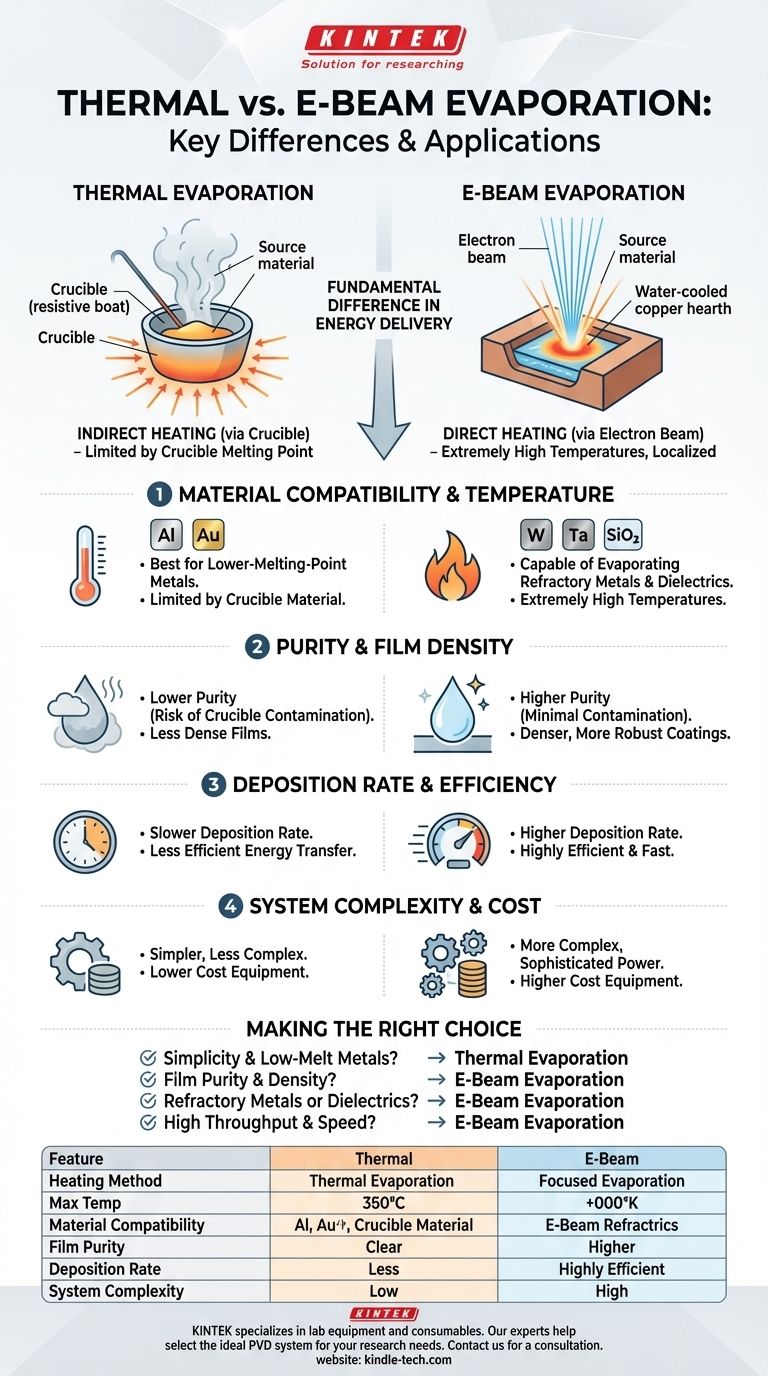
At its core, the difference between thermal evaporation and electron beam (e-beam) evaporation is the method used to heat and vaporize the source material. Thermal evaporation uses indirect heat, warming a container (crucible) which in turn heats the material, while e-beam evaporation uses a focused, high-energy beam of electrons to heat the material directly. This fundamental difference in heating mechanism dictates the types of materials that can be used, the purity of the resulting film, and the efficiency of the deposition process.
The choice between these two methods is not merely procedural; it's a strategic decision based on your material's properties and desired film quality. Thermal evaporation is a simpler process for low-temperature materials, whereas e-beam evaporation is a higher-performance technique required for high-melting-point materials and applications demanding superior purity.

The Fundamental Difference: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The way energy is delivered to the source material is the single most important distinction between these two physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques. It has cascading effects on every aspect of the process.
How Thermal Evaporation Works
In thermal evaporation, an electric current is passed through a resistive element, often called a "boat" or crucible, which holds the source material.
This boat heats up significantly, much like a filament in a light bulb. The heat is then transferred from the hot crucible to the source material, causing it to melt and eventually evaporate.
How E-Beam Evaporation Works
E-beam evaporation uses a completely different approach. A charged tungsten filament emits a stream of electrons, which are then accelerated and focused by magnetic fields into a high-energy beam.
This beam is aimed directly at the surface of the source material, which sits in a water-cooled copper hearth. The intense, localized energy from the electrons heats the material directly to its evaporation point, while the surrounding hearth remains cool.
Key Implications for Your Process
This distinction between direct and indirect heating is not just academic. It directly impacts material choice, film quality, and process speed.
Material Compatibility and Temperature
Thermal evaporation is limited by the melting point of the crucible itself. It is therefore best suited for materials with lower melting temperatures, such as aluminum or gold.
E-beam evaporation can generate extremely high temperatures in a very localized spot. This makes it capable of evaporating virtually any material, including refractory metals (like tungsten and tantalum) and dielectrics (like silicon dioxide) that have very high melting points.
Purity and Film Density
With thermal evaporation, the entire crucible becomes white-hot, creating a risk that the crucible material itself will outgas or evaporate, leading to impurities in the deposited film.
Because e-beam evaporation heats only the source material, the water-cooled hearth contributes very little contamination. This results in higher-purity films. The higher energy involved also typically produces denser, more robust coatings.
Deposition Rate and Efficiency
The direct and efficient energy transfer of an electron beam allows for a much higher deposition rate compared to the slower, indirect heating of thermal evaporation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While e-beam evaporation offers superior performance in many categories, the choice is not always straightforward.
The Simplicity of Thermal Evaporation
The primary advantage of thermal evaporation is its relative simplicity. The equipment is generally less complex and less expensive, making it a viable and effective choice for many standard applications involving suitable materials.
The Complexity and Versatility of E-Beam
E-beam systems are more complex and require more sophisticated power supplies and control systems. However, this complexity enables immense versatility, such as using multi-pocket, motorized carousels to deposit multiple different materials in a single vacuum cycle without breaking vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method depends entirely on the specific goals of your deposition process.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and lower-melting-point metals: Thermal evaporation is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is film purity and density: E-beam evaporation's direct heating method minimizes contamination and produces higher-quality films.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or dielectrics: E-beam evaporation is the only viable method due to its ability to reach extremely high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: E-beam evaporation provides a significantly faster deposition rate, increasing process efficiency.
Ultimately, understanding how each method delivers energy to your source material empowers you to select the technique that best aligns with your material requirements and quality standards.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (via crucible) | Direct (electron beam) |
| Max Temperature | Lower (limited by crucible) | Extremely High |
| Material Compatibility | Low-melting-point metals (Al, Au) | Refractory metals, dielectrics |
| Film Purity | Lower (risk of crucible contamination) | Higher (minimal contamination) |
| Deposition Rate | Slower | Faster |
| System Complexity | Simpler, lower cost | More complex, higher cost |
Still unsure which evaporation method is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal PVD system—whether it's a cost-effective thermal evaporation setup or a high-performance e-beam system—to achieve the material compatibility, film purity, and deposition rates your research demands.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK provide the reliable lab equipment solutions you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production



















