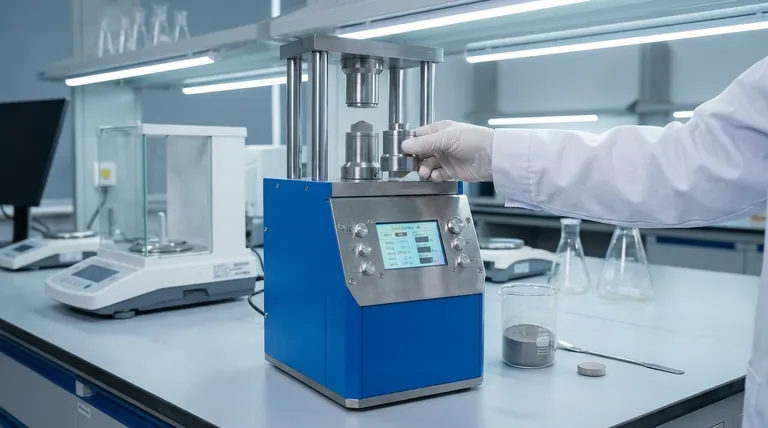
In essence, a pellet mill—often referred to as a pellet press in laboratory or research contexts—is a specialized machine designed to compress loose powder into a solid, dense, and uniform disc or pellet. This transformation is fundamental for a wide range of analytical, research, and manufacturing processes where the form and consistency of the material are critical for achieving accurate results or desired performance characteristics.
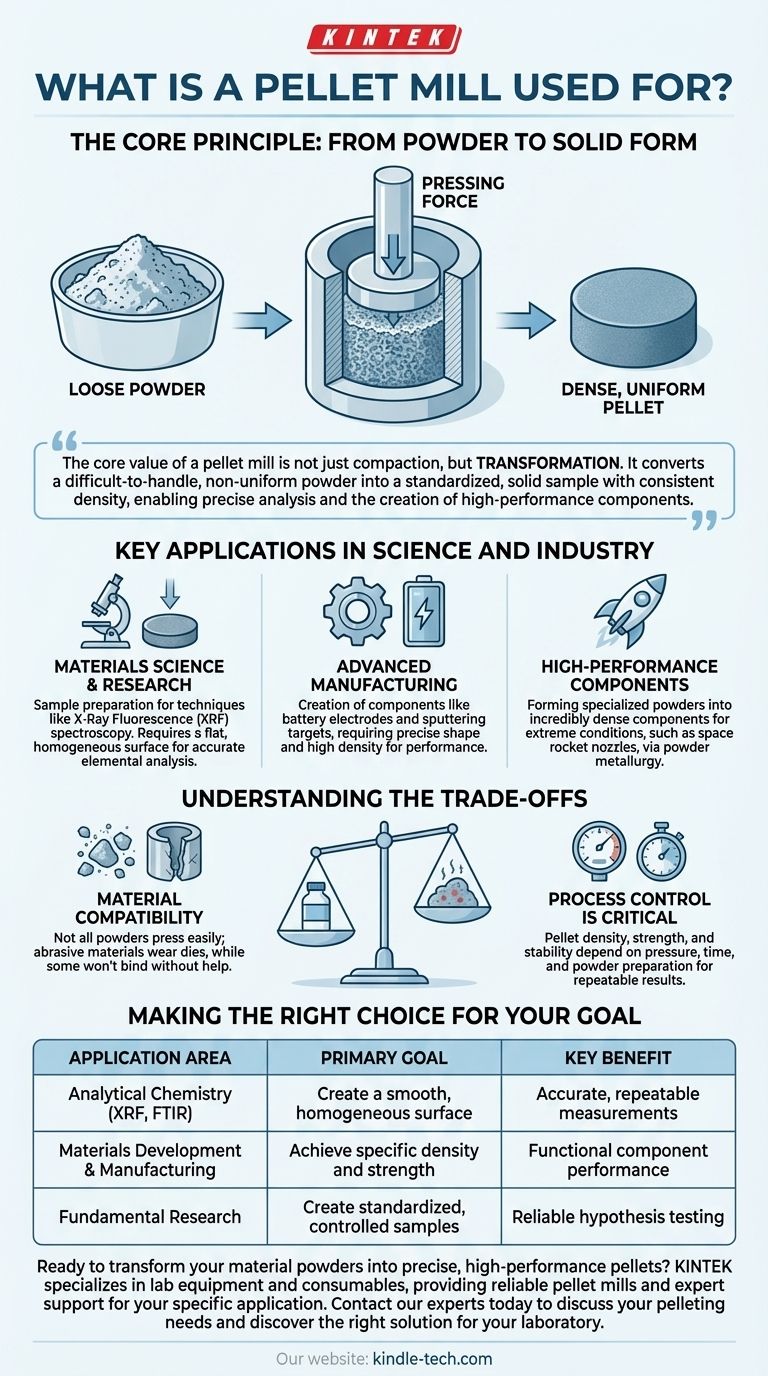
The core value of a pellet mill is not just compaction, but transformation. It converts a difficult-to-handle, non-uniform powder into a standardized, solid sample with consistent density, enabling precise analysis and the creation of high-performance components.

The Core Principle: From Powder to Solid Form
A pellet mill operates on a straightforward yet powerful mechanical principle. Understanding this is key to appreciating its applications.
How a Pellet Mill Works
The process involves placing a measured amount of powder into a cylindrical die. A plunger, or press, then applies immense force, often measured in tons, to compact the powder particles together. This extreme pressure eliminates voids and forces the particles to bind, forming a solid, stable pellet.
The Goal: Density and Uniformity
Loose powder is inherently inconsistent. Its density can vary, it can be difficult to measure accurately by volume, and its irregular surface makes many forms of analysis impossible.
By creating a solid pellet, you achieve a sample that is dense, uniform, and easy to handle. This consistency is the primary reason for using a pellet mill.
Key Applications in Science and Industry
The ability to create standardized solid samples from powders unlocks capabilities across numerous advanced fields.
Materials Science and Research
In university labs and R&D centers, pellet presses are workhorses for sample preparation. For techniques like X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, a flat, homogeneous surface is required for accurate elemental analysis. Pressing a powder into a pellet provides this ideal surface.
Advanced Manufacturing
The performance of many modern components depends on material density and uniformity. For example, the creation of battery electrodes or sputtering targets (used to deposit thin films in semiconductor manufacturing) requires raw materials to be formed into a specific, highly controlled shape and density.
High-Performance Components
The reference to materials for space rocket nozzles highlights an extreme application. Specialized ceramic or metallic powders are pressed into incredibly dense forms to create components that must withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. The pellet press is the first step in this fabrication process, known as powder metallurgy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the pelleting process is not a universal solution and requires careful consideration.
Material Compatibility
Not all powders can be easily pressed. Highly abrasive materials can cause excessive wear on the die set, while other powders may not bind well under pressure alone and will crumble once the force is removed.
The Role of Binders
To solve binding issues, a small amount of a binding agent is often mixed with the powder. However, this introduces a potential contaminant. For high-purity analysis, the presence of a binder can interfere with results, creating a trade-off between pellet stability and analytical purity.
Process Control is Critical
The final properties of the pellet—its density, strength, and stability—are directly dependent on factors like the amount of pressure applied, the duration of the press, and the initial preparation of the powder. Achieving repeatable results requires a controlled and well-documented process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your reason for using a pellet mill will determine how you approach the process.
- If your primary focus is analytical chemistry (e.g., XRF, FTIR): Your goal is to create a sample with a smooth, homogeneous, and representative surface for repeatable measurements.
- If your primary focus is materials development or manufacturing: Your goal is to achieve specific material properties like density, porosity, and mechanical strength for a functional component.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Your goal is to create highly controlled, standardized samples to reliably test a scientific hypothesis by eliminating variables related to sample form.
Ultimately, a pellet mill is a critical tool for giving physical form and functional integrity to the potential held within a raw powder.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Goal of Pelletizing | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Analytical Chemistry (XRF, FTIR) | Create a smooth, homogeneous surface | Accurate, repeatable measurements |
| Materials Development & Manufacturing | Achieve specific density and strength | Functional component performance |
| Fundamental Research | Create standardized, controlled samples | Reliable hypothesis testing |
Ready to transform your material powders into precise, high-performance pellets?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable pellet mills and expert support for your specific application—whether it's for analytical chemistry, materials development, or advanced research. Our solutions help you achieve the density, uniformity, and repeatability critical to your work's success.
Contact our experts today to discuss your pelleting needs and discover the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What size are extrusion pellets? Mastering Pellet Geometry for Optimal Extrusion Performance
- What is the mechanism by which a laboratory hydraulic press facilitates the sintering of TiB2-SiC? Optimize Density
- What are the specific conditions and steps in HPHT diamond growth? Master the Art of Synthetic Diamond Production
- What is a KBr pellet? A Guide to Preparing Solid Samples for IR Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed pellet technique in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to High-Quality Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the function of a hydraulic forging press? Shape Metal with Unmatched Force and Control
- What will you do to reduce prevent excessive heating of oil in a hydraulic system? A Guide to Boosting Efficiency & Reliability
- Significance of High Pressure in Lab Hydraulic Press for 304L Steel Green Compacts: Achieve 750 MPa Densification



















