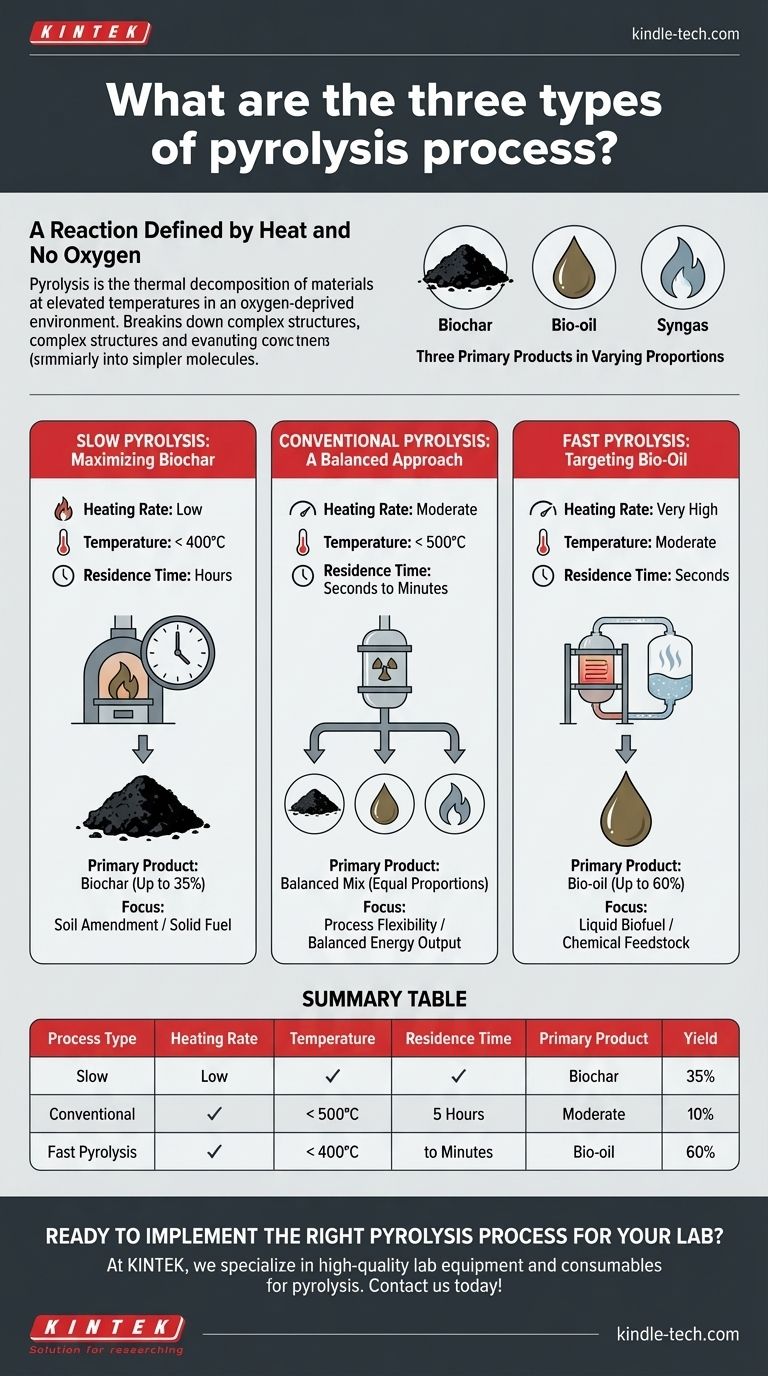
The three main types of pyrolysis are slow, conventional, and fast pyrolysis. These processes are distinguished primarily by their heating rate, operating temperature, and duration, which in turn dictate whether the primary output is solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or a balanced mixture of products.
The critical insight is that pyrolysis is not a single reaction but a highly tunable platform. By controlling the speed and intensity of the heating process, you can precisely steer the chemical decomposition of biomass to maximize the yield of the specific output—solid, liquid, or gas—that best suits your goal.

The Core Principle: What is Pyrolysis?
A Reaction Defined by Heat and No Oxygen
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-deprived environment.
Without oxygen, the material doesn't combust (burn). Instead, its complex polymeric structures break down into simpler molecules.
The Three Primary Products
This decomposition process consistently yields three core products in varying proportions:
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid residue, similar to charcoal.
- Bio-oil: A complex liquid mixture of oxygenated hydrocarbons, produced by condensing the pyrolysis vapors.
- Syngas: A mix of non-condensable, flammable gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
The Three Types of Pyrolysis Explained
The specific type of pyrolysis is defined by the process parameters used, which are chosen to deliberately maximize one of the three primary products.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
Slow pyrolysis involves very low heating rates over a long period, often several hours, at temperatures generally below 400°C.
This slow, prolonged heating encourages the formation of stable carbon structures. Historically, this is the method used for making charcoal, and its primary output is biochar, with a maximum yield of around 35%.
Conventional Pyrolysis: A Balanced Approach
Conventional pyrolysis uses lower heating rates than fast pyrolysis and moderate temperatures (typically below 500°C).
The material has a longer residence time in the reactor (from seconds to minutes), allowing for a more balanced decomposition. This process yields roughly equal proportions of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas, offering a flexible but non-specialized output.
Fast Pyrolysis: Targeting Bio-Oil
Fast pyrolysis uses an extremely high heating rate with moderate temperatures and a very short residence time—the entire reaction is completed in seconds.
This rapid heating and immediate cooling of the vapors "freezes" the reaction at the intermediate liquid stage, preventing further breakdown into gas or re-polymerization into char. The result is a maximized yield of bio-oil, which can be as high as 60%.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis method involves understanding the direct relationship between process conditions and product output. You are always trading one output for another.
The Yield Dilemma
You cannot maximize all three products simultaneously. The conditions that favor bio-oil production (high heating rates, short residence times) inherently suppress the formation of biochar.
Conversely, the long, slow conditions required for high-quality biochar will inevitably crack some of the valuable vapors that would have formed bio-oil.
Feedstock and Reactor Complexity
The chosen process also dictates engineering requirements. Fast pyrolysis, with its need for rapid heat transfer, often requires more complex and expensive reactors, such as fluidized-bed or ablative systems.
Slow pyrolysis can be accomplished with much simpler technology, like a basic kiln or retort, making it more accessible but less efficient for liquid fuel production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your end goal determines the correct pyrolysis process. The technology is simply a tool to achieve a desired chemical output.
- If your primary focus is soil amendment or solid fuel: Slow pyrolysis is the most direct path to maximizing high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is liquid biofuel or chemical feedstock: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary choice to achieve the highest possible yield of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility or a balanced energy output: Conventional pyrolysis provides a mixed stream of solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Ultimately, selecting the right type of pyrolysis is a strategic decision based entirely on the product you value most.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Heating Rate | Temperature | Residence Time | Primary Product | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slow Pyrolysis | Low | < 400°C | Hours | Biochar | Up to 35% |
| Conventional Pyrolysis | Moderate | < 500°C | Seconds to Minutes | Balanced Mix | Equal Proportions |
| Fast Pyrolysis | Very High | Moderate | Seconds | Bio-oil | Up to 60% |
Ready to implement the right pyrolysis process for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific pyrolysis needs. Whether you're focusing on biochar production, bio-oil extraction, or a balanced approach, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to maximize your yields and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies



















