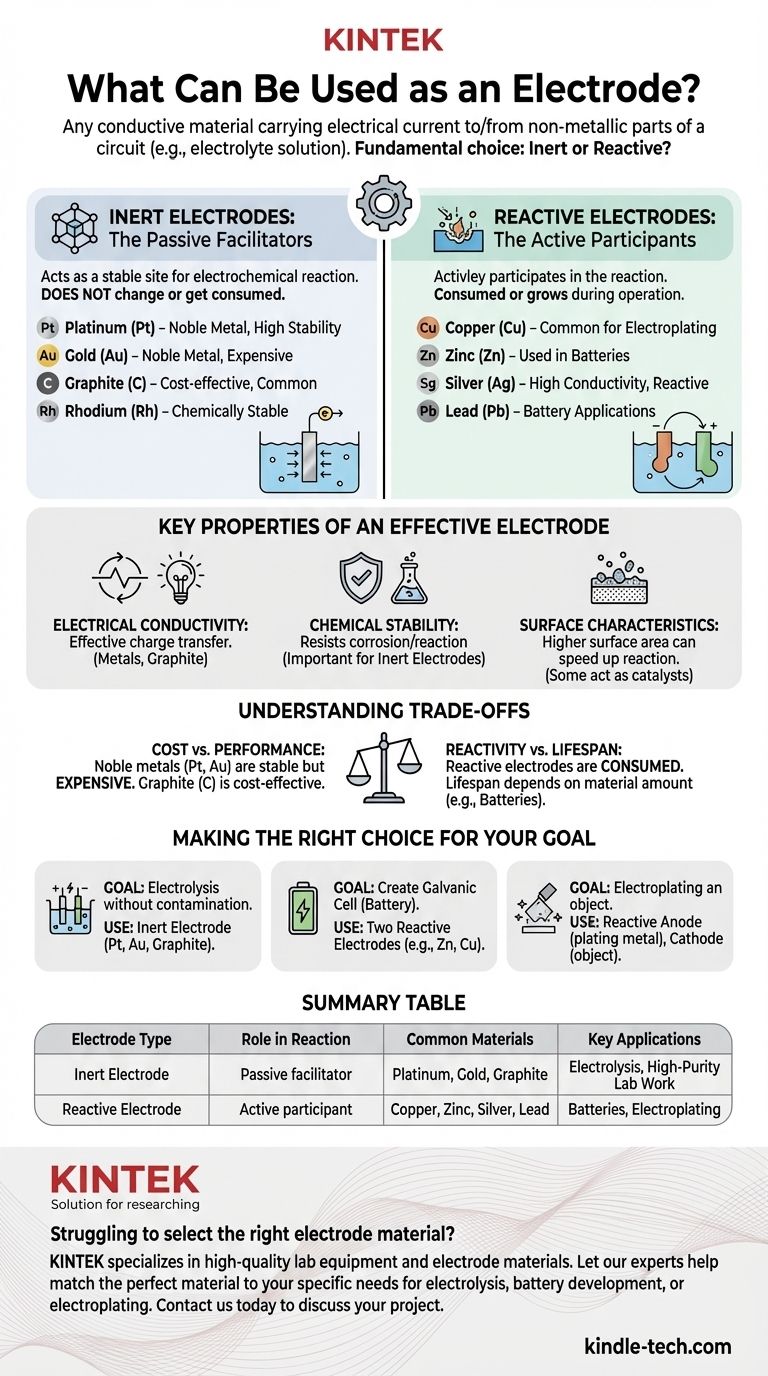
In short, an electrode is any conductive material that carries an electrical current into or out of a non-metallic part of a circuit, such as an electrolyte solution. Electrodes are broadly classified into two categories: inert electrodes, which do not participate in the chemical reaction, and reactive electrodes, which do. Common examples include metals like platinum, gold, copper, and zinc, as well as non-metals like graphite (carbon).
Choosing an electrode is a critical design decision in any electrochemical system. The fundamental choice is not just "what material conducts electricity," but whether you need a material that remains unchanged (inert) or one that actively participates in the chemical reaction (reactive).
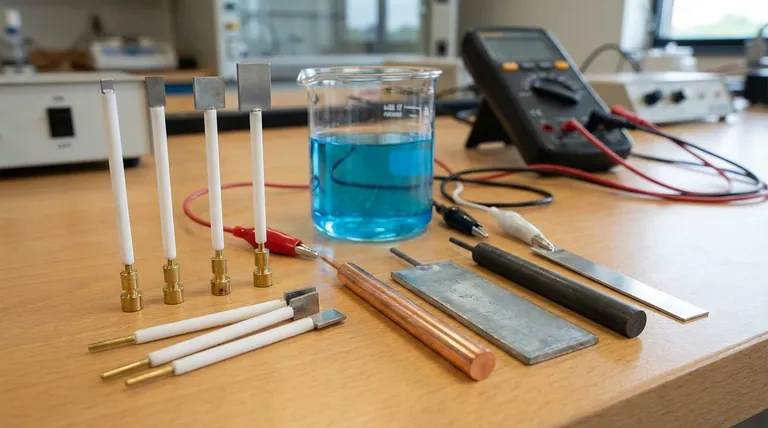

The Two Fundamental Types of Electrodes
The most important distinction when selecting an electrode material is its role in the intended chemical reaction. This separates all potential materials into two primary groups.
Inert Electrodes: The Passive Facilitators
An inert electrode acts as a stable, non-reactive site for an electrochemical reaction to occur. Its job is simply to conduct electrons to or from the electrolyte.
The material itself does not change, get consumed, or dissolve into the solution. It is merely a surface.
Because of this, inert electrodes must be made of materials that are chemically stable in the specific electrolyte being used. Common choices include noble metals and carbon.
Examples of inert electrodes:
- Platinum (Pt)
- Gold (Au)
- Graphite (C)
- Rhodium (Rh)
Reactive Electrodes: The Active Participants
A reactive electrode is an active participant in the electrochemical reaction. It is either oxidized (dissolving into the electrolyte) or is the product of reduction (plating onto the surface).
These materials are chosen specifically for their ability to react in a controlled way. This is the principle behind batteries and electroplating.
The electrode itself is consumed or grows during the operation of the electrochemical cell.
Examples of reactive electrodes:
- Copper (Cu)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Silver (Ag)
- Lead (Pb)
Key Properties of an Effective Electrode
Beyond the basic classification, several properties determine how well a material will function as an electrode for a specific purpose.
Electrical Conductivity
This is the most fundamental requirement. The material must be an effective conductor of electricity to transfer charge between the external circuit and the electrolyte. Metals and graphite are excellent choices for this reason.
Chemical Stability
For an electrode to be considered inert, it must resist corrosion or reaction with the electrolyte and any substances produced during the reaction. This is why noble metals like platinum and gold are highly valued for these applications.
Surface Characteristics
The reaction occurs on the electrode's surface. A material with a higher surface area can often support a faster reaction rate. Furthermore, some materials, like platinum, can act as catalysts, lowering the energy required for a reaction to proceed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The theoretically "best" electrode is not always the most practical one to use. Real-world applications require balancing performance against other factors.
Cost vs. Performance
Noble metals like platinum and gold are exceptional inert electrodes due to their extreme stability, but they are very expensive.
For many applications, graphite offers a vastly more cost-effective alternative. While it may be less durable or catalytically active than platinum, its low cost makes it the dominant choice for countless industrial processes.
Reactivity vs. Lifespan
By definition, reactive electrodes are consumed over time. This is a necessary function in applications like galvanic cells (batteries), where the electrode's consumption generates the electrical current.
This means the lifespan of the device is directly tied to the amount of reactive electrode material available. The choice of material dictates the cell's voltage and its longevity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection of an electrode material should be driven entirely by the goal of your electrochemical cell.
- If your primary focus is electrolysis without contamination: You need an inert electrode. Use platinum or gold for high-purity lab work, or graphite (carbon) for a cost-effective alternative.
- If your primary focus is creating a galvanic cell (a battery): You need two different reactive electrodes. Use materials like zinc and copper, whose difference in chemical potential drives the electrical current.
- If your primary focus is electroplating an object: Your anode (positive electrode) should be a reactive electrode made of the metal you want to plate (e.g., silver), and your cathode (negative electrode) will be the object itself.
Ultimately, the right electrode is the one whose chemical and physical properties are precisely matched to the specific function it must perform within your electrochemical cell.
Summary Table:
| Electrode Type | Role in Reaction | Common Materials | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert Electrode | Passive facilitator; does not react | Platinum, Gold, Graphite | Electrolysis, High-Purity Lab Work |
| Reactive Electrode | Active participant; is consumed or formed | Copper, Zinc, Silver, Lead | Batteries, Electroplating |
Struggling to select the right electrode material for your application? The performance of your electrochemical process depends on this critical choice. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of electrode materials like platinum, graphite, and reactive metals. Our experts can help you match the perfect material to your specific needs—whether it's for electrolysis, battery development, or electroplating—ensuring optimal results and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your project and let KINTEK be your partner in precision. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Gold Disc Electrode
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Electrochemical Data
- What is the proper post-treatment procedure for a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Long-Term Accuracy & Protect Your Investment
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be pretreated before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements



















