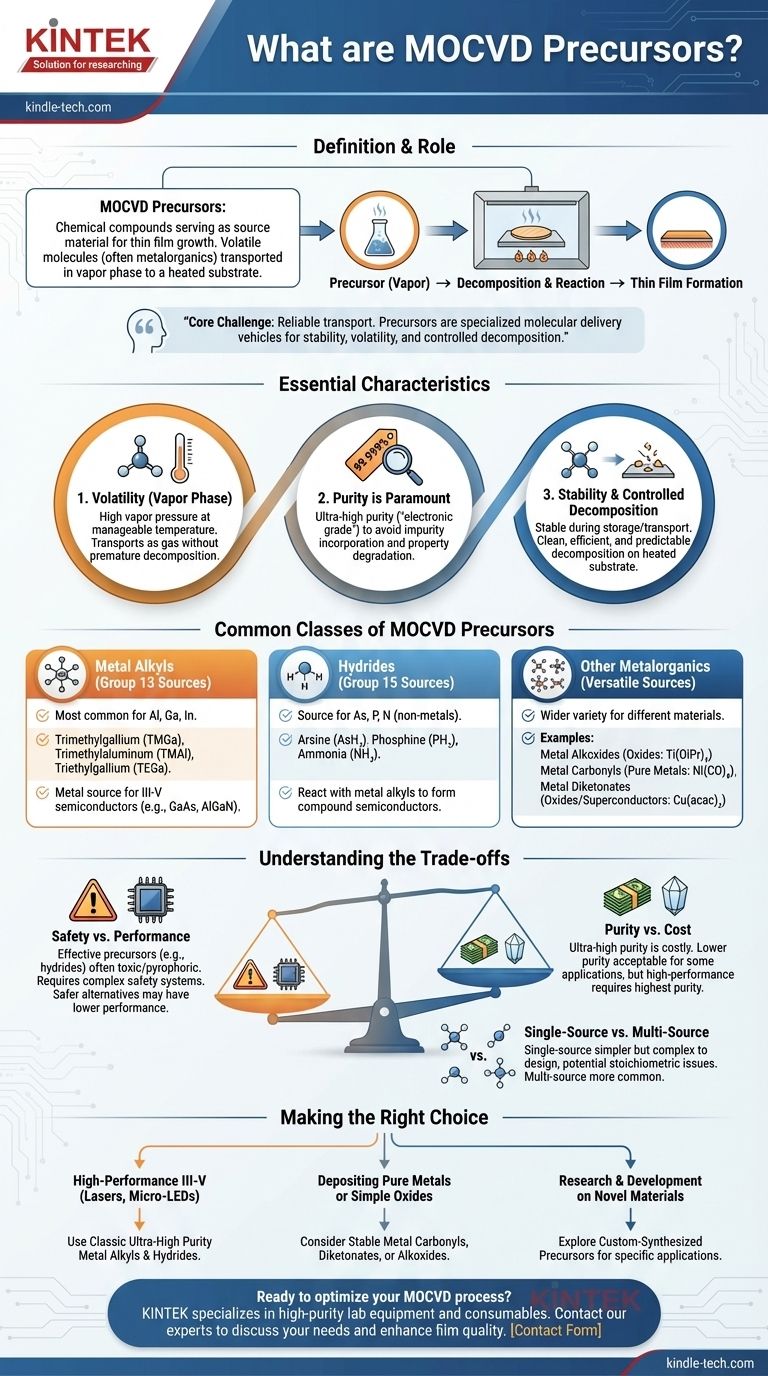
In short, precursors in MOCVD are the chemical compounds that serve as the source material for film growth. These are volatile molecules, often metalorganics, that contain the specific atoms you want to deposit. They are transported in a vapor phase to a heated substrate, where they decompose and react to form a thin, solid film.
The core challenge of MOCVD is not just what elements to deposit, but how to transport them reliably to a surface. Precursors are the solution: specialized molecular delivery vehicles designed for stability, volatility, and controlled decomposition.
What Makes a Chemical a "Precursor"?
To be effective in an MOCVD process, a compound must possess a specific set of characteristics. The success of the deposition hinges entirely on the quality and behavior of these source materials.
The Essential Requirement: Volatility
The "V" in MOCVD stands for "vapor." The precursor must be volatile enough to be transported into the reaction chamber as a gas.
This means it needs a sufficiently high vapor pressure at a manageable temperature. The goal is to get the material into the gas phase without it decomposing prematurely.
Purity is Paramount
Any impurity in the precursor material can become incorporated into the final thin film, potentially degrading its electronic or optical properties.
Therefore, precursors must be synthesized to extremely high levels of purity, often referred to as "electronic grade" or "five-nines" (99.999%) purity or higher.
Stability and Controlled Decomposition
A good precursor is a chemical paradox. It must be stable enough to be stored and transported without breaking down.
However, once it reaches the heated substrate, it must decompose cleanly and efficiently at a predictable temperature, leaving behind only the desired elements and volatile byproducts that can be easily removed.
Common Classes of MOCVD Precursors
MOCVD primarily utilizes metalorganic compounds, where a central metal atom is bonded to organic groups (ligands). The choice of ligand is critical as it dictates the precursor's volatility and decomposition behavior.
Metal Alkyls
These are the most common precursors for depositing Group 13 elements like aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), and indium (In).
- Examples: Trimethylgallium (TMGa), Trimethylaluminum (TMAl), Triethylgallium (TEGa).
- Function: They provide the metal source for compound semiconductors like GaAs and AlGaN.
Hydrides
Hydrides are typically used as the source for Group 15 elements (the non-metal component). They are simple, highly pure, but often highly toxic gases.
- Examples: Arsine (AsH₃), Phosphine (PH₃), Ammonia (NH₃).
- Function: They react with the metal alkyls to form the final compound semiconductor. For instance, TMGa and AsH₃ react to form GaAs.
Other Metalorganic Compounds
For different materials, a wider variety of metalorganic compounds are employed to achieve the right balance of volatility and reactivity. These include:
- Metal Alkoxides: Used for depositing metal oxides. (e.g.,
Ti(OiPr)₄). - Metal Carbonyls: Effective for depositing pure metals. (e.g.,
Ni(CO)₄). - Metal Diketonates: A versatile class often used in oxide and superconductor deposition. (e.g.,
Cu(acac)₂).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a precursor is not always straightforward and involves balancing competing factors.
Safety vs. Performance
Many of the most effective precursors, especially hydrides like arsine and phosphine, are extremely toxic and pyrophoric (ignite spontaneously in air). This necessitates complex and expensive safety and gas handling systems.
Researchers continually seek less hazardous liquid-source alternatives, but these often come with their own challenges, such as lower vapor pressure or carbon incorporation into the film.
Purity vs. Cost
Achieving the ultra-high purity required for electronic and photonic devices is a costly, multi-step chemical process.
For applications where film quality is less critical, a lower-purity (and thus lower-cost) precursor might be acceptable. However, for high-performance devices, there is no substitute for the highest possible purity.
Single-Source vs. Multi-Source
In most cases, multiple precursors are used (e.g., one for gallium, one for arsenic). However, "single-source precursors" exist that contain all the necessary elements in one molecule.
While simpler in concept, they can be difficult to design and may not decompose stoichiometrically, meaning the ratio of elements in the final film is not what is desired.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal precursor is entirely dependent on the material you are trying to grow and the required quality of the final film.
- If your primary focus is high-performance III-V semiconductors (e.g., for lasers or micro-LEDs): You will use classic, ultra-high purity metal alkyls (TMGa, TMIn) and hydrides (arsine, phosphine, ammonia).
- If your primary focus is depositing pure metals or simple oxides: You may find success with more stable and less hazardous metal carbonyls, diketonates, or alkoxides.
- If your primary focus is research and development on novel materials: You will be exploring a wide range of custom-synthesized precursors to find the one with the perfect decomposition pathway for your specific application.
Ultimately, the precursor is the foundational component that enables the entire MOCVD process, and its careful selection is critical to success.
Summary Table:
| Precursor Type | Common Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Alkyls | TMGa, TMAl, TEGa | Source for Group 13 metals (Ga, Al, In) in III-V semiconductors |
| Hydrides | AsH₃, PH₃, NH₃ | Source for Group 15 non-metals (As, P, N) in III-V semiconductors |
| Other Metalorganics | Metal Alkoxides, Carbonyls, Diketonates | Source for oxides, pure metals, and novel materials |
Ready to optimize your MOCVD process with the right precursors? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables for advanced thin film deposition. Our expertise can help you select the ideal precursors and systems for your specific semiconductor, LED, or research application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's MOCVD needs and enhance your film quality and process efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of CVD diamonds? From Jewelry to High-Tech Tools
- How much does CVD diamond equipment cost? A Breakdown of Investment from Lab to Production
- What is the use of CVD diamond? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Applications
- What is the application of diamond coating? Solve Complex Wear, Heat, and Corrosion Problems
- What is the newly discovered mechanism for diamond formation during CVD? Explore the Graphite-to-Diamond Transition



















