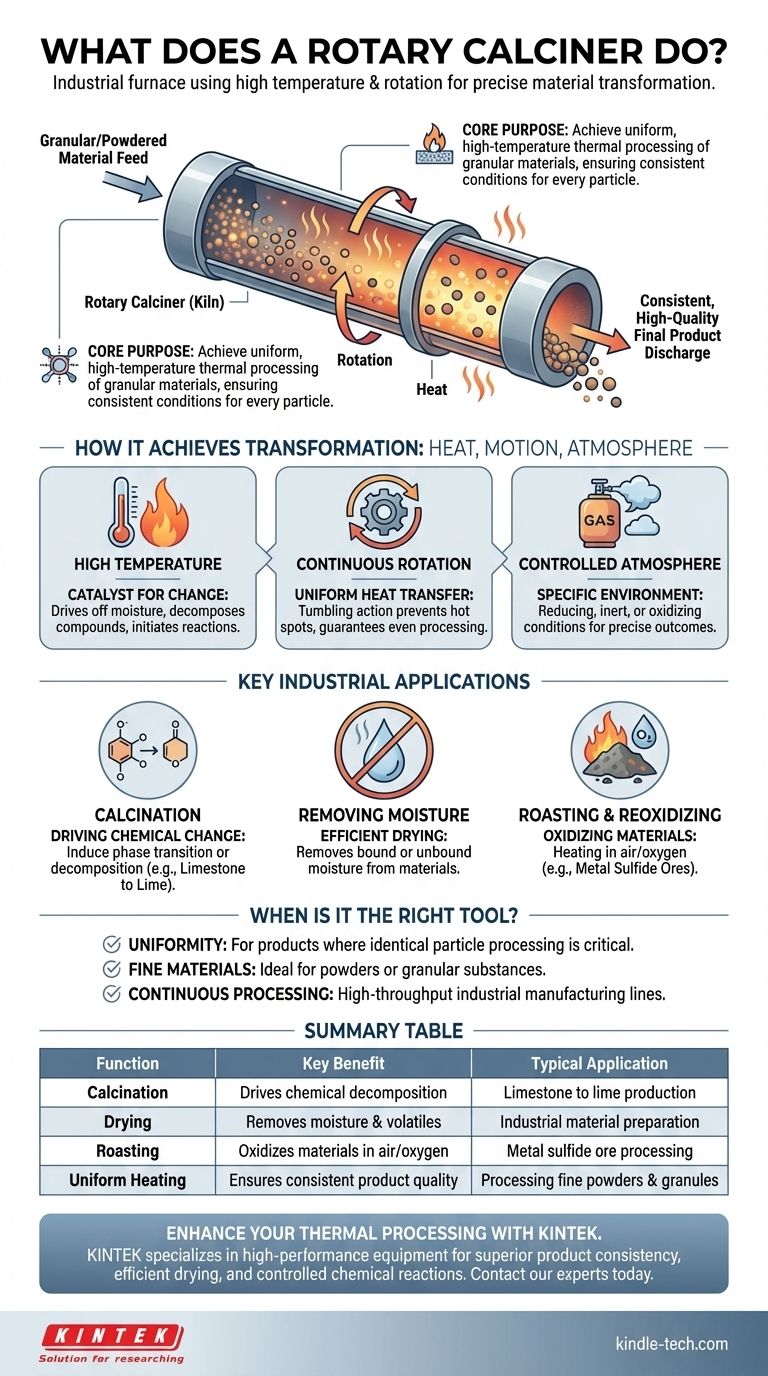
At its core, a rotary calciner is an industrial furnace that uses high temperatures and rotation to transform materials. It is engineered to precisely change the chemical or physical state of a substance, often by removing moisture, driving chemical reactions, or altering a material's composition under carefully controlled atmospheric conditions.
The essential purpose of a rotary calciner is to achieve uniform, high-temperature thermal processing of granular or powdered materials. Its continuous rotation ensures every particle is exposed to the same conditions, resulting in a consistent and high-quality final product.

How a Rotary Calciner Achieves Material Transformation
A rotary calciner, sometimes called a rotary kiln, combines three critical elements—heat, motion, and atmosphere—to process materials with a high degree of control.
The Role of High Temperature
The primary function is to heat materials to a specific temperature profile. This thermal energy is the catalyst for the desired physical or chemical changes.
These high temperatures are essential for processes like driving off water, decomposing compounds, or initiating chemical reactions that would not occur under normal conditions.
The Importance of Rotation
The "rotary" aspect is the key differentiator. A large, rotating cylindrical tube is angled slightly, causing material to tumble and move from the feed end to the discharge end.
This tumbling action ensures uniform heat transfer throughout the material bed. It prevents hot spots and guarantees that every particle is processed evenly, which is critical for product quality.
Controlled Atmospheric Conditions
Many advanced processes require a specific atmosphere inside the furnace. Rotary calciners are designed to operate with controlled environments.
This could involve a reducing atmosphere to deoxidize metals, an inert atmosphere to prevent unwanted reactions, or an oxidizing atmosphere for processes like roasting.
Key Industrial Applications
The combination of these elements makes rotary calciners versatile for several core industrial processes.
Calcination: Driving Chemical Change
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material to drive off a volatile fraction and induce a phase transition or chemical decomposition.
A common example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide.
Removing Moisture and Volatiles
At its simplest, a rotary calciner can function as a highly efficient industrial dryer. It removes bound or unbound moisture from a wide range of materials.
This is a fundamental step in preparing materials for further processing or creating a final, dry product.
Roasting and Reoxidizing
Roasting is a metallurgical process that involves heating a substance in the presence of air or oxygen.
This is often used to convert metal sulfide ores into metal oxides, which are easier to reduce to pure metal. It can also be used to precisely reoxidize fine metal oxide particles.
When a Rotary Calciner is the Right Tool
While other furnaces can achieve high temperatures, the rotary calciner is specifically chosen when the material characteristics and processing goals demand its unique capabilities.
The Need for Uniformity
If your final product's quality depends on every particle being processed identically, the tumbling action of a rotary calciner is a significant advantage over static batch furnaces.
Handling Fine or Granular Materials
The design is ideal for processing fine particles, powders, or granular materials that would be difficult to heat evenly in a static bed.
Continuous Processing Requirements
Rotary calciners are inherently continuous systems. Material is constantly fed in one end and discharged at the other, making them ideal for high-throughput industrial manufacturing lines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To determine if a rotary calciner is suitable, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is inducing a chemical change: The calciner's precise temperature and atmospheric control is essential for driving reactions like decomposition or phase changes.
- If your primary focus is consistent product quality: The continuous rotation and tumbling action provide unparalleled uniformity for processing granular materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume drying: A rotary system offers a continuous and efficient method for removing moisture from a constant flow of material.
Ultimately, this equipment is a powerful tool for achieving highly controlled and uniform thermal processing at an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Drives chemical decomposition | Limestone to lime production |
| Drying | Removes moisture & volatiles | Industrial material preparation |
| Roasting | Oxidizes materials in air/oxygen | Metal sulfide ore processing |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent product quality | Processing fine powders & granules |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing with precision and uniformity?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and industrial solutions for thermal processing. Our expertise in rotary calciner technology can help you achieve superior product consistency, efficient high-volume drying, and controlled chemical reactions for your granular or powdered materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary calciner can optimize your specific process and deliver the high-quality results you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process



















