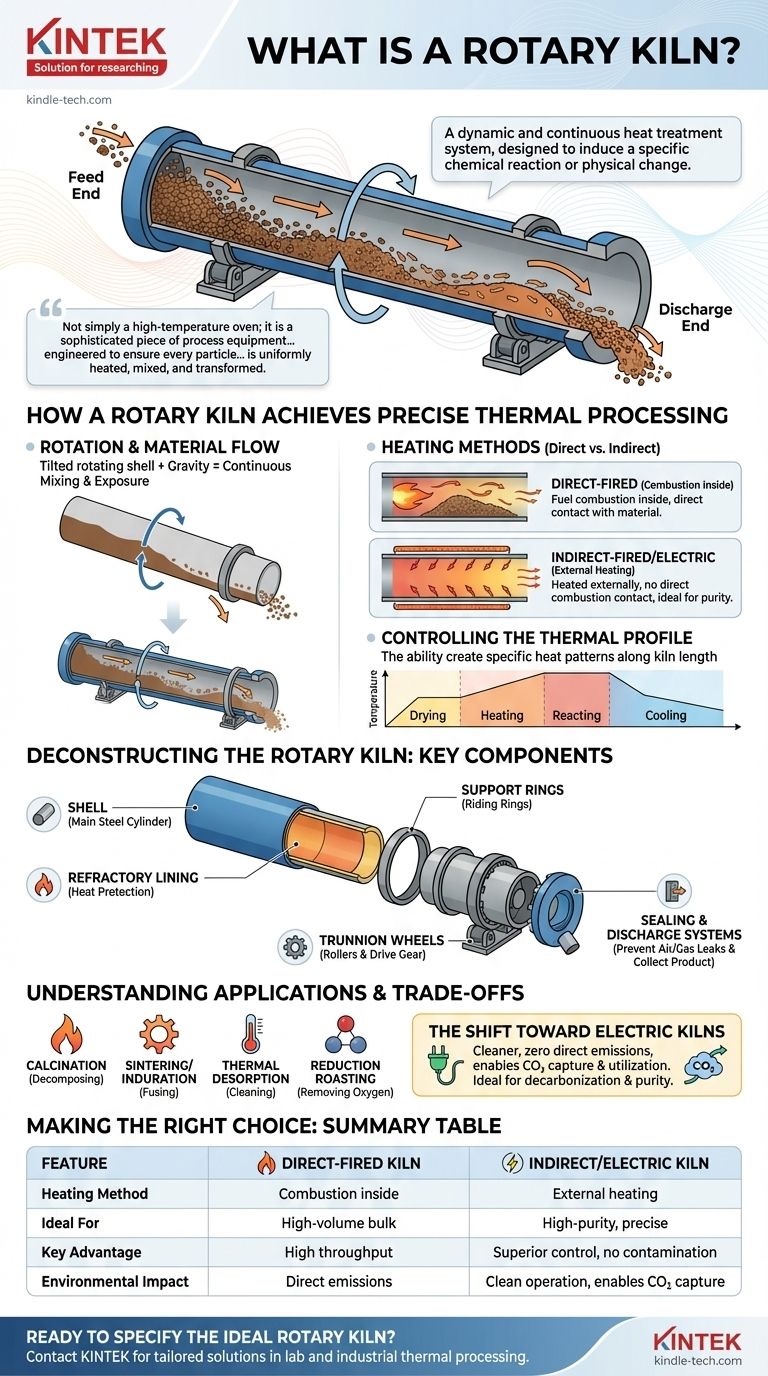
At its core, a rotary kiln is a large, rotating cylindrical furnace used for processing solid materials at extremely high temperatures. It functions as a dynamic and continuous heat treatment system, designed to induce a specific chemical reaction or physical change in the material being processed as it tumbles through the heated chamber.
A rotary kiln is not simply a high-temperature oven; it is a sophisticated piece of process equipment. Its defining feature—the rotation of a tilted cylinder—is engineered to ensure every particle of material is uniformly heated, mixed, and transformed as it moves from inlet to outlet.
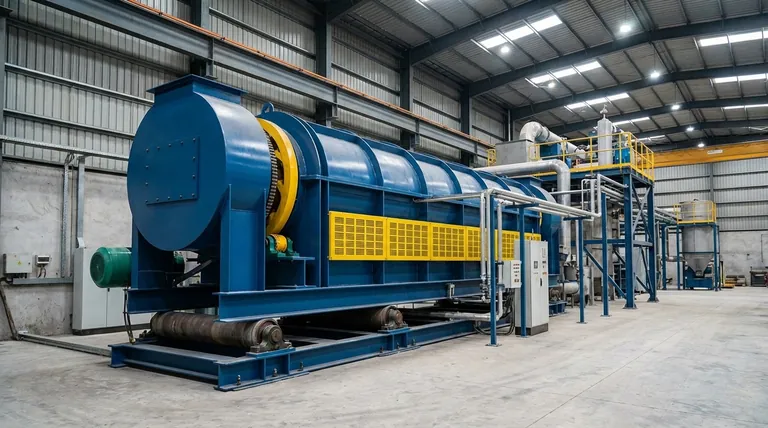

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Precise Thermal Processing
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln comes from its ability to combine material transport with controlled heat application. This dynamic process is what separates it from a static furnace.
The Principle of Rotation and Material Flow
A rotary kiln is essentially a long cylinder, often called a shell, that is mounted on a slight angle to the horizontal.
As the kiln rotates slowly on its axis, material fed into the higher end tumbles and mixes, gradually moving down toward the discharge end due to gravity. This continuous tumbling exposes the entire surface area of the material bed to the heat source.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating Methods
Heat can be applied in two primary ways. Direct-fired kilns combust a fuel source (like natural gas or coal) inside the kiln, where the flame and hot gases are in direct contact with the material.
Indirect-fired kilns heat the material from the outside. The shell is heated externally, and this heat radiates inward to the material. Electric rotary kilns, which use resistance heating elements, are a common example of an indirect heating design.
Controlling the Thermal Profile
A key advantage is the ability to create a specific heat pattern along the length of the kiln. This allows for precise stages of processing, such as drying, heating, and finally reacting or calcining at a peak temperature.
Features like 360° heater placement and integrated air cooling systems allow for highly stable and uniform temperature control, which is critical for producing a consistent final product.
Deconstructing the Rotary Kiln: Key Components
While designs are customized for specific materials, all rotary kilns share a set of fundamental components that work together.
The Shell and Refractory Lining
The shell is the main steel cylinder that forms the body of the kiln.
Inside, it is protected from extreme temperatures by a refractory lining made of specialized brick or castable material. This lining is crucial for thermal efficiency and protecting the steel shell from damage.
The Support and Drive System
The massive weight of the kiln is supported by two or more steel riding rings (or support tyres) that are attached to the shell.
These rings rest on trunnion wheels (rollers), which allow the kiln to rotate smoothly. A large gear and motor assembly, known as the drive gear, provides the rotational force. Thrust rollers prevent the kiln from sliding downhill off its supports.
Sealing and Discharge Systems
Effective seals at both the feed and discharge ends are critical. They prevent cold air from entering the kiln (which would disrupt the thermal profile) and stop valuable product or hot gases from escaping.
At the end of the kiln, the processed material exits through a discharge breeching into a designated product discharge area for cooling and collection.
Understanding the Applications and Trade-offs
Rotary kilns are versatile but must be properly specified for the task at hand. Their design impacts efficiency, product purity, and environmental footprint.
Common Industrial Applications
The primary function of a rotary kiln is to induce a change through heat. Common processes include:
- Calcination: Decomposing a material, like converting limestone into lime.
- Sintering/Induration: Causing fine particles to fuse together into a solid mass.
- Thermal Desorption: Removing contaminants from soil or waste.
- Reduction Roasting: Removing oxygen from metal oxides.
The Shift Toward Electric Kilns
Traditionally, kilns have relied on fossil fuels. However, electric rotary kilns offer a clean and highly efficient alternative.
They eliminate direct emissions from combustion and allow for the capture of pure CO2 released from the process material itself, which can then be sold or reused. This is a significant advantage for industries focused on decarbonization.
Considerations for Process Purity
In applications like processing specialty chemicals or metal oxides, preventing contamination is paramount. Indirect heating methods are often preferred for this reason.
Furthermore, kiln internals can be customized with specific materials to suppress metal contamination from the equipment itself, ensuring the final product meets stringent purity standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal kiln design depends entirely on your process requirements, from raw material characteristics to end-product specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk material processing (e.g., cement): A large, robust, direct-fired kiln is often the most cost-effective solution for its sheer throughput capacity.
- If your primary focus is product purity and precise temperature control (e.g., specialty chemicals): An indirect or electric rotary kiln provides superior control and eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is environmental performance and decarbonization: An electric rotary kiln is the definitive choice, enabling cleaner processing and creating opportunities for CO2 capture and utilization.
Ultimately, a well-specified rotary kiln transforms raw materials into valuable products with unparalleled thermal efficiency and control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct-Fired Kiln | Indirect/Electric Kiln |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Combustion inside kiln | External heating (e.g., electric elements) |
| Ideal For | High-volume bulk processing (e.g., cement) | High-purity products, precise control |
| Key Advantage | High throughput capacity | No combustion contamination, superior control |
| Environmental Impact | Direct emissions from fuel | Clean operation, enables CO2 capture |
Ready to specify the ideal rotary kiln for your process? Whether your priority is high-volume throughput, extreme product purity, or decarbonization, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial thermal processing equipment is your solution. We provide tailored rotary kilns for calcination, sintering, and more. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product



















