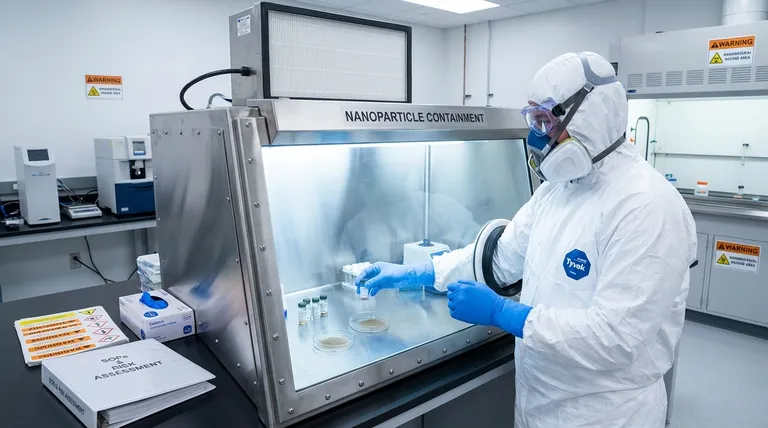
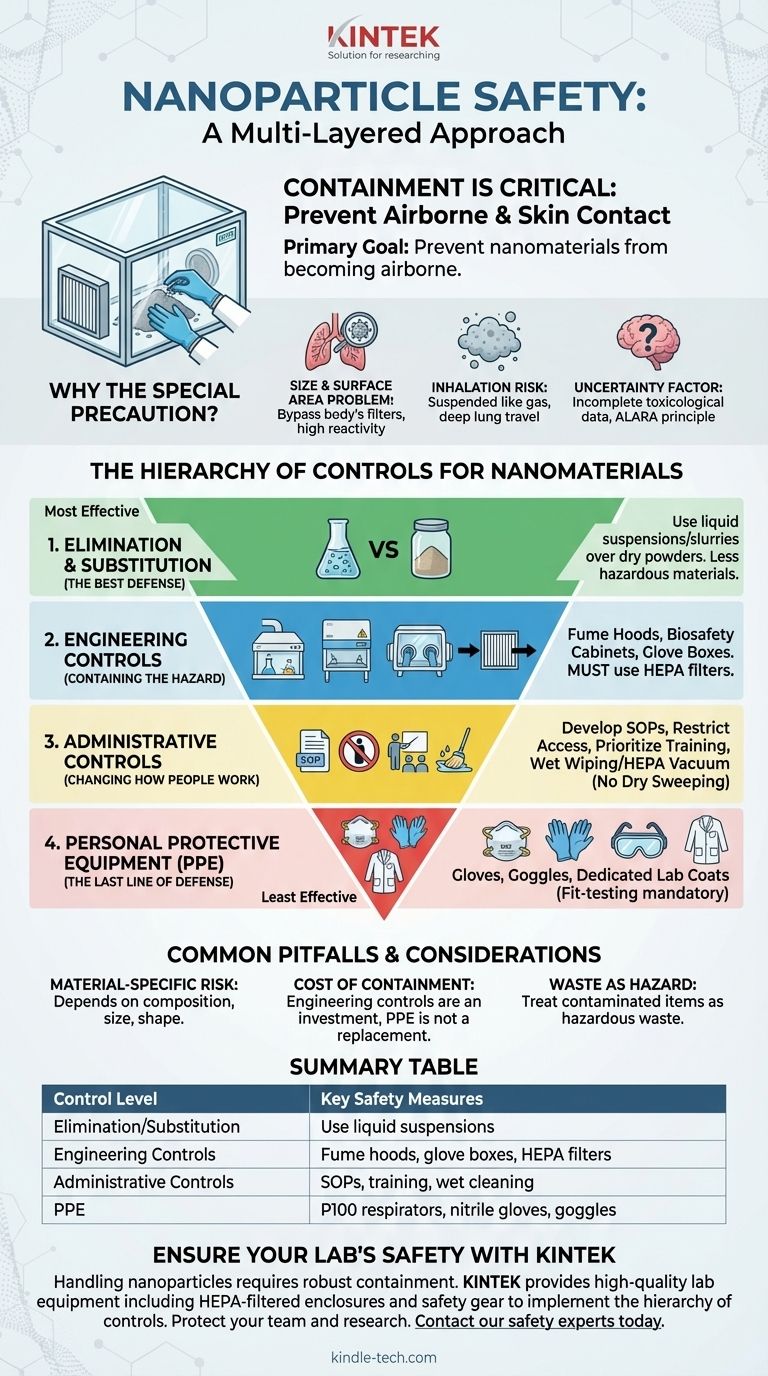
Handling nanoparticles safely requires a multi-layered approach that prioritizes preventing exposure, particularly through inhalation. The core precautions involve using a hierarchy of controls, beginning with engineering solutions like ventilated enclosures to contain particles at the source. This is then supplemented by strict work practices and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as respirators and non-porous gloves.
Because the primary danger of nanoparticles lies in their potential for inhalation and absorption into the body, the most critical safety principle is containment. Your first and most important goal is to prevent nanomaterials from becoming airborne or making contact with your skin.

Why Nanoparticles Demand Special Precaution
Before implementing controls, it is essential to understand why nanomaterials are not treated the same as their larger, bulk-material counterparts. Their unique physical properties are the source of their potential risk.
The Size and Surface Area Problem
Nanoparticles are exceptionally small, which allows them to bypass many of the body's natural filtration systems, such as those in the upper respiratory tract.
Their high surface-area-to-volume ratio can also make them more chemically or biologically reactive than the exact same material in bulk form.
The Inhalation Risk
Inhalation is the most significant and well-documented route of exposure for nanoparticles.
Once airborne, these particles can remain suspended for long periods, behaving more like a gas than a powder. If inhaled, they can travel deep into the lungs and potentially translocate to other organ systems.
The Uncertainty Factor
For many engineered nanomaterials, the long-term toxicological data is still incomplete. The scientific community is actively researching the chronic effects of exposure.
This uncertainty necessitates a conservative approach based on the Precautionary Principle and the goal of keeping exposure As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA).
The Hierarchy of Controls for Nanomaterials
The most effective safety programs are built on the "Hierarchy of Controls," a framework that prioritizes the most reliable measures first. You should always implement controls from the top of this list downward.
1. Elimination and Substitution (The Best Defense)
The most effective way to remove a hazard is to eliminate it entirely.
If possible, ask if you can achieve your goal with a less hazardous material. Can you use nanoparticles in a stable liquid suspension or a slurry instead of a dry, dusty powder? Working with liquids dramatically reduces the risk of inhalation.
2. Engineering Controls (Containing the Hazard)
This is the most critical step for physically containing nanomaterials. Engineering controls place a barrier between you and the hazard.
Key examples include:
- Chemical Fume Hoods: For general handling of nanomaterial suspensions or low-energy procedures.
- Biological Safety Cabinets: Provide a higher level of containment and are suitable for materials with potential biological activity.
- Glove Boxes: Offer the highest level of containment for handling highly hazardous or easily aerosolized dry nanopowders.
Ventilation systems for these enclosures should always be equipped with HEPA filters to capture nanoparticles before the air is exhausted.
3. Administrative Controls (Changing How People Work)
These controls are procedures and policies designed to reduce the duration, frequency, and intensity of exposure.
- Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Create clear, written protocols for every task involving nanomaterials.
- Restrict Access: Designate specific areas for nanoparticle handling and limit entry to trained personnel only.
- Prioritize Training: Ensure all personnel understand the specific risks of the materials they handle and are proficient in the control procedures.
- Practice Good Housekeeping: Never use dry sweeping or compressed air for cleanup. Use wet wiping or a HEPA-filtered vacuum to collect spills and clean surfaces.
4. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) (The Last Line of Defense)
PPE is essential, but it must be used in addition to, not as a replacement for, the controls listed above. It protects you only if the primary controls fail.
- Respirators: An N95 is the minimum, but a P100 respirator or powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR) offers superior protection against nanoparticles. Fit-testing is mandatory to ensure a proper seal.
- Gloves: Use disposable nitrile or other non-porous gloves. Double-gloving is recommended when handling powders. Never reuse disposable gloves.
- Eye Protection: Chemical splash goggles provide better protection than standard safety glasses.
- Lab Coats: Wear a dedicated lab coat, preferably made of a low-permeability material like Tyvek. Do not wear it outside of the designated work area.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Navigating nanoparticle safety requires acknowledging the complexities and avoiding common assumptions.
Risk Is Material-Specific
There is no single "nanoparticle risk." The hazard level depends entirely on the material's composition (e.g., carbon nanotubes vs. silver nanoparticles), size, shape, and surface chemistry. A thorough risk assessment for each specific material is required.
The Cost of Containment
Proper engineering controls represent a significant financial investment. However, relying solely on cheaper controls like PPE is a flawed strategy that places the burden of safety entirely on the individual's ability to use it perfectly every time.
Waste Is Also a Hazard
All waste materials, including gloves, wipes, and contaminated solutions, must be treated as hazardous waste. Collect them in clearly labeled, sealed containers for disposal according to your institution's hazardous waste protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific safety protocol must be tailored to your material, the quantity you are using, and the procedures you are performing.
- If your primary focus is working with dry nanopowders: Your absolute priority is using high-containment engineering controls like a glove box or, at a minimum, a properly functioning fume hood to prevent aerosolization.
- If your primary focus is handling nanoparticles in a stable liquid suspension: Concentrate on preventing skin and eye contact with proper gloves and goggles, but remain vigilant about procedures (like sonication or spraying) that could still generate aerosols.
- If your primary focus is planning a new process: Conduct a risk assessment before you start. Identify every step where particles could become airborne or contact skin and implement the appropriate controls from the hierarchy for each one.
Ultimately, a proactive and cautious mindset is the most critical safety tool when working with nanomaterials.
Summary Table:
| Control Level | Key Safety Measures |
|---|---|
| Elimination/Substitution | Use liquid suspensions instead of dry powders. |
| Engineering Controls | Fume hoods, biosafety cabinets, glove boxes with HEPA filters. |
| Administrative Controls | SOPs, restricted access, training, wet cleaning methods. |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | P100 respirators, nitrile gloves, goggles, dedicated lab coats. |
Ensure your lab's safety with the right equipment and protocols.
Handling nanoparticles requires robust containment solutions and reliable safety practices. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including HEPA-filtered enclosures and safety gear, to help you implement the hierarchy of controls effectively. Our products are designed to meet the specific needs of laboratories working with nanomaterials, ensuring you can operate safely and efficiently.
Protect your team and your research. Contact our safety experts today to discuss your nanoparticle handling requirements and find the perfect solutions for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 28L Compact Upright Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Laboratory
- 108L Vertical Ultra Low Temperature ULT Freezer
People Also Ask
- What is the role of an ultra-low temperature (ULT) freezer in the freeze-thaw synthesis of hydrogel nanocomposites?
- What are ultra-low temperature freezers designed for? Preserving Your Most Valuable Biological Samples
- How do ultra-low temperature freezers achieve such low temperatures? The Science Behind -80°C Cooling
- What is the temperature control capability of ultra-low freezers? Precise Stability Down to -86°C
- What features do ultra-low temperature freezers typically include? Ensuring Absolute Sample Security



















