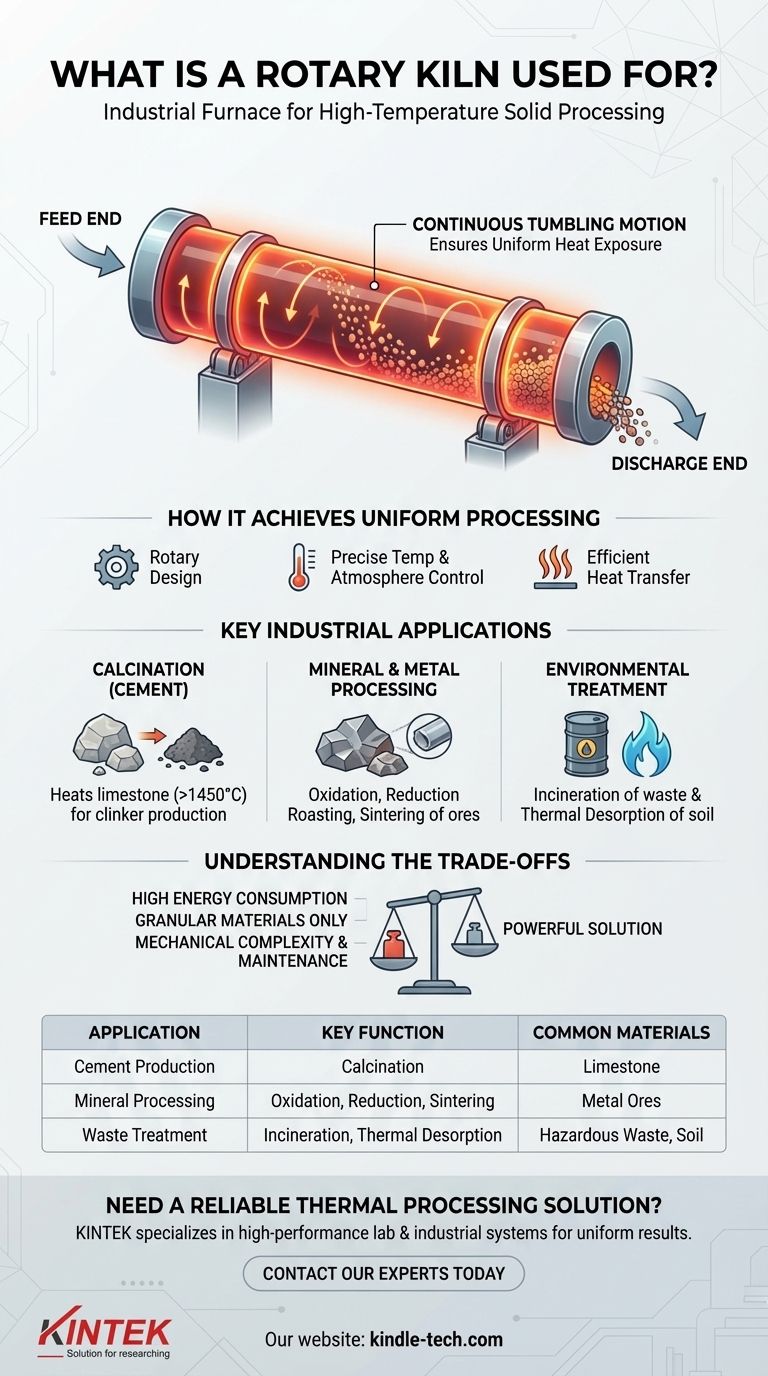
At its core, a rotary kiln is an industrial furnace used to process solid materials at extremely high temperatures. It functions as a versatile heat exchanger designed to induce a specific chemical reaction or physical change, making it essential for manufacturing products like cement, processing minerals, and treating waste.
The true value of a rotary kiln is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its unique rotating design. This continuous tumbling motion ensures every particle of material is heated uniformly, which is the critical factor for achieving consistent and controlled thermal transformation on an industrial scale.
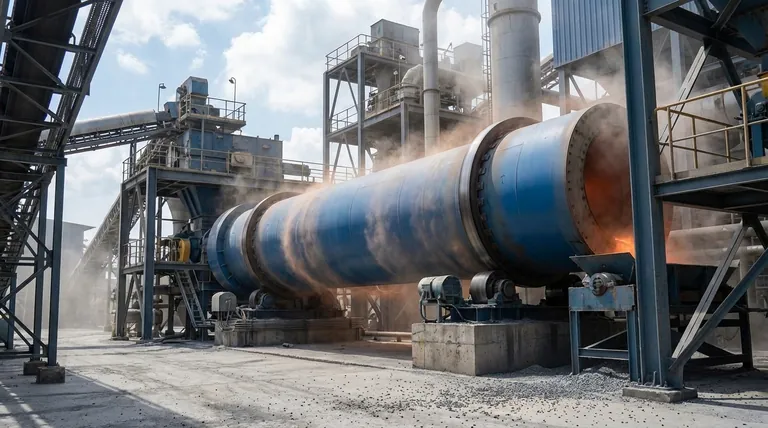

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Uniform Processing
The effectiveness of a rotary kiln comes from its fundamental design: a long, rotating cylinder mounted on a slight incline. This simple mechanical concept is the key to its widespread use.
The Core Principle: Tumbling and Heat Transfer
A rotary kiln is the heart of many thermal processing systems. As the cylinder rotates, the solid material inside is continuously lifted and cascaded down, a motion often described as "tumbling."
This action ensures the entire bed of material is constantly mixed. Unlike a static oven where the outer layers can scorch while the core remains under-processed, the kiln's tumbling guarantees uniform exposure to the heat source.
Precise Temperature and Atmosphere Control
The kiln's long body allows engineers to establish a precise temperature profile from the feed end to the discharge end. This means a material can be systematically dried, preheated, and then brought to its final reaction temperature all in a single pass.
Furthermore, specialized seals on either end allow for tight control over the internal atmosphere. This is crucial for carrying out specific chemical reactions, such as oxidation (using excess air) or reduction (in a low-oxygen environment).
Key Industrial Applications
The kiln's ability to deliver uniform heat to solids makes it indispensable across several major industries. Each application leverages the core principle of controlled, continuous processing.
Calcination: The Foundation of Cement
The most common use for rotary kilns is the calcination of limestone to produce clinker, the primary component of cement. This process requires heating limestone to over 1450°C (2640°F) to drive off carbon dioxide and trigger the necessary chemical changes. The kiln's efficiency at handling and uniformly heating huge volumes of material makes this possible.
Mineral and Metal Processing
Rotary kilns are used for a variety of high-temperature reactions involving ores and metal compounds.
- Oxidation: Creating metal oxides like zinc oxide or manganese oxide.
- Reduction Roasting: Removing oxygen from iron ores as a step in steelmaking.
- Sintering/Induration: Fusing fine mineral particles (like iron ore pellets) into strong, coarse lumps by heating them just below their melting point.
Environmental and Waste Treatment
The kiln's high temperatures and tumbling action make it an effective tool for destroying hazardous materials and recovering resources.
- Incineration: The constant mixing ensures the complete combustion of organic waste.
- Thermal Desorption: Contaminated soils are heated to vaporize and remove volatile pollutants like oil or mercury, which are then collected and treated separately.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary kiln is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining temperatures often exceeding 1000°C is an extremely energy-intensive process. Fuel costs represent a significant portion of the operational budget for any kiln system.
Material Suitability
Rotary kilns are designed for granular or powdered solid materials. They are not suitable for liquids or materials that become sticky and would adhere to the kiln walls, preventing the critical tumbling action.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
A rotary kiln is a massive piece of rotating heavy machinery. The drive systems, support rollers, refractory lining, and air seals all require regular inspection and significant maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is uniformly processing large volumes of solid, granular material: The rotary kiln is the definitive industrial standard for this task.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific chemical change like calcination or reduction: The kiln's ability to control both the temperature profile and internal atmosphere is its key advantage.
- If your primary focus is treating small batches or non-granular items: A static batch furnace or conveyor oven may be a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's genius lies in its simple mechanical principle: using rotation to master the complex challenge of uniform high-temperature material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Cement Production | Calcination (heating to drive off CO₂) | Limestone |
| Mineral Processing | Oxidation, Reduction Roasting, Sintering | Metal Ores (e.g., Iron, Zinc) |
| Waste Treatment | Incineration, Thermal Desorption | Hazardous Waste, Contaminated Soil |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and industrial-scale systems. Whether you are developing a new process or scaling up production, our expertise in thermal processing can help you achieve uniform and consistent results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application in cement, minerals, or waste treatment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















