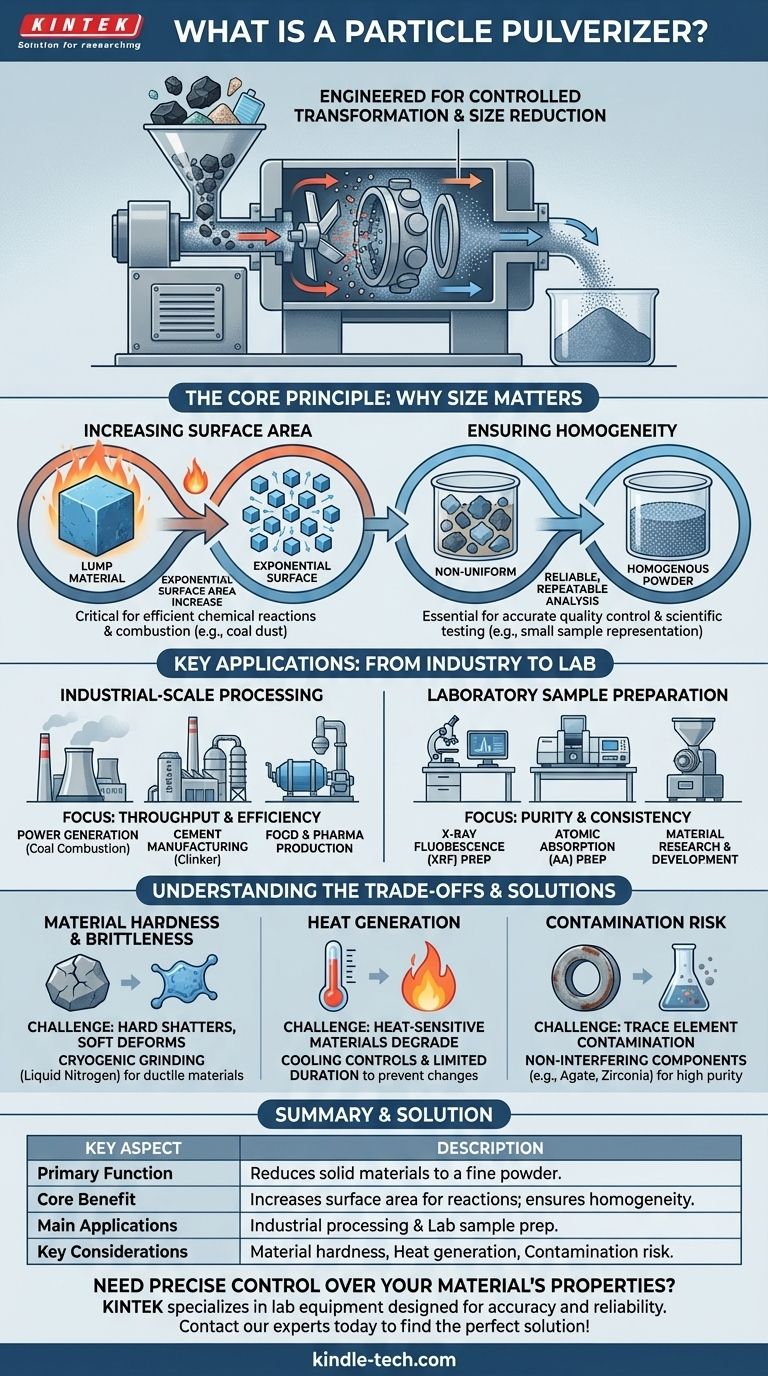
At its core, a particle pulverizer is a mechanical device engineered for size reduction. Its primary function is to take solid materials—ranging from coal and minerals to plastics and pharmaceuticals—and grind them into a fine powder or dust. This process is not about destruction, but controlled transformation to achieve specific material properties.
The true purpose of a pulverizer goes beyond simple grinding. By dramatically increasing a material's surface area and ensuring its uniformity, pulverizers are critical for enabling efficient chemical reactions, accurate scientific analysis, and the creation of materials with consistent, reliable properties.

The Core Principle: Why Particle Size Matters
Understanding the function of a pulverizer requires grasping why smaller particles are often more useful than larger ones. The benefits are rooted in fundamental physics and chemistry.
Increasing Surface Area
When you break a solid object into smaller pieces, you expose new surfaces. Pulverizing a material into a fine powder increases its total surface area exponentially for the same amount of mass.
This is critical for any process involving a chemical reaction. For example, a lump of coal burns slowly, but pulverized coal dust combusts almost instantly and completely, maximizing energy release in a power plant.
Ensuring Homogeneity
In quality control and scientific research, the goal is to analyze a small sample that accurately represents a much larger batch. A raw, chunky material is inherently non-uniform.
Pulverizing and mixing the material creates a homogenous powder. A small scoop taken from this powder will have the exact same composition as the rest of the batch, ensuring that analytical test results are reliable and repeatable.
Key Applications: From Industry to Laboratory
Pulverizers are used across countless fields, but their application generally falls into two categories: large-scale industrial processing and small-scale analytical preparation.
Industrial-Scale Processing
In manufacturing and production, the focus is on throughput and efficiency. Pulverizer mills are massive, powerful machines integrated into continuous production lines.
Key examples include power generation, where coal is pulverized for efficient combustion, and cement manufacturing, where "clinker" is ground into the fine powder we recognize as cement. This principle also applies to food production (milling grain) and pharmaceuticals (creating powders for uniform pill dosages).
Laboratory Sample Preparation
In a laboratory setting, the pulverizer is a smaller, high-precision instrument. Here, the priority is not volume but purity and consistency for accurate testing.
Scientists use lab pulverizers to prepare samples for analyses like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or atomic absorption (AA). A rock sample from a mine, a piece of plastic from a new product, or a soil sample must be ground into a uniform powder before its chemical makeup can be accurately measured.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, the pulverization process is not without its challenges. An expert must consider several factors to achieve the desired outcome without compromising the material itself.
Material Hardness and Brittleness
The effectiveness of a pulverizer depends heavily on the material's properties. Hard, brittle materials like minerals or ceramics shatter easily and are ideal for grinding.
However, soft or ductile materials can deform or smear rather than break. This may require specialized equipment or techniques like cryogenic grinding, where the material is frozen with liquid nitrogen to make it brittle before being pulverized.
Heat Generation
The mechanical energy and friction involved in grinding generate significant heat. For heat-sensitive materials, such as certain polymers or organic compounds, this can be a major problem.
Excessive heat can cause the material to melt, degrade, or undergo unwanted chemical changes, altering the very properties you wish to measure or create. This often requires controls for cooling or limiting the grinding duration.
Contamination Risk
The grinding components of a pulverizer (such as rings, pucks, or balls) are subject to wear. This wear can introduce trace amounts of the grinding material itself into the sample.
For routine industrial processes, this may be negligible. But for high-purity research or trace element analysis, this contamination can ruin results. In these cases, choosing a pulverizer with grinding components made from a non-interfering material, like agate or zirconia, is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection and application of a pulverizer must be directly aligned with your end goal. The "best" approach is entirely context-dependent.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production: Your goal is high throughput and operational efficiency, requiring industrial-grade mills designed for continuous processing of a specific material.
- If your primary focus is analytical accuracy: Your goal is sample homogeneity and purity, demanding laboratory-scale pulverizers with non-contaminating grinding media and precise controls.
- If your primary focus is material development: You must consider how the entire grinding process—including heat input and final particle shape—will influence the performance characteristics of your end product.
Ultimately, a particle pulverizer is a fundamental tool for precisely controlling the physical form of solid matter to meet exacting technical and scientific demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces solid materials to a fine powder or dust. |
| Core Benefit | Increases surface area for reactions and ensures sample homogeneity. |
| Main Applications | Industrial processing (cement, power) & lab sample prep (XRF, AA). |
| Key Considerations | Material hardness, heat generation, and risk of contamination. |
Need precise control over your material's properties? Whether your goal is high-volume industrial processing or pure, contamination-free samples for critical R&D, the right pulverizer is key. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with pulverizers designed for accuracy and reliability. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- How do stainless steel grinding jars and balls contribute to mechanical alloying? Optimize HEA Powder Synthesis
- Why use zirconia ball milling jars for SiC/ZTA composite powders? Ensure High Purity & Efficient Particle Refinement
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results



















