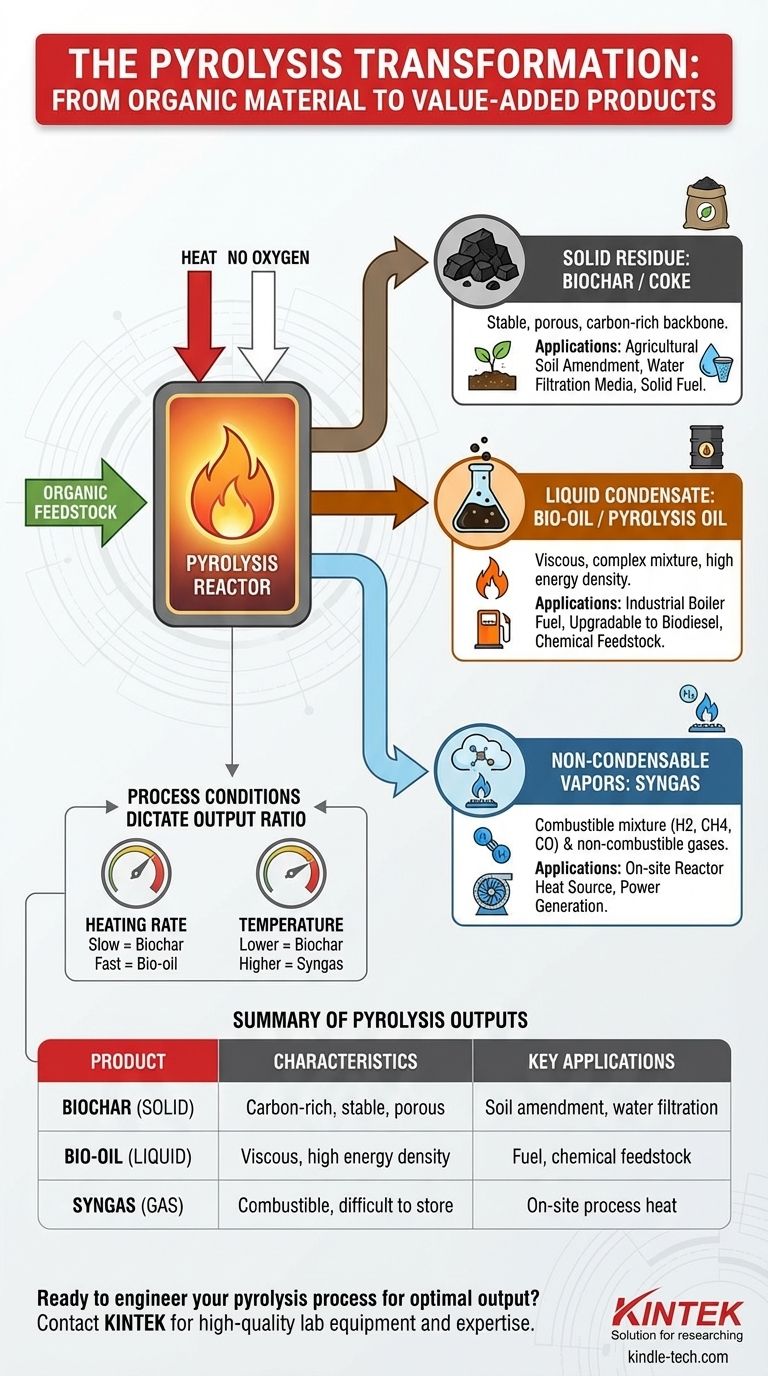
At its core, pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that breaks down organic material in the absence of oxygen, yielding three distinct types of products. The process consistently produces a solid carbon-rich residue called biochar, a liquid condensate known as bio-oil, and a mixture of non-condensable gases often referred to as syngas.
The crucial takeaway is that pyrolysis does not create a single output, but a portfolio of valuable products. The specific ratio and composition of these solid, liquid, and gas outputs are not accidental; they are deliberately controlled by the process conditions and the initial feedstock.

Deconstructing the Three Core Outputs
Pyrolysis transforms a single input stream into three separate, usable output streams. Understanding the nature and application of each is key to seeing the value of the process.
The Solid Residue: Biochar
The solid material left after the volatile components have been driven off is a stable, carbon-rich product called biochar or coke.
This product is the fixed-carbon backbone of the original material. Its porous structure makes it highly valuable.
Common applications include agricultural soil amendment, water filtration media, or as a solid fuel source through briquetting.
The Liquid Condensate: Bio-oil
As the feedstock heats up, volatile compounds vaporize. When these vapors are rapidly cooled, they condense into a liquid known as bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil).
This dark, viscous liquid is a complex mixture of water, organic acids, and hundreds of other organic compounds. It is essentially a raw, liquid form of biomass energy.
Bio-oil can be used as an industrial fuel for boilers, upgraded into transportation fuels like biodiesel, or refined to extract valuable chemical commodities. Its liquid form offers major advantages for storage and transport.
The Non-Condensable Vapors: Syngas
Not all the vapors produced during pyrolysis will condense into a liquid. The remaining light gases are collectively known as syngas or pyrolysis gas.
This gas is a mixture of combustible components, including hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), and carbon monoxide (CO), along with non-combustible gases like carbon dioxide (CO2).
Because it is difficult to store, syngas is most often used directly on-site to provide the heat required to power the pyrolysis reactor, making the entire process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
Why the Outputs Vary: Process Conditions Matter
You can dial in the pyrolysis process to favor one type of output over the others. The balance between solid, liquid, and gas is a direct function of the operating parameters.
The Influence of Heating Rate
The speed at which the feedstock is heated is arguably the most critical factor.
Slow pyrolysis, with its long residence times, maximizes the production of solid biochar. This process "bakes" the material slowly, driving off volatiles while leaving the carbon structure intact.
Fast pyrolysis, conversely, uses extremely rapid heating to vaporize the material almost instantly. This process is optimized to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil, often exceeding 70% by weight.
The Role of Temperature
The peak temperature reached inside the reactor also directs the final product distribution.
Lower temperatures (around 400-500°C) tend to favor higher yields of solid biochar.
As temperatures increase (above 500°C), they promote further thermal cracking of heavier molecules, which results in a greater yield of syngas at the expense of both char and oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the outputs of pyrolysis are versatile, they come with practical considerations that are important for real-world application.
Bio-oil: Energy Dense but Unrefined
The key advantage of bio-oil is its high energy density and liquid form. However, it is typically acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable compared to petroleum fuels.
It almost always requires some level of upgrading or refining before it can be used in standard engines or turbines, adding a layer of cost and complexity.
Biochar: A Stable Product with Market Nuances
Biochar is incredibly stable, making it an excellent vehicle for long-term carbon sequestration.
However, its economic value can vary widely. Its effectiveness as a soil amendment depends on its specific properties, which are tied to the feedstock and process, meaning not all biochar is created equal.
Syngas: Valuable but Captive
The energy value of syngas is significant, but its low density makes it impractical to compress, store, or transport economically.
This reality means its value is almost exclusively realized when it is consumed immediately on-site, limiting its application as a distributable commodity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" pyrolysis setup is entirely dependent on your desired outcome. By adjusting the process, you can transform the same input material to meet different needs.
- If your primary focus is creating a storable liquid fuel: You must optimize for a fast pyrolysis process with rapid heating and quenching to maximize bio-oil yield.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or carbon sequestration: A slow pyrolysis process is the ideal approach to produce the highest quantity and quality of stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy with maximum self-sufficiency: You will want a balanced process that effectively captures and utilizes the syngas to power the entire operation.
Ultimately, understanding these outputs allows you to treat organic waste not as a liability, but as a flexible resource that can be engineered for value.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Name | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid | Biochar / Coke | Carbon-rich, porous, stable | Soil amendment, water filtration, solid fuel |
| Liquid | Bio-oil / Pyrolysis Oil | Viscous, complex mixture, high energy density | Industrial boiler fuel, upgraded to biodiesel, chemical feedstock |
| Gas | Syngas | Mixture of combustible gases (H2, CH4, CO) | On-site heat source for the pyrolysis reactor |
Ready to engineer your pyrolysis process for optimal output?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for researching and optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you are developing a process to maximize biochar for carbon sequestration, bio-oil for liquid fuel, or syngas for energy efficiency, our reactors, analytical tools, and expert support can help you achieve precise control and reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can help you transform organic material into valuable products. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with an expert!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















