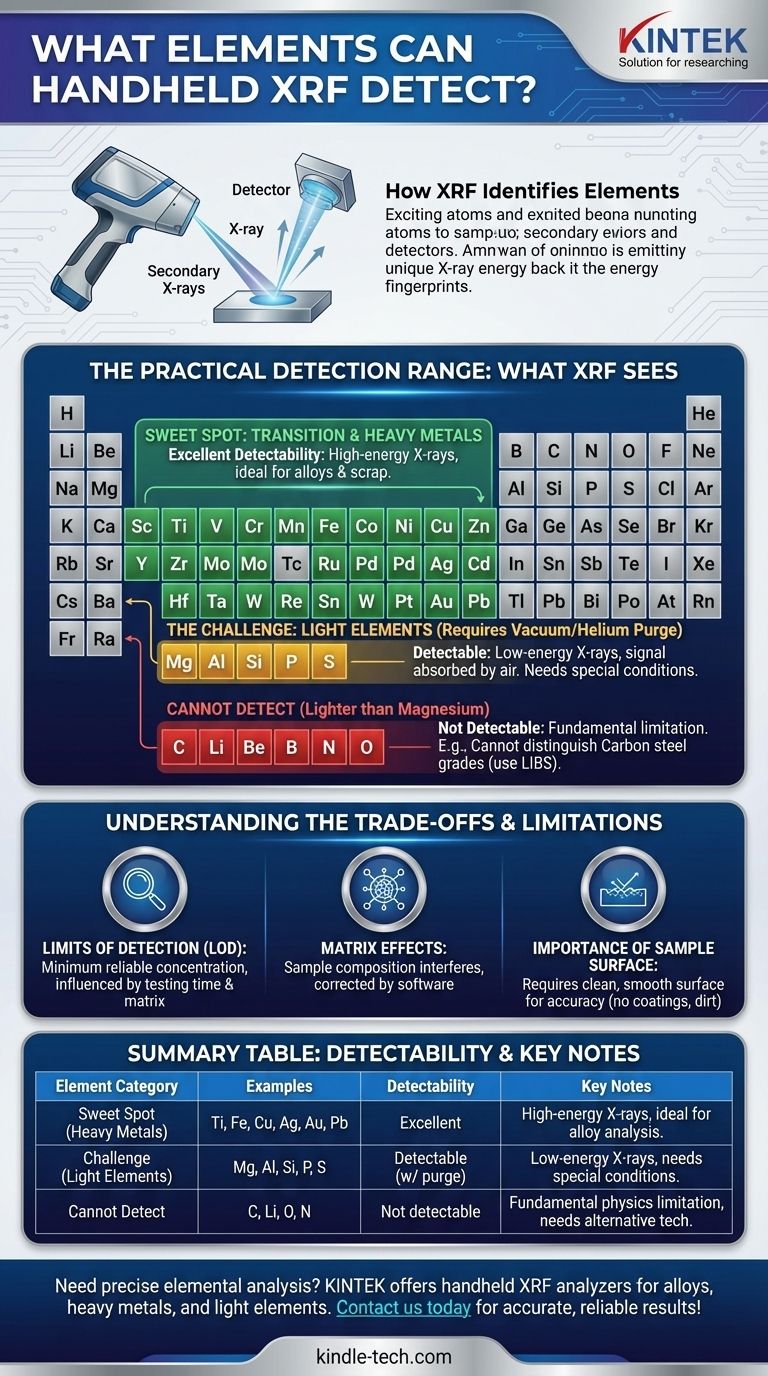
In short, a modern handheld XRF analyzer can detect most elements from Magnesium (Mg) to Uranium (U) on the periodic table. This wide range makes it an incredibly versatile tool for many industries, but its performance is not uniform across all elements. The key is understanding which elements it detects easily and which ones present a challenge.
A handheld XRF is not a simple "yes/no" device for element detection. Its true value is unlocked by understanding why it excels at identifying heavier metals but struggles with lighter elements, a limitation rooted in the fundamental physics of the technology.
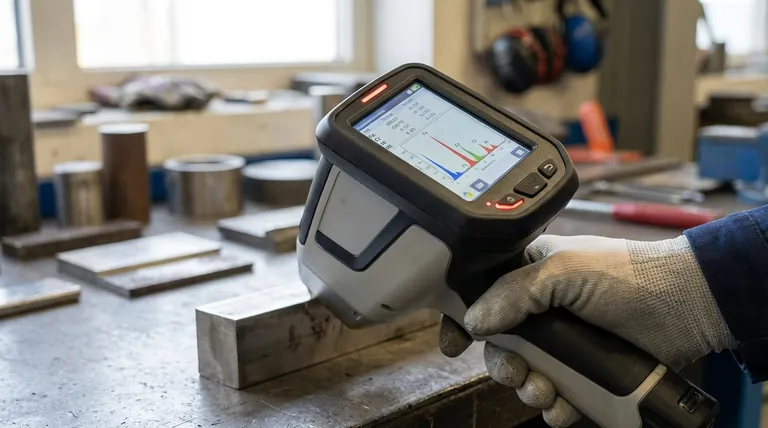

How XRF Identifies Elements
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) works by bombarding a sample with high-energy X-rays from a source inside the instrument. This energy excites the atoms within the sample, causing them to release their own secondary, lower-energy X-rays.
Each element emits these secondary X-rays at a unique, characteristic energy level—like a fingerprint. The instrument's detector measures both the energy (to identify the element) and the intensity (to determine its concentration).
The Practical Detection Range: What XRF Sees
While the theoretical range is vast, the practical effectiveness of a handheld XRF varies significantly depending on the element's atomic weight.
The Sweet Spot: Transition and Heavy Metals
Handheld XRF excels at rapidly and accurately identifying transition metals and heavy metals. This is its primary strength and the reason for its widespread use in alloy analysis, scrap metal sorting, and precious metals verification.
Elements in this category include Titanium (Ti), Vanadium (V), Chromium (Cr), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), Nickel (Ni), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Zirconium (Zr), Molybdenum (Mo), Palladium (Pd), Silver (Ag), Tin (Sn), Tungsten (W), Platinum (Pt), Gold (Au), and Lead (Pb).
The X-rays emitted by these heavier elements are high-energy, allowing them to travel easily from the sample to the detector without being absorbed by the air.
The Challenge: Light Elements
Lighter elements are those with low atomic numbers, specifically Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), and Sulfur (S). While detectable, they present a significant challenge.
These elements emit very low-energy "fluorescence" X-rays. These weak signals are easily absorbed by air before they can even reach the analyzer's detector. High-performance models overcome this by using a vacuum or helium purge system to create a clear path for the signal.
What Handheld XRF Cannot Detect
There is a hard limit to what XRF can see. Handheld XRF cannot detect elements lighter than Magnesium.
This list of undetectable elements includes some of the most common elements in engineering and nature: Carbon (C), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Boron (B), Nitrogen (N), and Oxygen (O).
This is a critical limitation. For example, an XRF analyzer cannot distinguish between different grades of carbon steel (e.g., 1020 vs. 1045 steel) because it cannot measure the carbon content. For that, a different technology like Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Effective use of XRF requires acknowledging that it is a surface analysis technique with inherent limitations beyond its elemental range.
Limits of Detection (LOD)
Every element has a Limit of Detection (LOD), which is the minimum concentration the analyzer can reliably detect. An element might be present in a sample, but if its concentration is below the LOD, the XRF will report it as not present.
LODs vary for each element and are influenced by the testing time and the other elements in the sample (the "matrix").
Matrix Effects
The overall composition of the sample—the matrix—can interfere with the accuracy of the readings. X-rays from one element can be absorbed or enhanced by another, potentially skewing the quantitative results. Modern analyzers use sophisticated software algorithms to correct for these matrix effects.
The Importance of the Sample Surface
Handheld XRF analyzes a very small and shallow area of the sample surface. Therefore, the condition of the surface is critical for an accurate reading.
Coatings (paint, plating), contamination (dirt, oil), and surface roughness can all lead to incorrect results. The ideal sample is clean, dry, and has a smooth, flat surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if XRF is the right tool, match its capabilities to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is sorting common alloys like stainless steel or nickel alloys: Standard handheld XRF is the ideal, industry-standard tool for this task.
- If your primary focus is analyzing aluminum, magnesium, or silicon alloys: You must use a high-performance XRF model equipped with a vacuum or helium purge system for accurate light element analysis.
- If your primary focus is determining carbon content in steel: XRF is the wrong tool; you need a handheld LIBS or a lab-based OES (Optical Emission Spectrometry) analyzer.
- If your primary focus is screening for heavy metals in soil, consumer products, or filters (RoHS/environmental): Standard handheld XRF is perfectly suited for this, as it excels at detecting lead, mercury, cadmium, and chromium.
Understanding both the power and the physical boundaries of XRF technology is the first step toward generating results you can trust.
Summary Table:
| Element Category | Examples | Detectability | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweet Spot (Heavy Metals) | Titanium (Ti), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Silver (Ag), Gold (Au), Lead (Pb) | Excellent | High-energy X-rays, ideal for alloy analysis and scrap sorting |
| Challenge (Light Elements) | Magnesium (Mg), Aluminum (Al), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S) | Detectable with vacuum/helium purge | Low-energy X-rays require special conditions for accurate reading |
| Cannot Detect | Carbon (C), Lithium (Li), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N) | Not detectable | Fundamental physics limitation; alternative technologies needed |
Need precise elemental analysis for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering handheld XRF analyzers tailored to your specific application—whether you're sorting alloys, screening for heavy metals, or analyzing light elements. Our experts will help you choose the right tool to ensure accurate, reliable results. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and accuracy!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- Why is a hydraulic press used to apply 380 MPa to battery bilayers? Achieve Superior Density & Safety
- How do a laboratory hydraulic press and alumina molds ensure ASSB integrity? Achieve Perfect Solid-State Densification
- What are the failures in a hydraulic system? Prevent Costly Downtime with Expert Diagnosis
- Is compression molding a fast process? A Guide to Faster Time-to-Market for Low-Volume Production
- What is the alternative to XRF? Choose the Right Elemental Analysis for Your Lab
- How many types of hydraulic presses are there? A Guide to Frame Designs for Your Application
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in platinum recovery research? Enhancing Sample Precision
- How is a hydraulic press helpful for making KBr pellets? Achieve Superior FTIR Sample Preparation



















