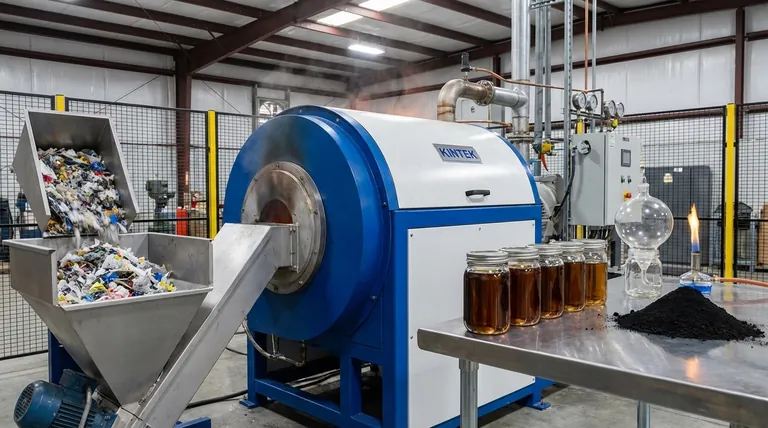
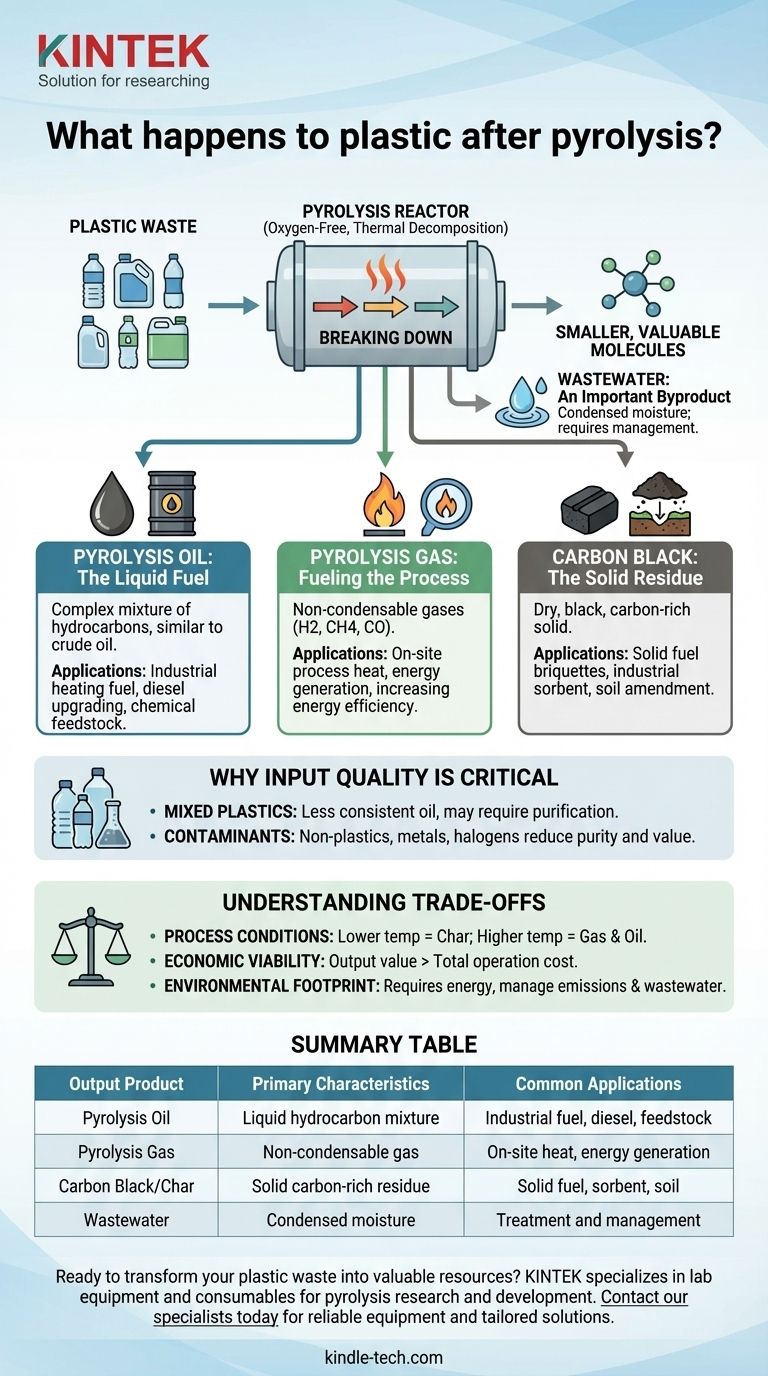
When plastic undergoes pyrolysis, it is thermally decomposed in an oxygen-free environment, breaking down its long polymer chains into smaller, more valuable molecules. This process fundamentally transforms plastic waste into three primary products: a liquid synthetic oil, a non-condensable synthetic gas, and a solid carbon-rich char.
Plastic pyrolysis is not simply destruction; it is a chemical conversion process. It deconstructs low-value plastic waste and reclaims it as marketable commodities, though the quality and proportion of these outputs depend entirely on the input plastic and the process conditions.

The Three Primary Outputs of Plastic Pyrolysis
The pyrolysis process sorts the complex chemistry of plastic into distinct gas, liquid, and solid streams. Each has its own characteristics and potential applications.
Pyrolysis Oil: The Liquid Fuel
This liquid product, often called pyrolysis oil or "bio-oil," is the most valuable output for many operators. It is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons similar in many ways to crude oil.
This synthetic oil can be used directly as an industrial heating fuel or, with further refining, be upgraded into higher-grade fuels like diesel or blended into feedstocks for new chemical and plastic production.
Pyrolysis Gas: Fueling the Process
The process also generates a stream of non-condensable gases, often referred to as syngas or pyrolysis gas. This gas is rich in compounds like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
In most modern pyrolysis plants, this gas is not wasted. It is captured and combusted on-site to provide the heat energy required to run the pyrolysis reactor, making the process more energy-efficient and reducing reliance on external fuel sources.
Carbon Black: The Solid Residue
After the volatile components have been driven off as gas and liquid, a dry, black, carbon-rich solid remains. This material is known as carbon black, char, or coke.
Its properties make it useful as a solid fuel (often pressed into briquettes), an industrial sorbent for filtration, or a soil amendment in agriculture. The amount of non-plastic contaminants in the original waste stream will largely end up in this solid fraction.
Wastewater: An Important Byproduct
If the plastic feedstock contains significant moisture, it will be vaporized during the heating process and condensed as wastewater. This stream must be managed and treated, adding another layer to the operational plan.
Why Input Quality is Critical
The core challenge and opportunity in plastic pyrolysis lie in managing the feedstock. The type and purity of the plastic waste directly dictate the yield and quality of the final products.
The Problem of Mixed Plastics
Real-world plastic waste is rarely a single, pure polymer. A mix of different plastic types (e.g., PET, HDPE, PVC) along with labels, adhesives, and food residue will result in a less consistent pyrolysis oil that may require more intensive purification.
The Impact of Contaminants
Non-plastic content like dirt, glass, or metal does not pyrolyze. Instead, it remains in the reactor and exits with the solid carbon black, reducing its purity and value. Halogens like chlorine from PVC plastic can also introduce corrosive acids into the system.
Achieving Consistent Quality
To overcome this variability, many operations invest in pre-processing steps like sorting, shredding, and washing the plastic waste. Additionally, post-pyrolysis technologies like oil purification units can be used to produce a stable, high-quality oil even when the input material varies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Viewing pyrolysis as a "magic box" for plastic is a mistake. It is an industrial chemical process with specific trade-offs that must be managed for both economic and environmental success.
Process Conditions Dictate Yield
Operators can "steer" the output by controlling the process variables. Lower temperatures and slower heating rates tend to favor char production, while higher temperatures and faster processing favor gas and oil production. The desired output determines the optimal operating parameters.
Economic Viability
The business case for pyrolysis rests on a simple equation: the market value of the oil, gas, and char must exceed the total cost of operation. This includes feedstock acquisition, pre-processing, energy consumption, maintenance, and residue disposal.
Environmental Footprint
While pyrolysis is a powerful tool for diverting plastic from landfills and oceans, the process itself requires energy and has an environmental footprint. Proper management of emissions and byproducts like wastewater is essential for the process to be a net positive.
Matching Pyrolysis Outputs to Your Goal
To apply this technology effectively, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is generating liquid fuel: You must prioritize securing a clean, consistent feedstock (like sorted polyolefins) and optimizing your reactor for high oil yield.
- If your primary focus is maximum waste volume reduction: You can accept more varied, mixed-plastic feedstocks, but you must have a clear plan for utilizing or disposing of the lower-quality char and oil produced.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value chemical feedstocks: You must invest heavily in both feedstock pre-treatment and oil purification systems to meet the stringent purity requirements of the chemical industry.
Ultimately, plastic pyrolysis is a technology that reframes our perception of waste, turning a persistent liability into a potential resource.
Summary Table:
| Output Product | Primary Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil | Liquid hydrocarbon mixture similar to crude oil | Industrial heating fuel, diesel production, chemical feedstock |
| Pyrolysis Gas | Non-condensable gas (hydrogen, methane, CO) | On-site process heat, energy generation |
| Carbon Black/Char | Solid carbon-rich residue | Solid fuel briquettes, industrial sorbent, soil amendment |
| Wastewater | Condensed moisture from feedstock | Requires treatment and management |
Ready to transform your plastic waste into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing process conditions, analyzing output quality, or scaling up your operations, our precision instruments and expert support can help you achieve consistent, high-yield results. Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can support your pyrolysis projects with reliable equipment and tailored solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















