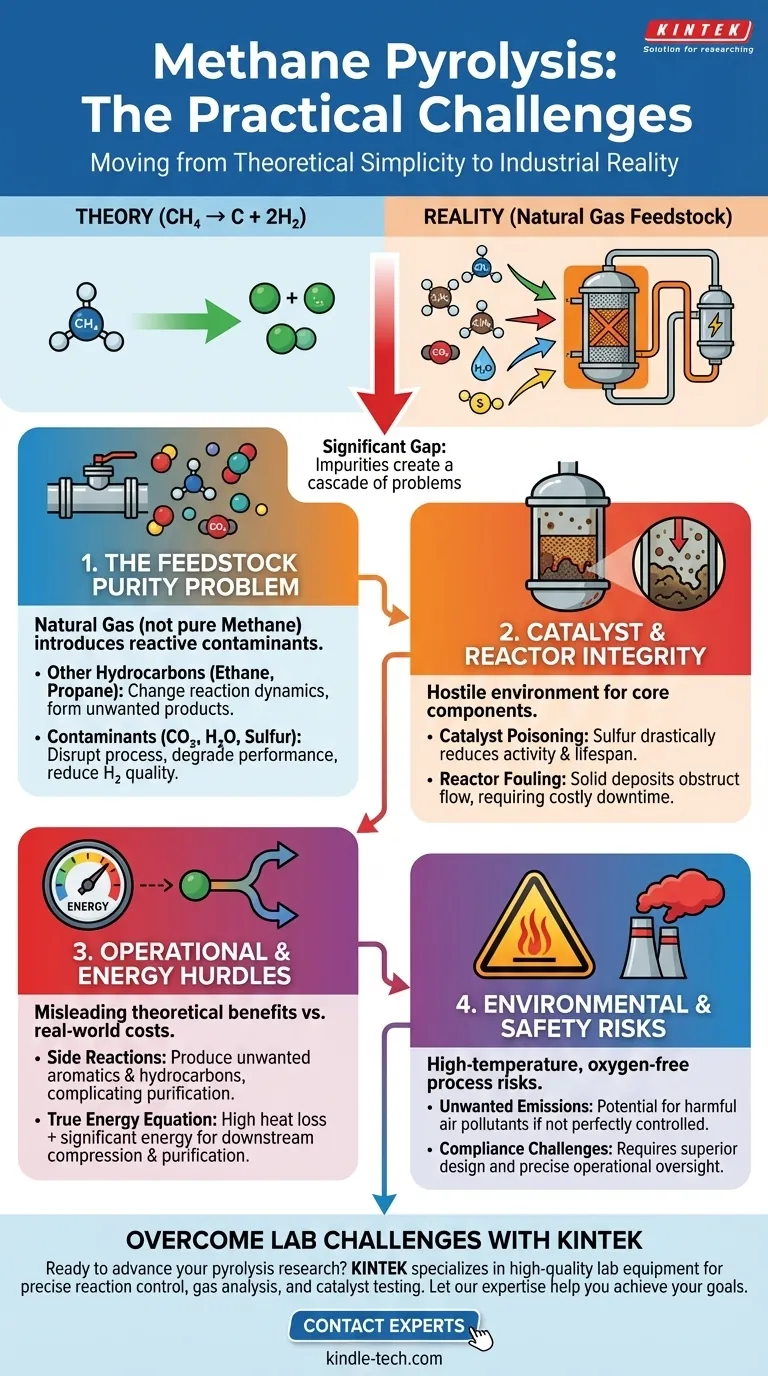
While promising on paper, methane pyrolysis faces significant practical challenges that complicate its real-world application. The core problems stem from using impure natural gas as a feedstock instead of pure methane, leading to catalyst degradation, unwanted side reactions, and unpredictable energy efficiency. Furthermore, the high-temperature process carries a risk of creating harmful air emissions if not managed with precision.
The central challenge of methane pyrolysis is the significant gap between its theoretical simplicity (CH₄ → C + 2H₂) and the engineering reality of using natural gas. Impurities inherent in natural gas introduce a cascade of problems that affect process stability, product purity, and overall environmental and economic viability.

The Feedstock Purity Problem: Natural Gas vs. Methane
The most significant hurdle is that industrial processes use natural gas, not pure methane. This distinction is critical because the additional compounds in natural gas interfere with the pyrolysis reaction.
The Impact of Other Hydrocarbons
Natural gas contains minor components like ethane and propane. While these can also be converted, their presence changes the reaction dynamics and can lead to the formation of unintended secondary products.
The Role of Contaminants
More problematic are non-hydrocarbon contaminants like carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and sulfur compounds. These substances are reactive under pyrolysis conditions and can disrupt the entire process.
Consequences for the Process
These impurities directly degrade performance by negatively affecting conversion rates, product selectivity, and the final quality of the hydrogen gas. They make it difficult to predict and control the reaction outcome reliably.
Catalyst and Reactor Integrity Challenges
The impurities in natural gas create a hostile environment for the core components of a pyrolysis system: the catalyst and the reactor itself.
Catalyst Deactivation and Stability
Catalysts are essential for enabling the reaction at lower, more economical temperatures. However, compounds like sulfur are notorious catalyst poisons, drastically reducing the catalyst's activity and service life, which increases operational costs.
Solid Deposits and Reactor Fouling
The process is designed to produce solid carbon, but impurities can lead to the formation of undesirable solid deposits inside the reactor. This "fouling" can obstruct gas flow, reduce efficiency, and require costly shutdowns for maintenance.
Understanding the Practical Hurdles
The theoretical benefits of methane pyrolysis can be misleading without acknowledging the operational and energetic costs required to make it work safely and efficiently.
The Risk of Unwanted Emissions
Pyrolysis operates at very high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. If the system is not perfectly designed, operated, and maintained, it can produce emissions that negatively impact air quality.
The True Energy Equation
A simple energy balance is incomplete. You must account for process-specific heat loss from the high-temperature reactor and the significant energy required for downstream hydrogen compression and purification.
The Problem of Side Reactions
Side reactions can produce unwanted byproducts, including aromatic compounds and other hydrocarbons. If the goal is to produce high-purity hydrogen for industrial use (e.g., fuel cells), these contaminants must be removed, adding complexity and cost.
Making an Informed Assessment
When evaluating methane pyrolysis, your primary goal will determine which challenges are most critical to your project's success.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity hydrogen: Your main challenge will be managing side reactions and accounting for the significant energy cost of downstream gas purification.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and longevity: You must prioritize feedstock pre-treatment to remove contaminants like sulfur and higher hydrocarbons before they enter the reactor.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Your critical task is investing in superior reactor design and operational controls to capture any potential fugitive emissions.
Successfully implementing methane pyrolysis depends on moving beyond its simple chemical equation and rigorously addressing the complex realities of industrial feedstocks and energy dynamics.
Summary Table:
| Problem Category | Key Challenges | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Purity | Impurities in natural gas (CO₂, H₂O, sulfur) | Reduced conversion rates, poor hydrogen purity, unpredictable outcomes |
| Catalyst & Reactor | Catalyst poisoning, reactor fouling from solids | Increased operational costs, frequent maintenance, reduced longevity |
| Process Efficiency | Side reactions, high energy for purification/compression | Lower overall efficiency, higher operational complexity and cost |
| Environmental Risk | Potential for harmful emissions if poorly controlled | Compliance challenges, negative environmental impact |
Ready to overcome the challenges of pyrolysis and advanced gas processing in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable tools you need for precise reaction control, gas analysis, and catalyst testing. Let our expertise help you navigate complex processes and achieve your research or quality control goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and find the right solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What role does an autoclave play in simulating PWR conditions? Advanced Material Validation for Nuclear Safety



















