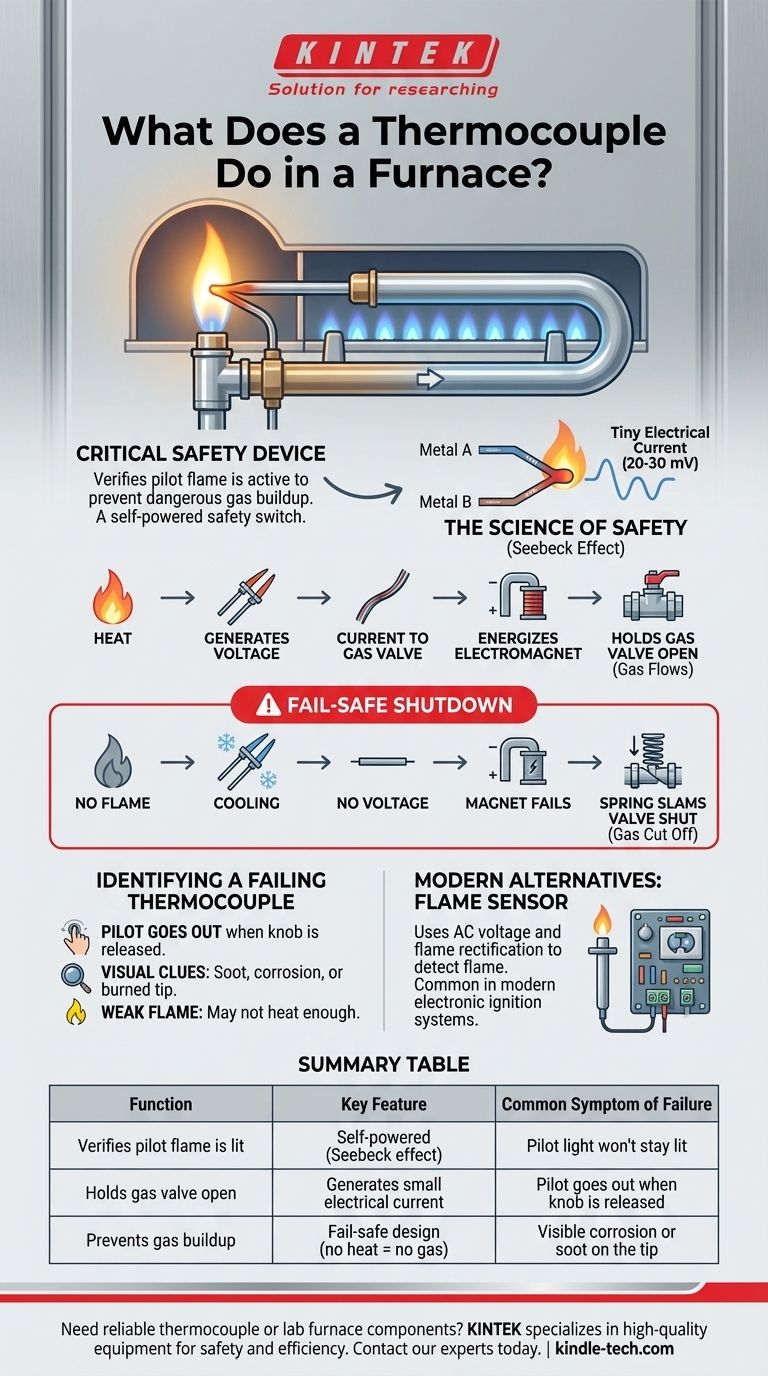
In essence, a thermocouple is a critical safety device used in furnaces with a standing pilot light. Its sole purpose is to verify that the pilot flame is active before allowing gas to flow to the main burners. If the pilot light goes out, the thermocouple immediately signals the gas valve to shut, preventing a dangerous and potentially explosive buildup of unburned natural gas.
The thermocouple is not just a sensor; it is a self-powered safety switch. It converts the pilot light's heat directly into a tiny electrical current, which is the only thing holding the gas valve open. No heat means no current, and the valve slams shut.

How a Thermocouple Works: The Science of Safety
A thermocouple's operation is based on a simple but brilliant scientific principle. It requires no external power from your home's electrical system to perform its vital safety function.
The Principle of Operation
A thermocouple consists of two different types of metal wires joined together at one tip. This junction is placed directly in the pilot flame. When heated, this junction of dissimilar metals generates a very small, measurable DC voltage—a phenomenon known as the Seebeck effect.
The Electrical Signal's Role
This small electrical current (typically 20-30 millivolts) travels down the thermocouple's lead to the main gas valve. Inside the valve, the current energizes a small electromagnet (solenoid) that holds a spring-loaded safety valve open.
Think of it as a magnetic gatekeeper. As long as the thermocouple is hot and generating voltage, the magnet is strong enough to hold the gate open against the pressure of a spring that is trying to close it.
The Safety Shutdown Sequence
If the pilot flame is extinguished for any reason—be it a draft or a disruption in the gas supply—the thermocouple's tip begins to cool rapidly. As it cools, the voltage it produces immediately drops to zero.
Without voltage, the electromagnet de-energizes instantly. The spring's mechanical force takes over and slams the safety valve shut, cutting off the flow of gas. This is a fail-safe mechanism; it requires constant proof (heat) to permit gas flow.
Identifying a Failing Thermocouple
Because thermocouples are subjected to constant, intense heat cycles, they are a common point of failure in older furnaces. The symptoms are usually very distinct.
The Primary Symptom
The most common sign of a bad thermocouple is a pilot light that goes out as soon as you release the control knob or reset button. You can light the pilot, but the flame extinguishes the moment you let go.
This happens because the failing thermocouple is no longer producing enough voltage to energize the electromagnet and hold the gas valve open on its own.
Visual Inspection Clues
Visually inspect the thermocouple tip that sits in the pilot flame. If it is covered in heavy soot, severely corroded, or visibly burned or eroded, it likely needs replacement. A dirty tip can't sense heat effectively, and a damaged one can't generate the required voltage.
Is It Always the Thermocouple?
Remember that a weak, flickering, or yellow pilot flame may not be hot enough to properly heat the thermocouple. Before replacing the thermocouple, ensure the pilot flame itself is a steady, strong blue flame that fully envelops the top 1/2 inch of the thermocouple tip. A dirty pilot orifice can cause a weak flame.
Understanding the Alternatives in Modern Furnaces
The thermocouple is a hallmark of older, standing-pilot furnace technology. Modern heating systems have evolved to use more efficient and sophisticated methods of flame detection.
The Shift from Standing Pilots
Most furnaces manufactured in the last two decades do not have a pilot light that is on 24/7. Instead, they use electronic ignition systems, such as a hot surface ignitor (HSI) or a spark ignitor, which only activate when there is a call for heat.
The Modern Equivalent: The Flame Sensor
In these modern systems, the job of confirming a flame is present is done by a flame sensor (or flame rectification rod). This is a simple metal rod positioned in the path of the main burner flame.
Instead of generating its own voltage from heat, the furnace's control board sends a low AC voltage to the flame sensor. The properties of a flame "rectify" this AC current into a tiny DC signal, which is read by the control board. If the board doesn't detect this specific DC signal within a few seconds of opening the gas valve, it concludes the gas did not ignite and immediately shuts the valve.
Making the Right Diagnosis
Understanding the difference between these components is key to troubleshooting your furnace correctly.
- If your pilot light will not stay lit: Your thermocouple is the most likely culprit and is a common, inexpensive component to replace.
- If your furnace clicks but fails to ignite: You likely have a modern system, and the problem could be the ignitor or the flame sensor, not a thermocouple.
- If you are ever unsure or smell gas: Your first priority is safety. Do not attempt a diagnosis; leave the area immediately and contact a qualified HVAC professional or your gas utility.
By acting as a simple, heat-powered gatekeeper, the thermocouple provides a foundational layer of safety for your heating system.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Common Symptom of Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Verifies pilot flame is lit | Self-powered (Seebeck effect) | Pilot light won't stay lit |
| Holds gas valve open | Generates small electrical current | Pilot goes out when knob is released |
| Prevents gas buildup | Fail-safe design (no heat = no gas) | Visible corrosion or soot on the tip |
Need a reliable thermocouple or other essential lab furnace components? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, ensuring the safety and efficiency of your laboratory operations. Our products are designed for durability and precision, serving the critical needs of laboratories worldwide. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your furnace and heating requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design



















