In essence, calcination is a critical thermal process used to change the chemical and physical properties of solid materials. Its primary applications include the production of cement, the extraction of metals from ores, and the removal of volatile substances like water or carbon dioxide from solids by heating them to a high temperature below their melting point.
The core purpose of calcination is not to melt a material, but to use controlled heat to decompose it or drive off a volatile component. This fundamentally alters the substance, preparing it for its next industrial use.
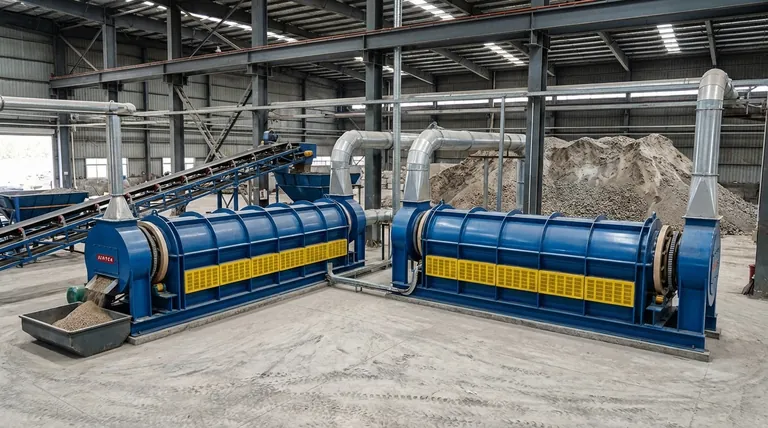

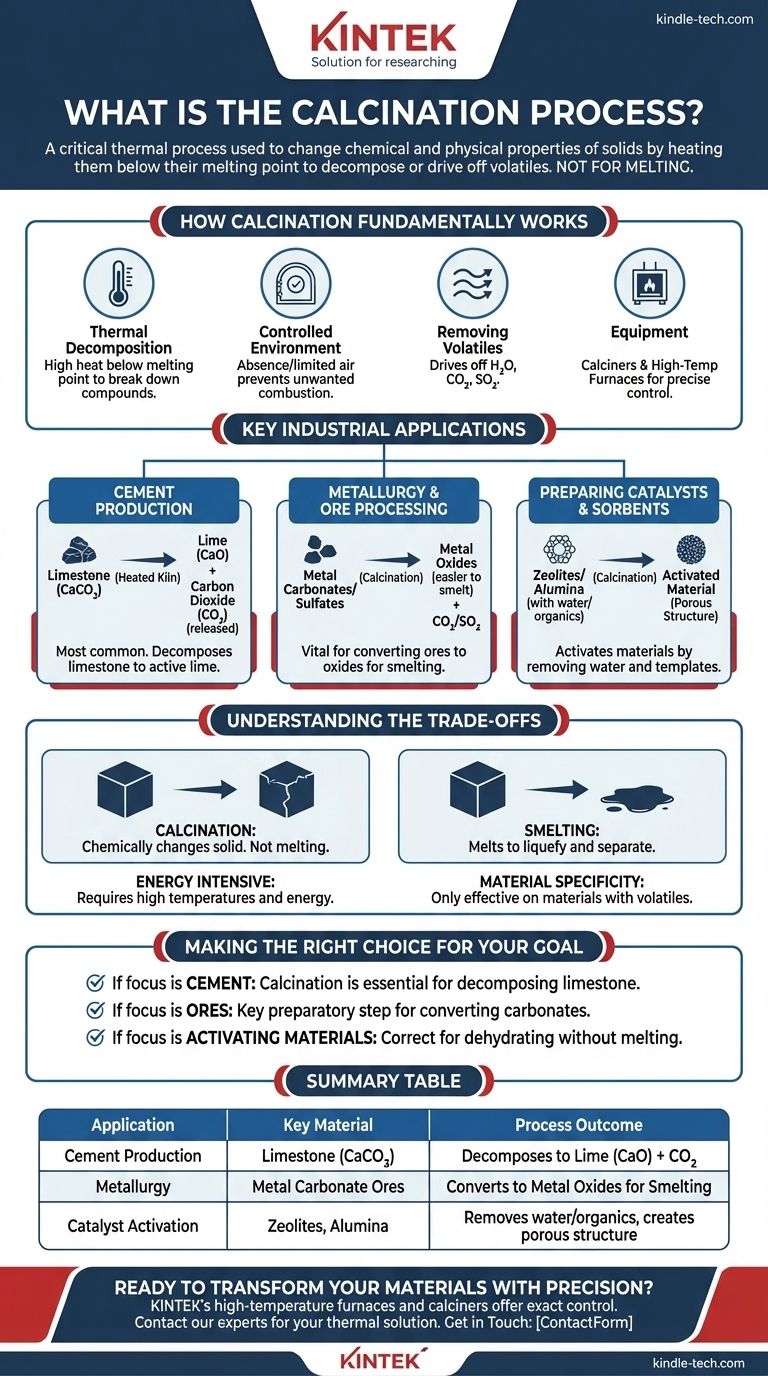
How Calcination Fundamentally Works
Calcination is a precise heat treatment technique. Understanding its core principles is key to appreciating its wide range of applications.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
The process relies on thermal decomposition, using high heat to break down compounds into simpler substances. Crucially, the temperature is kept just below the material's melting point to ensure the solid structure is maintained.
The Controlled Environment
Calcination is performed in the absence or a limited supply of air. This controlled atmosphere prevents unwanted combustion and ensures that the intended chemical decomposition is the primary reaction that occurs.
The Primary Goal: Removing Volatiles
The main objective is to remove a volatile fraction from the material. This often includes driving off chemically bound water (dehydration), carbon dioxide from carbonates, or sulfur dioxide from sulfates.
The Equipment: Calciners and Furnaces
This process is typically conducted in a specialized cylindrical reactor called a calciner or a high-temperature furnace. These pieces of equipment allow for precise control over temperature and atmospheric conditions.
Key Industrial Applications
The principles of calcination are applied across several major industries, often as a foundational preparatory step.
Cement Production
This is the most common application of calcination. Limestone (calcium carbonate) is heated in a kiln, causing it to decompose into lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide. The resulting lime is the primary active ingredient in cement.
Metallurgy and Ore Processing
Calcination is a vital step in extracting metals from certain ores. It is used to convert metal carbonates or sulfates into their corresponding metal oxides, which are easier to reduce to pure metal in subsequent smelting operations.
Preparing Catalysts and Sorbents
Materials like zeolites, alumina, and silica gel are often calcined to remove water and organic templates used during their synthesis. This process activates them, creating the porous structure necessary for them to function as catalysts or sorbents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, calcination is a specific tool with inherent limitations that dictate its use.
Not a Melting Process
It is essential to distinguish calcination from smelting. Calcination aims to chemically change the solid itself, whereas smelting involves heating a material well past its melting point to liquefy and separate it.
Energy Intensive
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for thermal decomposition demands a significant amount of energy. This makes calcination a potentially costly and resource-intensive part of a larger industrial process.
Material Specificity
The process is only effective on materials that contain a volatile component that can be driven off by heat. It is not a universal method for altering all solids; its utility is tied directly to the chemical makeup of the starting material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying calcination correctly depends entirely on the desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is producing lime for cement: Calcination is the essential, non-negotiable process for decomposing limestone into calcium oxide.
- If your primary focus is preparing metal ores for extraction: Calcination is the key preparatory step for converting carbonate ores into oxides before smelting.
- If your primary focus is simply activating a material by removing water: A carefully controlled calcination process is the correct approach to dehydrate the substance without altering its fundamental structure.
Ultimately, understanding calcination allows you to see it not merely as heating, but as a precise and transformative tool for material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Material | Process Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Cement Production | Limestone (CaCO₃) | Decomposes to Lime (CaO) + CO₂ |
| Metallurgy | Metal Carbonate Ores | Converts to Metal Oxides for Smelting |
| Catalyst Activation | Zeolites, Alumina | Removes water/organics, creates porous structure |
Ready to Transform Your Materials with Precision?
Whether you're developing new catalysts, processing ores, or working on advanced ceramics, precise thermal treatment is critical. KINTEK's high-temperature furnaces and calciners are engineered for the exact control needed for successful calcination processes.
We provide robust lab equipment tailored to your research and production goals. Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your application.
Get in Touch to Discuss Your Calcination Needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields



















