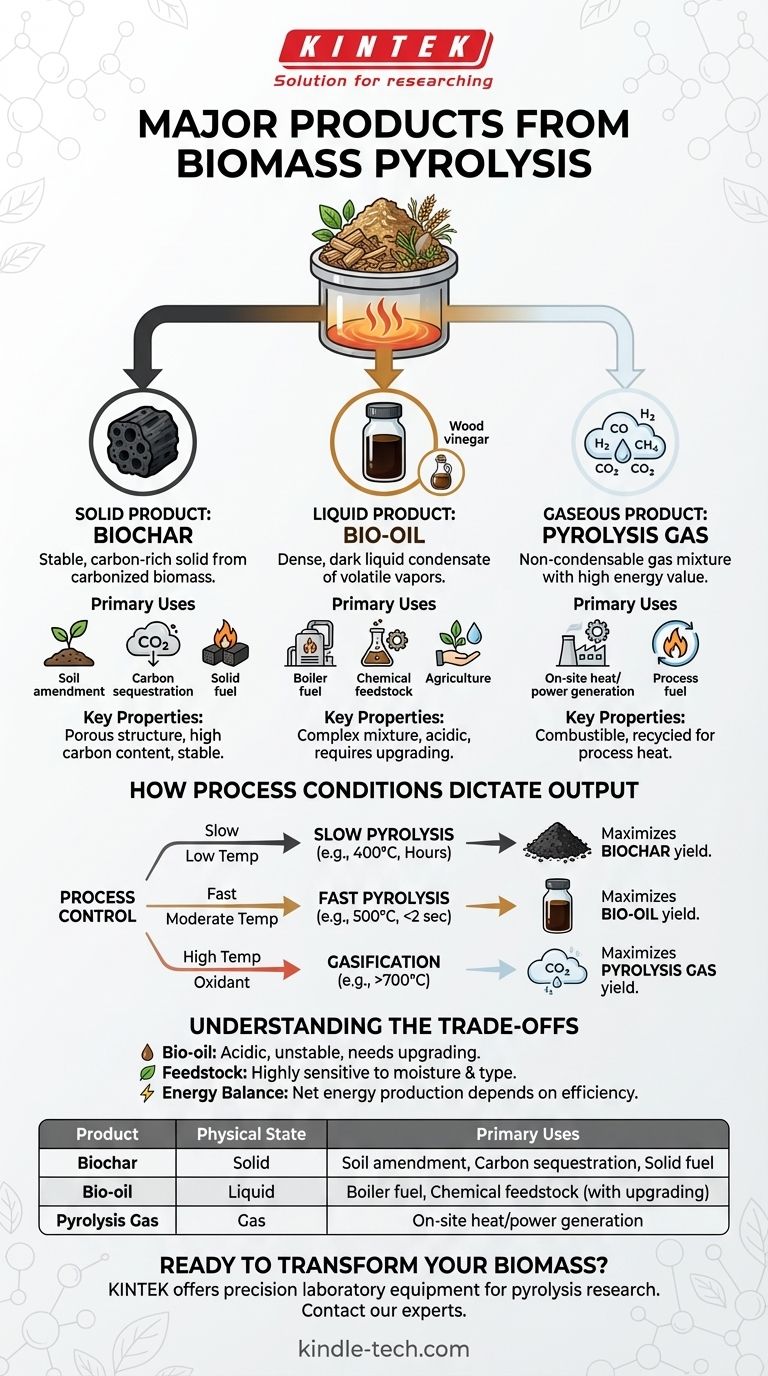
In short, biomass pyrolysis yields three primary products categorized by their physical state: a solid known as biochar, a liquid called bio-oil, and a non-condensable pyrolysis gas. These are the fundamental outputs from the thermal decomposition of organic material in the absence of oxygen. The specific proportions and characteristics of each depend entirely on the input biomass and the process conditions used.
The core principle to grasp is that biomass pyrolysis is not a single process but a tunable platform. By controlling temperature and processing time, you are not just creating products; you are deciding which product to maximize—the solid, the liquid, or the gas—to meet a specific goal.
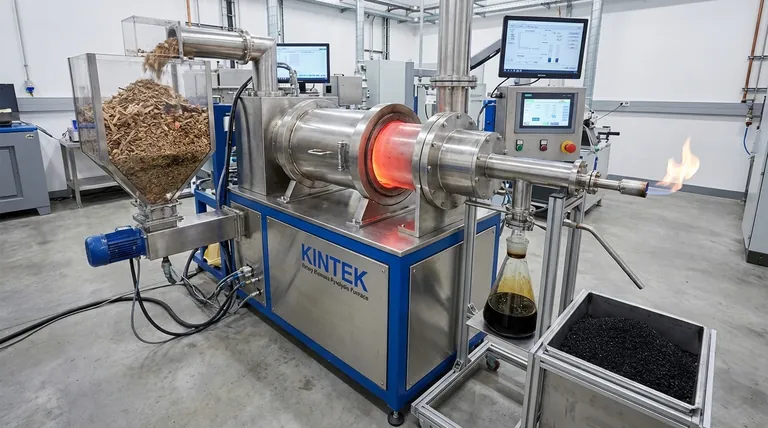

The Three Primary Product Categories
Pyrolysis breaks down complex organic polymers in biomass into simpler, smaller molecules. These molecules are then separated into solid, liquid, and gaseous streams.
The Solid Product: Biochar
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components of the biomass have been driven off. It is essentially a form of charcoal.
Its primary uses are determined by its properties. As a soil amendment, its porous structure improves water retention and provides a habitat for beneficial microbes. As a form of stable carbon, it is a key tool for long-term carbon sequestration. It can also be compressed into briquettes and used as a solid fuel, often called biocoal.
The Liquid Product: Bio-oil
Bio-oil, sometimes called pyrolysis oil or tar, is a dark, dense liquid formed by cooling and condensing the volatile vapors produced during pyrolysis. It is a complex mixture of water, oxygenated organic compounds, and acids.
This liquid can be combusted directly in boilers or furnaces for heat and power generation. However, due to its acidity and instability, it often requires upgrading to be used as a transportation fuel or as a feedstock for producing renewable chemicals. A secondary liquid, wood vinegar (pyroligneous acid), is the aqueous fraction of this condensate and has applications in agriculture.
The Gaseous Product: Pyrolysis Gas
This is the fraction that does not condense into a liquid when cooled. Often called syngas or non-condensable gas, it is primarily composed of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
This gas has a significant energy value. In most pyrolysis plants, it is not sold as a final product but is instead recycled back into the system to provide the heat required to sustain the pyrolysis reaction, making the process more energy-efficient.
How Process Conditions Dictate the Output
You can steer the pyrolysis process to favor one product over the others by adjusting key parameters. The most important factors are temperature and the residence time of the biomass in the reactor.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
This process uses lower temperatures (around 400°C) and a much longer processing time (hours). The slow heating rate allows for the gradual release of volatiles, leaving behind a high yield of the solid char. This is the traditional method for making charcoal.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-oil
To produce the most liquid fuel, fast pyrolysis is used. This involves moderate temperatures (around 500°C) but an extremely rapid heating rate and very short residence time (typically less than two seconds). This quenches the chemical reactions at an intermediate stage, maximizing the yield of condensable vapors that form bio-oil.
Gasification: Maximizing Gas
Though technically a related process, gasification demonstrates the end of the spectrum. By using much higher temperatures (above 700°C) and introducing a small amount of an oxidant (like air or steam), the process is designed to break down nearly all components, including the char and tars, into the simplest gaseous molecules (CO and H₂), maximizing the yield of syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, biomass pyrolysis is not a perfect solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for any practical application.
Bio-oil Quality and Stability
Raw bio-oil is not a "drop-in" replacement for petroleum fuels. It is acidic, corrosive to standard pipes and engines, and chemically unstable, thickening over time. It requires significant and often costly refining, or "upgrading," before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Feedstock Variability
The process is highly sensitive to the type and quality of the input biomass. Woody biomass produces a different product slate than agricultural residues or manure. Moisture content is particularly critical, as high moisture requires significant energy input to evaporate water before pyrolysis can begin.
Overall Energy Balance
While recycling the pyrolysis gas makes the system more efficient, there is always a net energy calculation to consider. The energy required to prepare the feedstock (drying, grinding) and run the equipment must be less than the energy value of the final products for the system to be a net energy producer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis approach is defined entirely by your objective.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or agricultural soil improvement: Your goal is to maximize the solid product, which points directly to slow pyrolysis to create stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock: Your goal is to maximize the liquid product, requiring the rapid heating and cooling of a fast pyrolysis system.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site power or high-quality fuel gas: Your goal is to maximize the gas product, which means operating at higher temperatures closer to a gasification regime.
Ultimately, understanding pyrolysis means seeing it as a versatile conversion technology that can be precisely engineered to transform low-value biomass into a variety of high-value solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Summary Table:
| Product | Physical State | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Solid | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, solid fuel (biocoal) |
| Bio-oil | Liquid | Boiler fuel, chemical feedstock (requires upgrading) |
| Pyrolysis Gas | Gas | On-site heat/power generation (recycled to fuel the process) |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable products? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment for pyrolysis research and development. Whether your goal is to maximize biochar for carbon sequestration, produce bio-oil for fuel, or optimize gas yields, our reactors and analytical tools provide the precision and control you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific biomass conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs


















