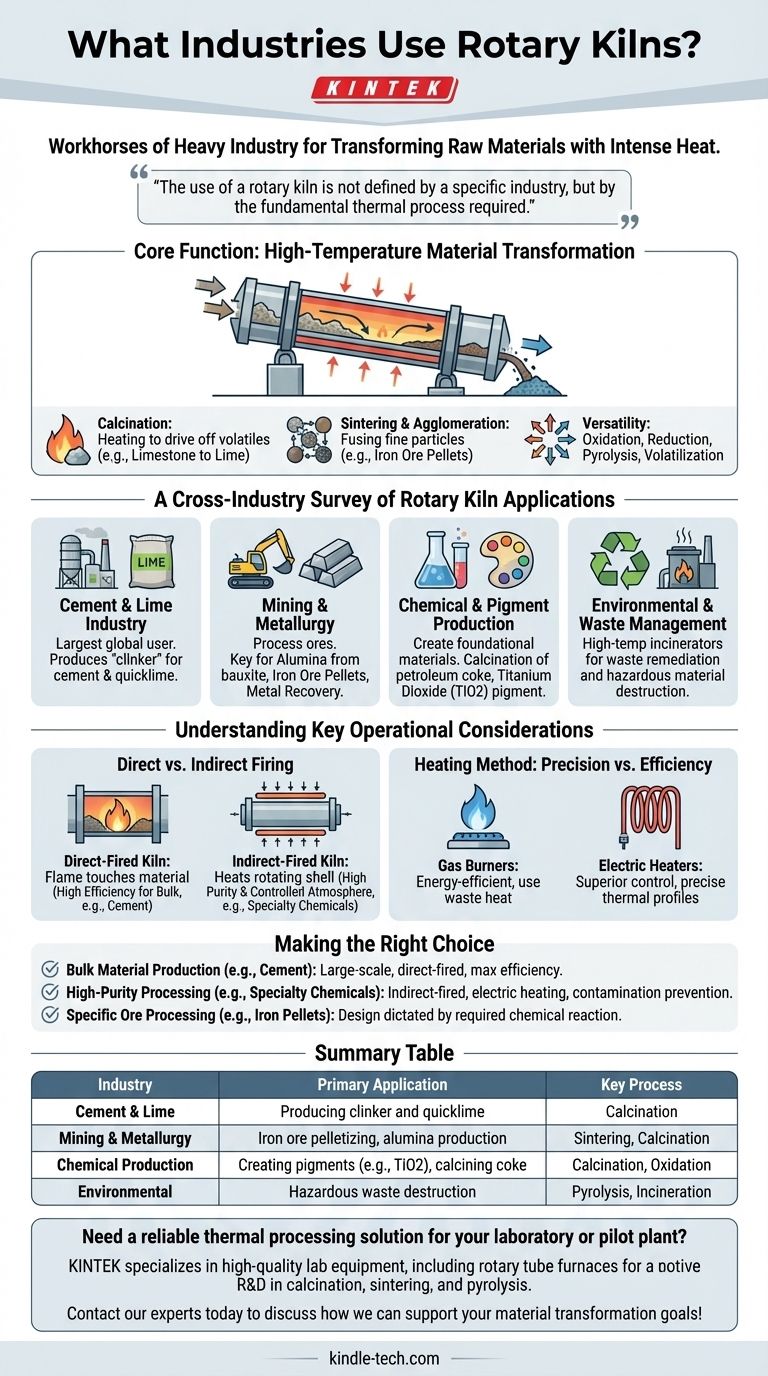
At their core, rotary kilns are the workhorses of heavy industry. They are essential in any field that requires transforming raw materials with intense heat, most notably in the cement, lime, mining, and chemical manufacturing sectors. Their purpose is to enable continuous thermal treatment processes like calcination and sintering on a massive scale.
The use of a rotary kiln is not defined by a specific industry, but by the fundamental thermal process required. If a material needs to be heated to extreme temperatures to drive a chemical or physical change, a rotary kiln is often the most effective tool for the job.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Material Transformation
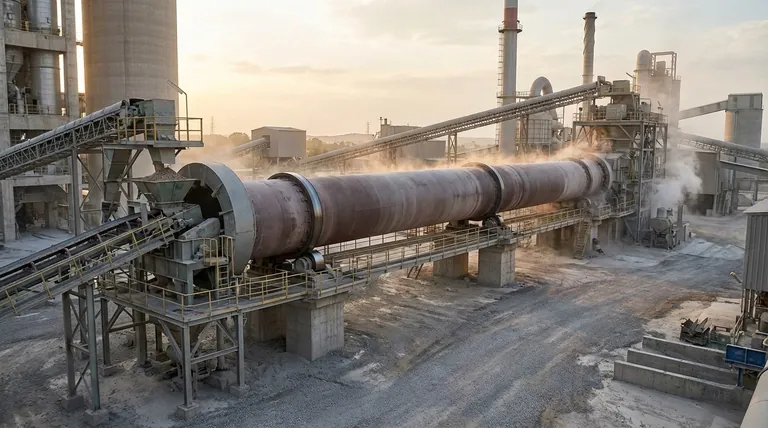
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical furnace, typically sloped at a slight angle. This design allows for the continuous and uniform processing of materials as they pass from one end to the other under controlled high temperatures.
Calcination: The Most Common Application
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material to drive off a volatile component. This is the primary function of rotary kilns in the cement and lime industries.
For example, limestone (calcium carbonate) is fed into a kiln and heated to break it down into lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide, which is released as a gas.
Sintering and Agglomeration
Sintering uses heat to fuse fine particles into a solid, coherent mass without melting them completely. This is crucial in metallurgy.
Rotary kilns are used to agglomerate fine iron ore particles into durable pellets, which are then used as feedstock for blast furnaces in steel production.
Versatility Through Other Processes
Beyond these primary uses, rotary kilns are adapted for a wide range of thermal treatments.
This includes oxidation (adding oxygen), reduction (removing oxygen), pyrolysis (decomposition without oxygen), and volatilization (turning a solid into a gas to separate it).
A Cross-Industry Survey of Rotary Kiln Applications
The versatility of these thermal processes means rotary kilns are found across a surprising number of industrial sectors.
The Cement and Lime Industry
This is the largest user of rotary kilns globally. Kilns are the heart of the cement manufacturing process, where they produce "clinker," the primary component of cement. The lime industry uses them similarly to produce quicklime.
Mining and Metallurgy
In this sector, kilns are used for processing a variety of ores. Key applications include producing alumina from bauxite, creating iron ore pellets, and recovering valuable metals like zinc, lead, and mercury through volatilization.
Chemical and Pigment Production
The chemical industry uses kilns for creating foundational materials. This includes the calcination of petroleum coke and the production of titanium dioxide (TiO2), a brilliant white pigment used in everything from paint to sunscreen.
Environmental and Waste Management
On a smaller scale, rotary kilns serve as high-temperature incinerators. They are effective for waste remediation and destroying hazardous materials by breaking them down into safer, more stable components.
Understanding Key Operational Considerations
The choice to use a rotary kiln is just the first step. The specific design and heating method are critical for achieving the desired outcome and are tailored to the material being processed.
Direct vs. Indirect Firing
A direct-fired kiln exposes the material directly to the flame and combustion gases. This is highly efficient for bulk materials like cement and ore where direct contact is acceptable.
An indirect-fired kiln heats the outside of the rotating shell, never allowing the flame to touch the material inside. This method is essential for high-purity applications or processes requiring a controlled atmosphere, such as specialty chemical production.
Heating Method: Precision vs. Efficiency
Gas burners are a common, energy-efficient choice, often designed to use waste heat from the process itself as a fuel source.
Electric heaters offer superior control over heating rates and temperature distribution. This precision is vital for sensitive processes where exact thermal profiles must be maintained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal rotary kiln configuration depends entirely on the material and the intended transformation.
- If your primary focus is bulk material production (like cement or lime): A large-scale, direct-fired kiln designed for maximum energy efficiency is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material processing (like specialty chemicals): An indirect-fired kiln, often with electric heating, is necessary to prevent contamination and ensure precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is specific ore processing (like iron pellets or alumina): The kiln design will be dictated by the required chemical reaction, whether it's oxidation, reduction, or simple calcination.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's value lies in its unique ability to transform raw, granulated materials into the foundational products that build our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Rotary Kiln Application | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Cement & Lime | Producing clinker and quicklime | Calcination |
| Mining & Metallurgy | Iron ore pelletizing, alumina production | Sintering, Calcination |
| Chemical Production | Creating pigments (e.g., TiO2), calcining coke | Calcination, Oxidation |
| Environmental | Hazardous waste destruction | Pyrolysis, Incineration |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution for your laboratory or pilot plant? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including rotary tube furnaces ideal for R&D in calcination, sintering, and pyrolysis. Our expertise helps you scale your processes efficiently. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your material transformation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions



















