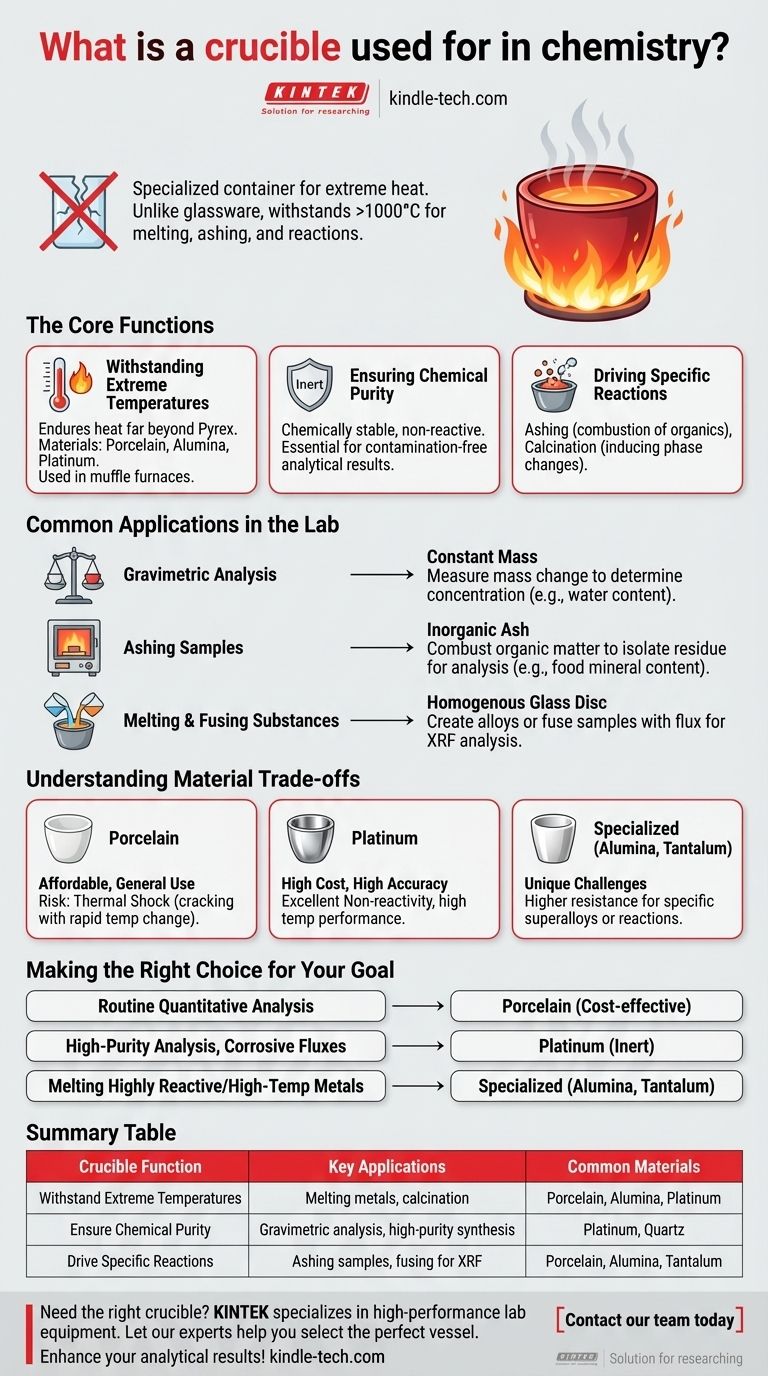
In chemistry, a crucible is a specialized ceramic or metal container designed to hold substances that need to be heated to extremely high temperatures. Unlike standard laboratory glassware, which would shatter under such conditions, crucibles are built to withstand intense heat, allowing for processes like melting metals, ashing samples, and driving high-temperature chemical reactions.
A crucible's fundamental purpose is to provide a chemically stable and heat-resistant vessel. This allows chemists to isolate and manipulate substances under extreme thermal stress, which is essential for accurate analysis and material synthesis.

The Core Functions of a Crucible in Chemistry
A crucible is not simply a heat-proof bowl; its design and material composition are critical for specific scientific tasks. Its utility is rooted in three key properties.
Withstanding Extreme Temperatures
The most basic function of a crucible is to endure temperatures that far exceed the limits of borosilicate glass (Pyrex), which can fail above 500°C.
Crucibles are made from refractory materials like porcelain, alumina, quartz, or platinum. This allows them to be used in high-temperature environments like muffle furnaces, often reaching over 1000°C.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
In analytical chemistry, sample contamination is a critical failure. The crucible itself must not react with the substance being heated.
This property, known as chemical inertness, ensures that the results of an analysis reflect the sample itself, not a reaction byproduct with the container. This is vital for determining the composition of a substance with high accuracy.
Driving Specific Chemical Reactions
Many chemical procedures require intense heat to proceed. A crucible provides the necessary environment for these reactions.
This includes ashing, where organic matter is burned away to isolate inorganic residue, and calcination, where materials are heated to drive off water or carbon dioxide to induce a phase change.
Common Applications in the Lab
In a practical setting, crucibles are indispensable for several common analytical and preparative techniques.
Gravimetric Analysis
This is a cornerstone technique in quantitative chemistry. A substance is heated in a crucible until it reaches a constant mass.
By measuring the mass of the sample before and after heating, a chemist can precisely determine the concentration of a component, such as the water content in a hydrate or the mineral content in food.
Ashing Samples
To determine the inorganic mineral content of an organic sample (like food, soil, or plastic), the sample is placed in a crucible and heated in a furnace.
The intense heat combusts all the organic material, leaving behind only a small amount of non-combustible ash, which can then be weighed or analyzed further.
Melting and Fusing Substances
Crucibles are essential for melting metals to create alloys or for preparing samples for certain types of analysis, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF).
In this process, a sample may be mixed with a flux (like lithium borate) in a crucible and heated until they melt and fuse into a homogenous glass disc, which is then analyzed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material Choice Matters
Not all crucibles are created equal. The choice of material is a critical decision based on the required temperature, the chemical nature of the sample, and budget.
Porcelain Crucibles
These are the most common and affordable crucibles in a general chemistry lab. They are excellent for many applications, like determining volatile compounds, but can crack if heated or cooled too quickly (thermal shock).
Platinum Crucibles
For the highest-accuracy work, platinum is the material of choice. It has excellent high-temperature performance and is extremely non-reactive. However, its high cost restricts its use to specialized analytical applications.
Specialized Crucibles
For unique challenges, other materials are used. Alumina crucibles offer higher temperature resistance than porcelain. Tantalum crucibles are used for melting superalloys and serve as a substitute for platinum in some applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible is essential for a successful experiment. Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your procedure.
- If your primary focus is routine quantitative analysis (like ashing food): A standard porcelain crucible is typically the most cost-effective and suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity analysis or working with corrosive fluxes: An expensive but highly inert platinum crucible is necessary to avoid sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is melting highly reactive or very high-temperature metals: A specialized crucible made of a material like alumina, zirconium oxide, or tantalum is required.
Ultimately, the crucible enables chemists to perform reactions and analyze materials under conditions far beyond the limits of standard laboratory glassware.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Function | Key Applications | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Withstand Extreme Temperatures | Melting metals, calcination | Porcelain, Alumina, Platinum |
| Ensure Chemical Purity | Gravimetric analysis, high-purity synthesis | Platinum, Quartz |
| Drive Specific Reactions | Ashing samples, fusing for XRF | Porcelain, Alumina, Tantalum |
Need the right crucible for your specific lab application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles made from porcelain, alumina, platinum, and more. Our experts can help you select the perfect vessel to ensure chemical purity and withstand the extreme temperatures your work demands. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and enhance your analytical results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 synthesis? Ensure Purity in NVPF Production
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- What are the advantages of high-purity alumina crucibles for molten ZnNaK//Cl salts? Ensure Experimental Purity



















