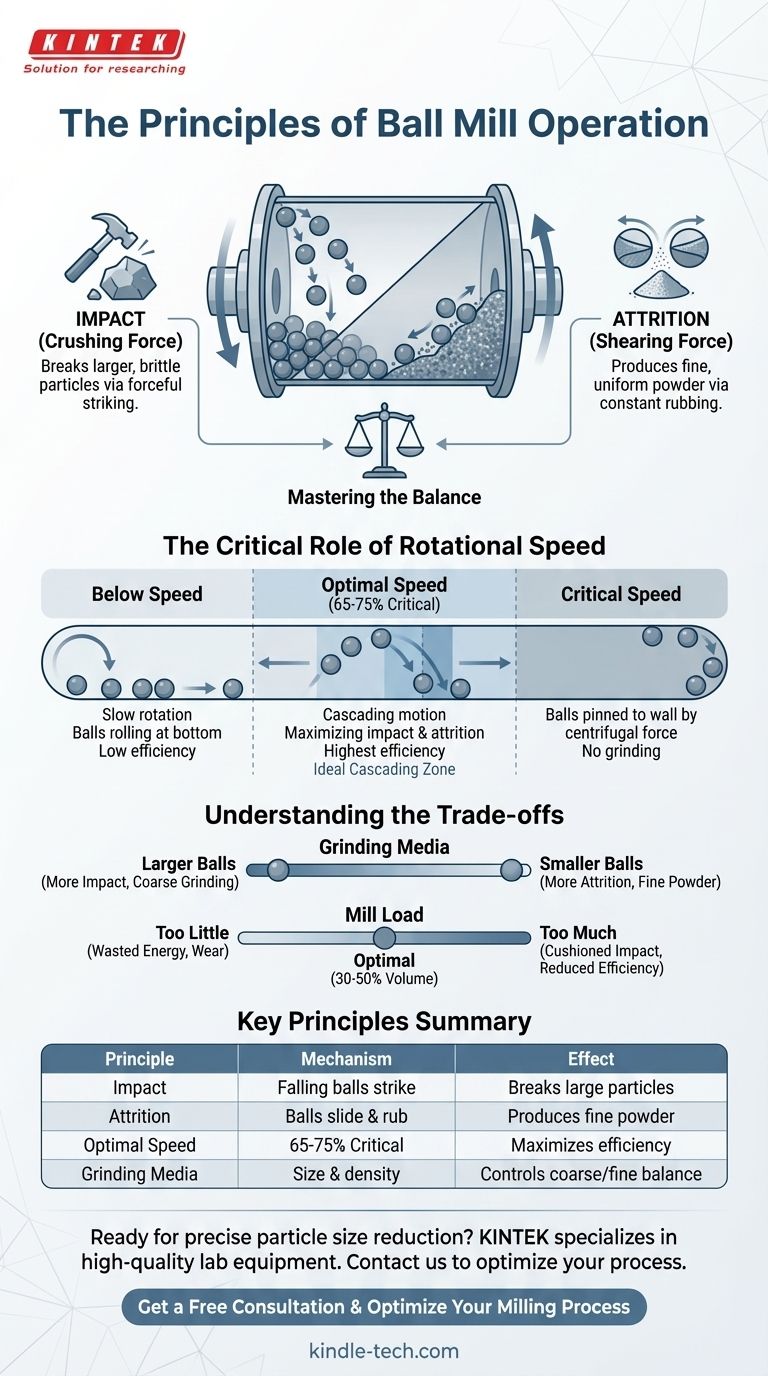
At its core, a ball mill operates on two fundamental principles: impact and attrition. As the cylindrical mill rotates, the grinding media (balls) inside are lifted up the side before cascading back down. This downward fall creates a powerful impact that crushes the material, while the constant rubbing and sliding of the balls against each other and the chamber walls produces attrition, a shearing force that grinds the particles down.
The effectiveness of a ball mill is not random; it's a controlled process governed by the balance between impact and attrition. Mastering this balance by adjusting rotational speed and the grinding media is the key to achieving your desired particle size efficiently.

The Two Mechanisms of Size Reduction
A ball mill does not simply smash material; it employs two distinct but complementary actions to achieve size reduction. Understanding both is crucial for process control.
The Force of Impact
Impact is the primary mechanism for breaking down larger, brittle particles. As the mill drum rotates, the balls are carried partway up the interior wall.
Gravity then takes over, causing the balls to detach and fall onto the material resting at the bottom of the mill. This repeated, forceful striking is highly effective at fracturing coarse feed material into smaller pieces.
The Grinding Action of Attrition
Attrition is a shearing and grinding action responsible for creating finer particles. It occurs in the "toe" of the mill charge, where the balls are cascading and rolling over one another.
As the balls slide and tumble, they trap material between their surfaces and the mill wall, grinding it down through friction. This mechanism is essential for achieving a uniform and very fine final product.
The Critical Role of Rotational Speed
The speed of the mill's rotation is the single most important variable in controlling the grinding process. It directly dictates the behavior of the balls and thus the balance between impact and attrition.
Below Operating Speed: Ineffective Agitation
If the mill rotates too slowly, the balls will simply roll over each other at the bottom of the chamber. This results in minimal impact force and very low grinding efficiency, as the balls are never lifted high enough to create a meaningful drop.
At Critical Speed: The Centrifuge Effect
Critical speed is the theoretical speed at which the centrifugal force is strong enough to pin the grinding balls to the inner wall of the mill.
At this speed, the balls simply travel in a circle with the drum, and no tumbling or falling occurs. Consequently, both impact and attrition cease entirely, and no grinding takes place.
The Optimal Speed: The Cascading Zone
The most efficient grinding occurs when the mill operates at a speed that is a percentage of the critical speed, typically between 65% and 75%.
In this optimal range, the balls are carried high enough up the wall to create a powerful impact when they fall but not so high that they are pinned to the side. This creates a continuous cascading motion that maximizes both impact and attrition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing a ball mill requires balancing several key factors. The choices you make will directly affect the final product and the efficiency of the process.
Grinding Media: Size and Density
The balls themselves are a critical variable. Larger, denser balls produce a greater impact force, making them ideal for breaking down large feed material quickly.
Conversely, a larger number of smaller balls increases the surface area available for attrition. This is more effective for producing a very fine, uniform powder. The media material (e.g., stainless steel, ceramic) is chosen to prevent contamination and resist wear.
Mill Load: The Ball-to-Powder Ratio
The volume of grinding media and material inside the mill must be carefully controlled. A typical ball charge fills 30% to 50% of the mill's internal volume.
If there is too much material in the mill, it will cushion the ball impacts and reduce grinding efficiency. If there is too little material, the balls will grind against each other and the mill liner, wasting energy and causing excessive wear.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct application of these principles depends entirely on your desired outcome. Use the following guidelines to tailor the process to your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is coarse grinding or breaking large particles: Prioritize impact by using larger grinding balls and operating at a speed on the higher end of the optimal range (around 75% of critical speed) to maximize the cascading drop height.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very fine, uniform powder: Prioritize attrition by using a higher volume of smaller grinding balls, which increases the total surface area for grinding action.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Carefully optimize the mill speed to stay within the 65-75% of critical speed range and maintain the correct ball-to-powder charge ratio to avoid wasted energy.
By understanding these core principles, you can transform the ball mill from a simple machine into a precision tool for material processing.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Key Mechanism | Effect on Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Impact | Balls fall and strike material | Breaks down large, brittle particles |
| Attrition | Balls slide and rub against each other | Produces fine, uniform powder |
| Optimal Speed | 65-75% of critical speed | Maximizes both impact and attrition efficiency |
| Grinding Media | Size and density of balls | Controls the balance between coarse and fine grinding |
Ready to achieve precise particle size reduction in your lab?
The principles of impact and attrition are key to unlocking your ball mill's full potential. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including ball mills and grinding media, tailored to your specific research and production goals.
Our experts can help you select the right equipment to optimize for coarse grinding, fine powder creation, or maximum process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your application and let KINTEK be your partner in precision milling.
Get a Free Consultation & Optimize Your Milling Process
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a hammer mill essential for processing raw materials in garden waste pelletization? Optimize Feedstock Sizing.
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding tools like agate mortars? Optimize LTO Electrode Performance
- What role does a high-frequency ultrasonic homogenizer play in PEO? Achieve Superior Coating Uniformity and Stability
- What is the difference between grinder and pulverizer? A Guide to Particle Size and Efficiency
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- How does the use of grinding equipment benefit iron-substituted manganese oxide? Optimize Energy Storage Performance
- What is the role of an agate mortar and pestle in preparing sulfur and iron oxide mixtures? Ensure Purity in Research
- What are the factors that affect the efficiency of a milling operation? Optimize Your Grinding Circuit for Peak Performance



















