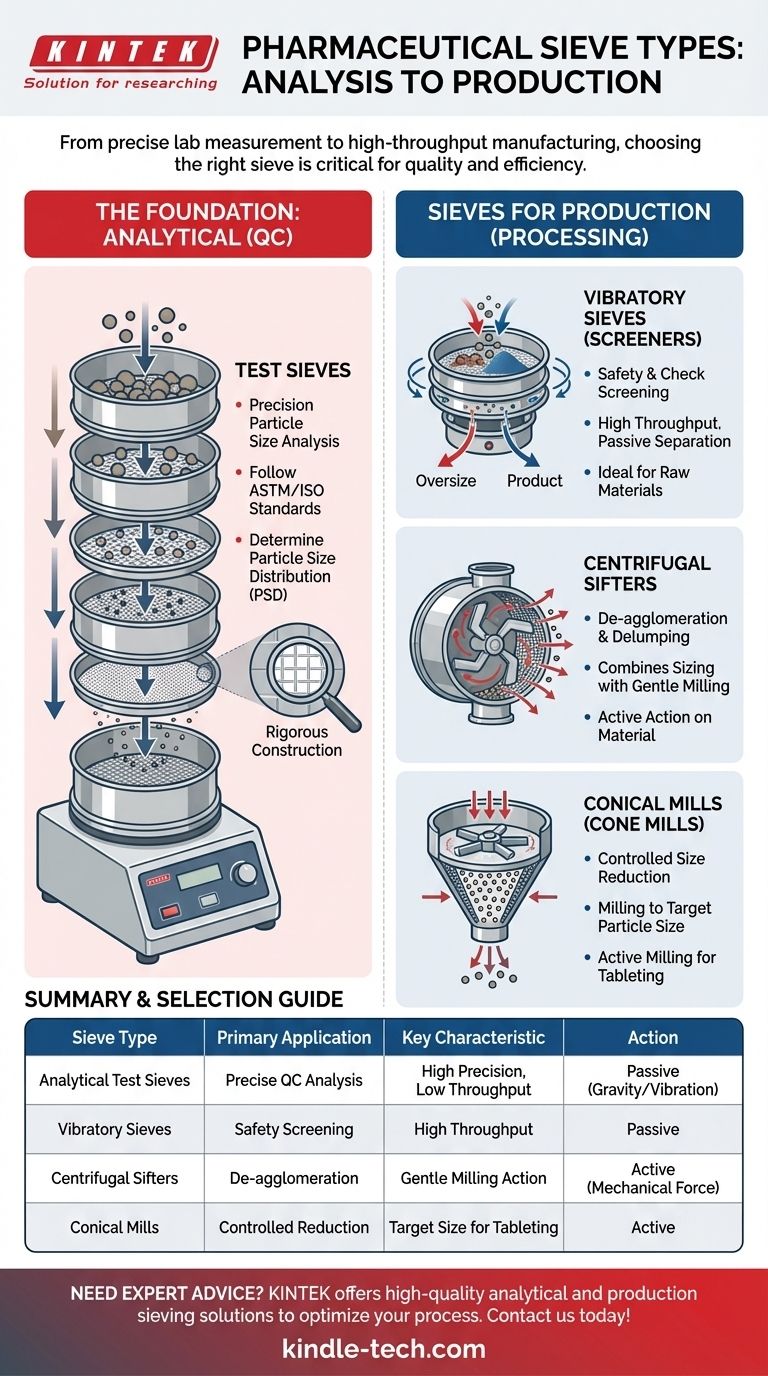
In the pharmaceutical industry, the primary types of sieves are woven wire mesh test sieves for analysis, and production-scale equipment like vibratory sieves, centrifugal sifters, and conical mills for processing. Each is designed for a distinct purpose, ranging from precise laboratory measurement to high-throughput manufacturing.
The core principle to understand is that a "sieve" in pharmaceuticals is not just a simple screen. It is a critical component within a specific process, and the choice of sieve type is dictated entirely by the goal: precise analysis, gentle separation, or active size reduction.

The Foundation: Analytical Test Sieves
The most recognizable type of sieve is the woven wire mesh test sieve, which forms the bedrock of particle size analysis in pharmaceutical quality control (QC).
Construction and Standards
Test sieves consist of a screen with precisely sized openings, or apertures, held under tension in a rigid frame, typically made of stainless steel.
Their construction is rigorously controlled by international standards like ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization). This ensures that results are repeatable and comparable between different labs and manufacturing sites.
Primary Application: Particle Size Analysis
These sieves are used in a "stack" on a shaker. A pre-weighed sample of powder or granules is placed on the top sieve (largest aperture), and the shaker agitates the entire stack.
Particles pass down through the sieves until they are retained on a mesh they cannot pass through. By weighing the material retained on each sieve, analysts determine the particle size distribution (PSD) of the material, a critical quality attribute.
Sieves for Production Processes
Beyond the lab, sieving equipment is essential for manufacturing processes. These systems are designed for higher throughput and are integrated directly into production lines.
Vibratory Sieves (Screeners)
A vibratory sieve uses a motor to create multi-plane, inertial vibration. This motion both stratifies the material and encourages particles to pass through the screen.
Their primary role is often "check screening" or "safety screening." They are placed at the beginning of a process to remove oversized contaminants from raw materials or at the end to ensure a uniform final product before packaging.
Centrifugal Sieves (Sifters)
Centrifugal sifters use rotating paddles or bars inside a cylindrical screen chamber. This rotation throws the material against the screen, efficiently forcing on-size particles through the apertures.
This action is more aggressive than a vibratory sieve, making it highly effective for de-agglomerating or delumping powders that have become compacted during storage or transport. It combines sizing with a gentle milling action.
Conical Mills (Cone Mills)
A conical mill is technically a size reduction machine that uses a screen to control its output. An impeller rotates within a cone-shaped screen, forcing material through the screen's apertures.
This equipment is used for more controlled size reduction and homogenization. It's ideal for milling dried granules to a uniform size before tableting or for creating consistent dispersions. The final particle size is determined by the screen size, impeller speed, and impeller type.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong sieving technology can compromise product quality or process efficiency. The choice always involves balancing competing factors.
Throughput vs. Precision
Analytical test sieves are built for maximum precision but have virtually no throughput. Production equipment like vibratory and centrifugal sifters is designed for high throughput but is less precise for analytical measurement.
Action on the Material: Passive vs. Active
Vibratory sieves are largely passive; they rely on gravity and vibration to separate particles.
In contrast, centrifugal sifters and conical mills are active. They use mechanical force to push material through the screen, which helps break lumps but can also damage fragile granules if not carefully controlled.
Matching the Sieve to the Powder
The characteristics of the powder itself are paramount. Fine, sticky, or electrostatically charged powders can easily block the apertures of a standard sieve, a problem known as blinding.
For these challenging materials in a lab setting, an Air Jet Sieve is often used. This instrument uses a rotating jet of air from below to fluidize the powder and keep the mesh clear, allowing for accurate analysis of otherwise difficult materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process goal is the single most important factor in selecting the correct sieving technology.
- If your primary focus is precise Quality Control (QC) analysis: Use a stack of certified woven wire test sieves on a sieve shaker.
- If your primary focus is high-volume safety screening of raw materials: A vibratory sieve is the most reliable and common choice.
- If your primary focus is breaking lumps and ensuring powder flowability: A centrifugal sifter provides the necessary de-agglomeration action.
- If your primary focus is controlled milling of granules to a target size: A conical mill offers the most precision and control over the final particle distribution.
Choosing the right sieving method is a foundational step in ensuring pharmaceutical product consistency, safety, and efficacy.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Type | Primary Application | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Test Sieves | Precise Particle Size Analysis (QC) | High precision, low throughput, follows ASTM/ISO standards |
| Vibratory Sieves | Safety Screening / Check Screening | High throughput, passive separation, ideal for raw materials |
| Centrifugal Sifters | De-agglomeration / Delumping | Combines sizing with gentle milling action |
| Conical Mills | Controlled Size Reduction / Milling | Active milling to a target particle size for tableting |
Need help selecting the right sieving equipment for your pharmaceutical process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide high-quality analytical test sieves, sieve shakers, and expert advice to ensure your particle size analysis is accurate and compliant. For high-throughput production, we can help you choose the ideal vibratory sieves, centrifugal sifters, or conical mills to optimize your manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect sieving solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What are the components of a sieving machine? Unlock the Anatomy of Precision Particle Separation
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material
- What does a vibrating sieve do? Automate Particle Size Analysis for Accurate Results
- What is the principle of sieving machine? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Separation



















