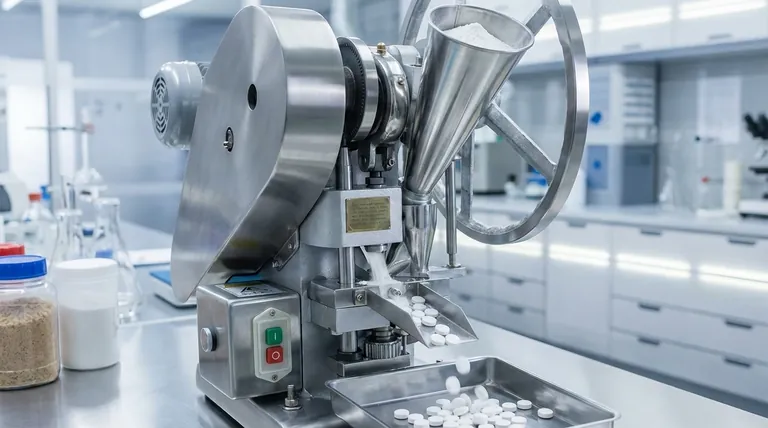
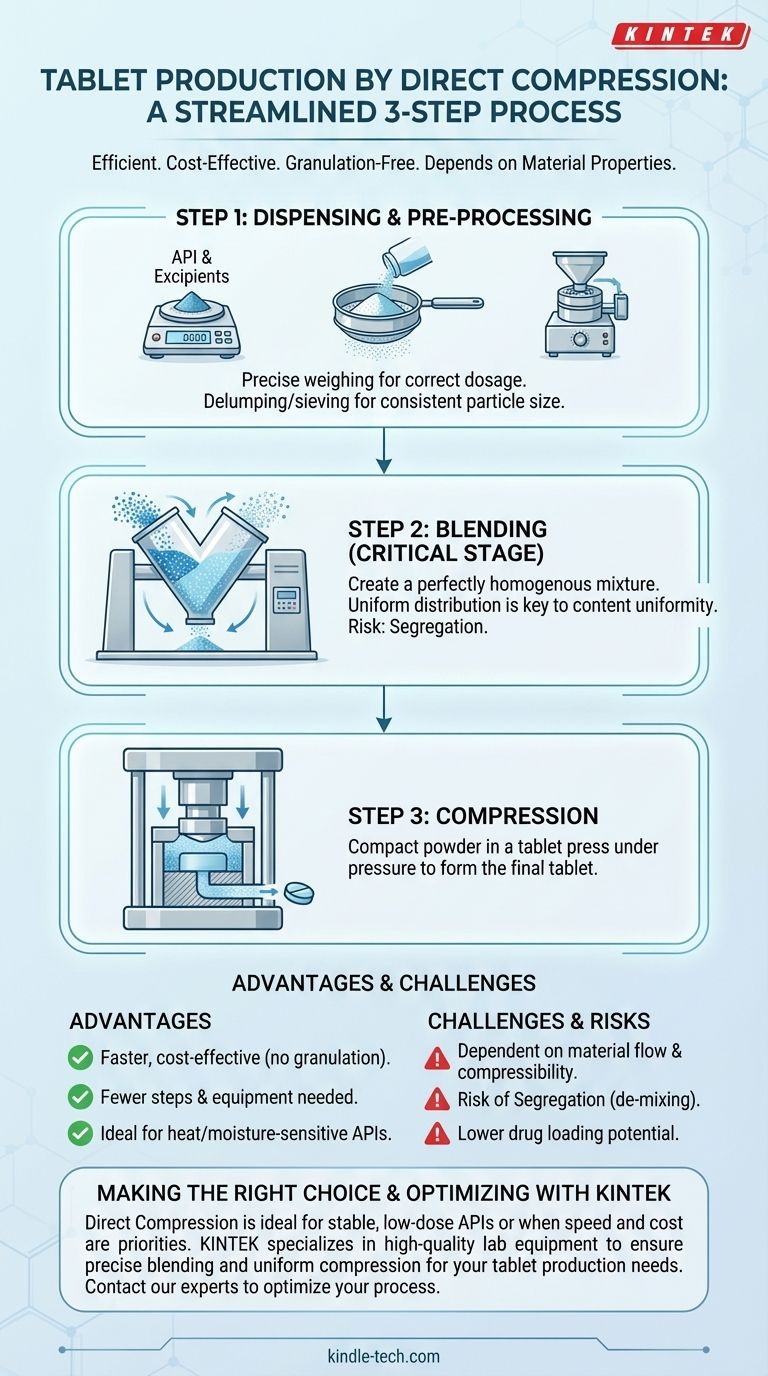
In its simplest form, the direct compression method for tablet manufacturing consists of three primary stages: dispensing the raw materials, blending them into a uniform powder mix, and compressing that mix directly into tablets. This process is notable for its efficiency because it completely bypasses the granulation steps required by other methods.
Direct compression is the most streamlined and cost-effective method for producing tablets, but its success is entirely dependent on the inherent physical properties—specifically the flow and compressibility—of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and the chosen excipients.

The Principle of Direct Compression
Direct compression (DC) is favored for its simplicity. Unlike wet or dry granulation, it avoids the intermediate steps of creating granules before compression.
The entire process relies on a powder blend that is ready for compression "as is." This makes it faster, requires less equipment, and consumes less energy.
Why It's Often the First Choice
The primary drivers for choosing DC are speed and cost. By eliminating granulation, you reduce processing time, labor, validation requirements, and the factory footprint needed for equipment.
It is also the preferred method for APIs that are sensitive to moisture or heat, as it avoids the liquid binders and high temperatures often used in wet granulation.
The Direct Compression Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
While conceptually simple, each step in the DC process must be executed with precision to ensure a successful final product. The quality of the final tablet is built during these stages.
Step 1: Dispensing and Pre-Processing
The first step is the precise weighing, or dispensing, of the API and all excipients according to the master batch formula. This is a critical control point for ensuring correct dosage.
Following dispensing, materials may undergo delumping or sieving. This is done to break up any aggregates formed during storage and to ensure a consistent particle size, which is vital for the next step.
Step 2: Blending
Blending is arguably the most critical stage in the direct compression process. The goal is to create a perfectly homogenous mixture where the API and excipients are uniformly distributed throughout the batch.
This powder mix is loaded into a blender, such as a V-blender, bin blender, or container blender. The blending time and speed are carefully controlled parameters, as both under-mixing and over-mixing can lead to poor content uniformity.
Step 3: Compression
The final, blended powder is then transferred to a tablet press. The press feeds the blend into a series of dies.
In the press, upper and lower punches move together to compact the powder within the die cavity under immense pressure, forming the finished tablet. The tablets are then ejected from the press for collection.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The simplicity of direct compression comes with significant technical challenges and limitations. It is not a universally applicable method.
The Critical Role of Raw Materials
The success of DC is entirely dependent on the physical characteristics of the powder blend. The blend must have both excellent flowability to move consistently through the press and high compressibility to form a strong, intact tablet.
If the API itself has poor flow or is "fluffy," it cannot be used in a high concentration. In these cases, DC relies heavily on specially engineered excipients (often called DC-grade excipients) to carry the functional load.
The Risk of Segregation
Because you are blending powders with potentially different particle sizes and densities, there is a constant risk of segregation. This is the de-mixing of the blend during transfer or in the hopper of the tablet press.
Segregation is a major cause of production failure, as it leads to unacceptable variations in tablet weight and, more importantly, API content (content uniformity), putting patient safety at risk.
Lower Drug Loading Potential
Direct compression is generally best suited for low-dose drugs. High-dose APIs often have poor flow and compressibility properties that dominate the blend, making it difficult to form a good tablet without a granulation step to improve these characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Choosing your manufacturing method is a strategic decision based on the properties of your API, your timeline, and your budget.
- If your primary focus is cost and speed: Use direct compression for stable, low-dose APIs with excellent physical properties or when using highly functional DC-grade excipients.
- If your primary focus is API stability: Direct compression is the ideal choice for APIs sensitive to heat or moisture, as it avoids both.
- If you are working with a high-dose or poorly flowing API: You will likely need to use wet or dry granulation to densify the powder and improve its flow and compressibility before tableting.
Understanding these core principles empowers you to select the most robust and efficient manufacturing path for your specific product.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Dispensing | Precisely weigh API & excipients | Ensure correct dosage |
| 2. Blending | Mix powders to a uniform blend | Achieve content uniformity |
| 3. Compression | Compact powder in a tablet press | Form the final tablet |
Ready to optimize your tablet production with the right equipment? The direct compression method is efficient, but its success depends on precise blending and compression. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pharmaceutical development. Our solutions help you achieve perfect powder flow and uniform tablet compression. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your lab's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Manual Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the two classifications of press machines? Single Punch vs. Rotary Presses Explained
- How does a larger area affect the pressure of the same force? Master the Physics of Force Distribution
- What are the different parts of a single punch tablet machine? The Core Components Explained
- What does a tablet punching machine consist of? Core Components for Efficient Tablet Production
- What is die compression ratio? Master Your Pelleting Process for Optimal Quality & Efficiency



















