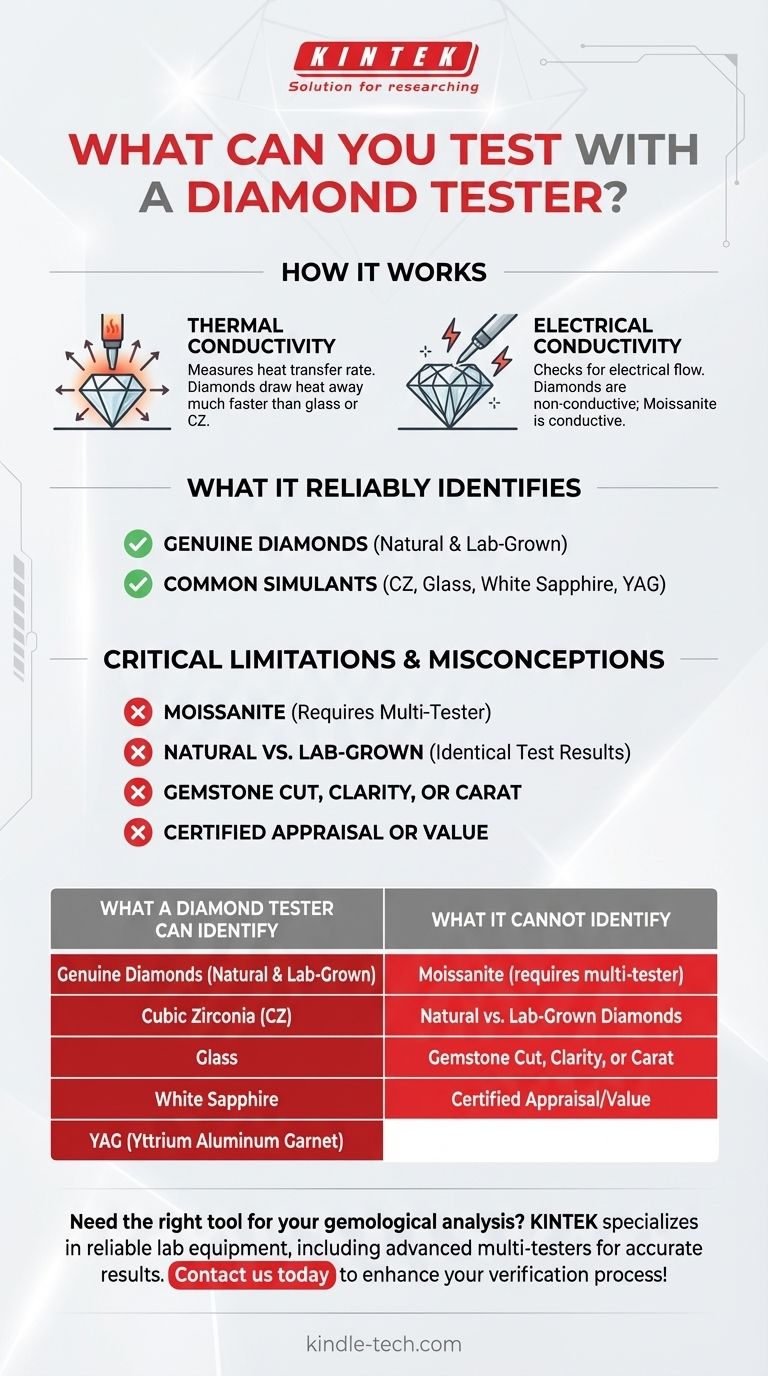
At its core, a diamond tester is a portable electronic instrument designed for a single primary purpose: to distinguish a genuine diamond from common non-diamond imitations. It works by measuring how a stone reacts to a small amount of heat or electricity, as diamonds have unique thermal and electrical properties that separate them from most fakes.
A standard diamond tester is highly effective at identifying common simulants like glass or cubic zirconia. However, its most critical limitation is its inability to differentiate a diamond from moissanite, requiring more advanced tools for a definitive result.

How a Diamond Tester Works
A diamond tester doesn't analyze a stone's visual characteristics like cut or clarity. Instead, it measures specific physical properties that are invisible to the naked eye.
Measuring Thermal Conductivity
The most common method involves thermal conductivity. A small, spring-loaded probe at the tip of the tester is heated.
When this probe touches the surface of a gemstone, it measures the rate at which heat is pulled away from the tip.
Because diamonds are exceptionally efficient thermal conductors, they draw heat away from the probe much faster than simulants like glass or cubic zirconia, triggering a positive reading on the device.
Checking for Electrical Conductivity
Some stones, particularly moissanite, have a thermal conductivity that is very close to that of a diamond, which can fool a basic thermal-only tester.
To solve this, more advanced "multi-testers" also check for electrical conductivity.
Diamonds are not electrically conductive, while moissanite is. This second test provides a crucial data point to separate the two very similar stones.
What a Diamond Tester Reliably Identifies
Understanding what these tools can and cannot do is essential for using them effectively.
Genuine Diamonds
The primary function of a tester is to give a positive result for a genuine diamond.
It's important to note that because lab-grown diamonds are physically and chemically identical to natural diamonds, they will also test positive as "diamond."
Common Simulants
A diamond tester is extremely effective at quickly weeding out common, less-sophisticated fakes.
Stones like cubic zirconia (CZ), white sapphire, YAG, or plain glass have vastly different thermal properties and will not pass the test.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
A diamond tester is a tool for indication, not a certified appraisal. Its results are only as reliable as the technology it uses and the knowledge of the operator.
The Moissanite Problem
The most significant pitfall for basic testers is moissanite. This lab-created gemstone is a popular diamond alternative and its thermal signature can easily fool a tester that only checks for heat conductivity.
Without a secondary test for electrical conductivity, you can easily get a false positive, believing moissanite to be a diamond.
No Distinction Between Natural and Lab-Grown
A standard diamond tester cannot tell the difference between a diamond mined from the earth and one grown in a laboratory.
Both are structurally identical and will pass the thermal and electrical tests. Distinguishing between them requires specialized equipment found in a gemological lab.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To use a tester effectively, you must match the tool to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is avoiding common fakes: A standard, entry-level thermal tester is a reliable and cost-effective tool for separating diamonds from glass or cubic zirconia.
- If your primary focus is distinguishing diamonds from moissanite: You must use a multi-tester that checks for both thermal and electrical conductivity to get an accurate result.
- If your primary focus is verifying if a diamond is natural or lab-grown: A diamond tester is the wrong tool; this task requires professional analysis by a certified gemologist.
Ultimately, understanding a tool's capabilities and its limitations is the key to making an informed and confident assessment.
Summary Table:
| What a Diamond Tester Can Identify | What It Cannot Identify |
|---|---|
| Genuine Diamonds (Natural & Lab-Grown) | Moissanite (requires multi-tester) |
| Cubic Zirconia (CZ) | Natural vs. Lab-Grown Diamonds |
| Glass | Gemstone Cut, Clarity, or Carat |
| White Sapphire | Certified Appraisal/Value |
| YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) |
Need the right tool for your gemological analysis? KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including advanced diamond testers that check both thermal and electrical conductivity to accurately distinguish diamonds from moissanite. Whether you're a jeweler, pawnbroker, or gem enthusiast, our equipment ensures confident and precise results. Contact us today to find the perfect tester for your needs and enhance your verification process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using PTFE filters for ionic component analysis? Ensure Accurate Sample Quantification
- Why is coating thickness important? Achieve Optimal Performance and Cost Control
- How do you test a lithium battery to see if it's good? A Guide to Measuring Voltage, Capacity & Health
- What is the minimum coating thickness? How Steel Thickness Determines Your Galvanizing Needs
- What is the water content of pyrolysis oil? A Key Factor in Bio-Oil Quality and Use














