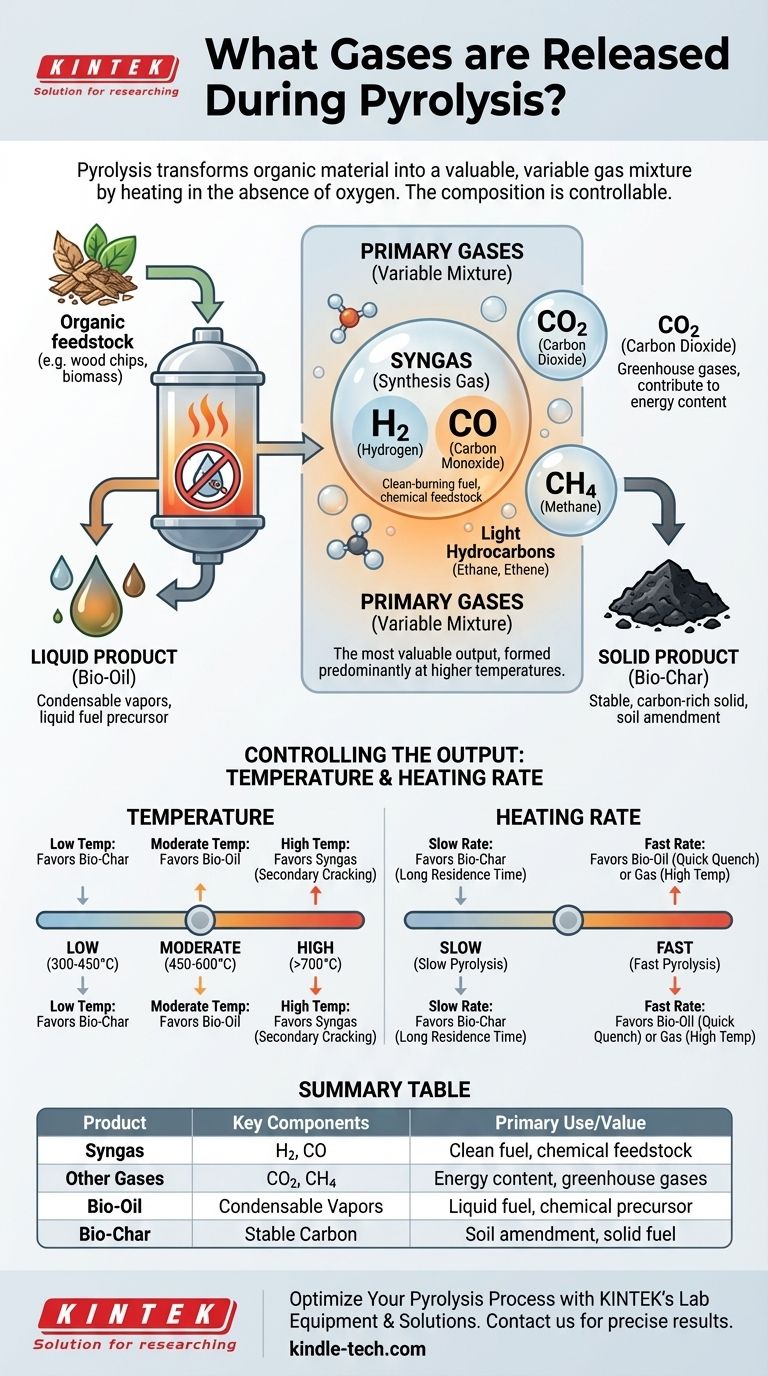
The primary gases released during pyrolysis are a combustible mixture known as synthesis gas (syngas), which is mainly composed of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO). In addition to syngas, the process also generates other non-condensable gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄), along with smaller amounts of light hydrocarbons such as ethane and ethene.
The crucial insight is that pyrolysis doesn't produce a single, fixed gas. Instead, it creates a variable mixture whose composition you can control by tuning process conditions—primarily temperature and heating rate—to target the production of either gas, liquid (bio-oil), or solid (bio-char).

How Pyrolysis Creates Gaseous Products
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal decomposition. By heating an organic material, or "feedstock," in an environment without oxygen, you prevent it from burning (combustion) and instead cause its complex molecules to break apart.
The Core Principle: Heating Without Oxygen
The absence of oxygen is the defining characteristic of pyrolysis. Instead of reacting with oxygen to produce flame, CO₂, and water, the feedstock's chemical bonds are broken solely by heat. This thermal cracking results in a mix of smaller, more volatile molecules (gas and liquid) and a stable, carbon-rich solid (char).
Deconstructing the Feedstock
For organic matter like biomass, the primary components being broken down are cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
- Cellulose and Hemicellulose: These simpler polymers break down at lower temperatures (300-500°C) and are primarily responsible for producing the condensable vapors that form bio-oil and the non-condensable gases like CO and CO₂.
- Lignin: This more complex and resilient polymer requires higher temperatures to decompose. It is a major contributor to the final yield of bio-char but also releases phenolic compounds and methane.
The Primary Gases Explained
The gaseous output is a mixture of valuable fuels and byproducts. Understanding each component is key to utilizing the output effectively.
Syngas: The Engine of the Process
Syngas, the mixture of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO), is the most valuable gaseous product. It is a clean-burning fuel that can be used to generate electricity or upgraded into liquid fuels and valuable chemicals. Its formation is favored at higher pyrolysis temperatures.
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) and Methane (CH₄)
Carbon dioxide is an inevitable byproduct, formed when carboxyl groups (-COOH) within the feedstock break off. Methane, the simplest hydrocarbon, is formed from the cracking of more complex organic structures. While both are greenhouse gases, they also contribute to the overall energy content of the gas mixture.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Controlling the Output
The final distribution of gas, liquid, and solid products is not random. It is a direct result of the process conditions you choose, creating a set of predictable trade-offs.
Temperature's Dominant Role
Temperature is the most critical variable for steering the output.
- Low Temperatures (300-450°C): This range favors the production of bio-char, as the decomposition is slow and incomplete.
- Moderate Temperatures (450-600°C): This is the optimal range for producing bio-oil, as thermal cracking is aggressive enough to create vapors but not so extreme that it breaks them down further into gas.
- High Temperatures (>700°C): This favors "secondary cracking," where the vapors that would have formed bio-oil are broken down even further into smaller, non-condensable gas molecules like H₂ and CO, maximizing syngas yield.
The Impact of Heating Rate
How quickly you apply the heat also has a profound impact.
- Slow Pyrolysis (Slow Heating Rate): A long residence time in the reactor allows for more secondary reactions that favor the formation of stable, solid bio-char.
- Fast Pyrolysis (Fast Heating Rate): Rapidly heating the feedstock maximizes the initial breakdown into vapors. If these vapors are then cooled quickly (quenched), the bio-oil yield is maximized. If they are kept at a high temperature, the gas yield is maximized.
The Influence of Feedstock
The nature of your input material matters. A plastic feedstock, rich in hydrocarbons, will yield a different gas profile (often with more complex hydrocarbons) compared to woody biomass, which is rich in cellulose and lignin.
Optimizing Pyrolysis for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, you must first define your desired output. The "best" process is the one that aligns with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas production: Utilize very high temperatures (>700°C) and a moderate heating rate to encourage the secondary cracking of all volatile compounds into permanent gases.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality bio-char: Employ a slow heating rate and relatively low peak temperatures (around 400-500°C) to minimize the breakdown of the carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is generating bio-oil: Use a very fast heating rate to a moderate temperature (~500°C) followed by immediate quenching of the resulting vapors to prevent them from breaking down into gas.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively engineer the pyrolysis process to yield the specific products you need.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Key Components | Primary Use/Value |
|---|---|---|
| Syngas | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Clean-burning fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Other Gases | Carbon Dioxide (CO₂), Methane (CH₄) | Contribute to gas mixture energy content |
| Bio-Oil | Condensable vapors | Liquid fuel, chemical precursor |
| Bio-Char | Stable, carbon-rich solid | Soil amendment, solid fuel |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum syngas, bio-oil, or bio-char yield?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific pyrolysis research and development needs. Whether you are developing new biofuels, optimizing waste-to-energy processes, or conducting advanced material synthesis, our reliable reactors, temperature control systems, and analytical tools are designed to help you achieve precise and reproducible results.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What are the characteristics of the slipping, slumping, and rolling modes of bed motion? Optimize Your Rotary Process
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















