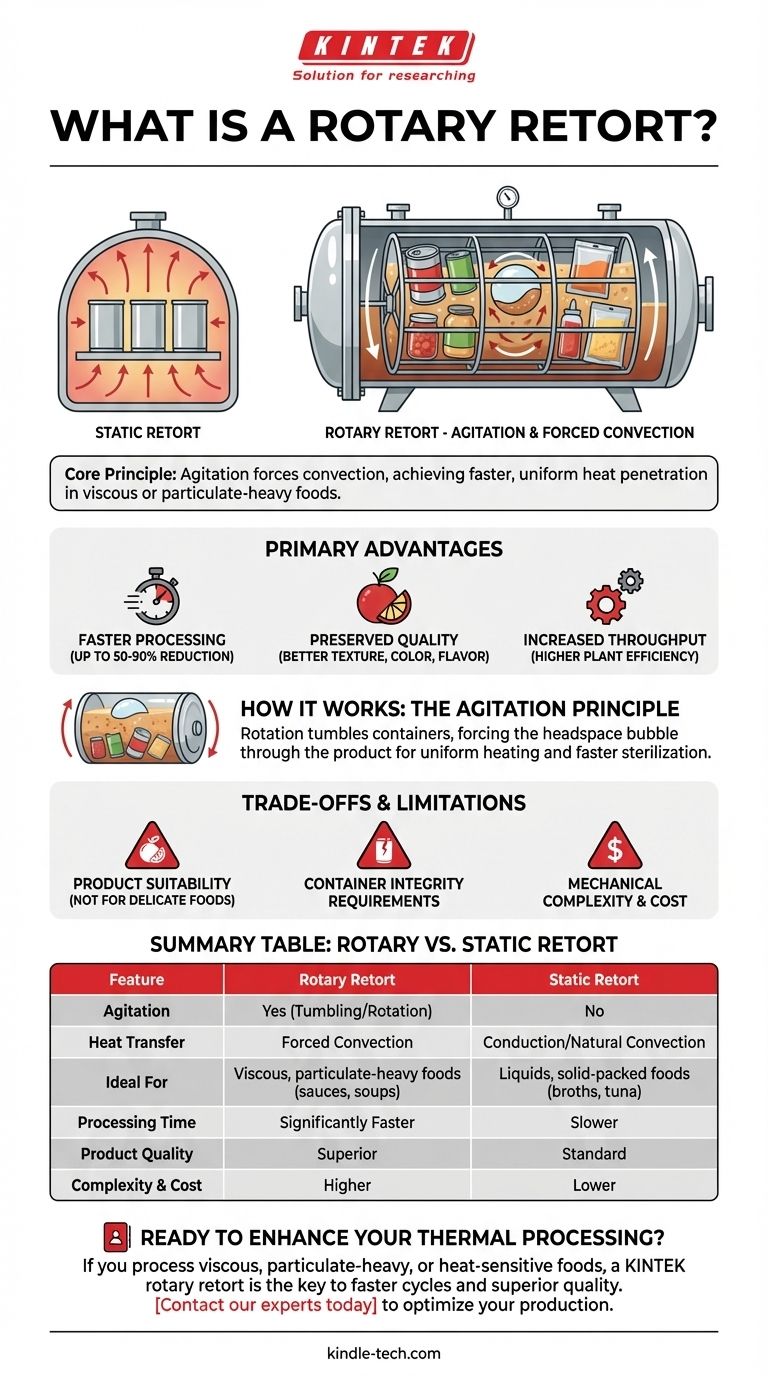
At its core, a rotary retort is a sterilization vessel used in the food and beverage industry that agitates or tumbles containers during the thermal processing cycle. Unlike a standard static retort where containers remain still, this rotation is specifically designed to stir the contents inside the sealed package, dramatically improving the efficiency and quality of the heating process for certain types of products.
The central purpose of a rotary retort is to leverage mechanical agitation to force convection inside the container. This achieves faster, more uniform heat penetration in viscous or particulate-heavy foods, resulting in higher product quality and significantly reduced processing times compared to static methods.

How Rotary Retorts Work: The Principle of Agitation
The key difference between static and rotary retorts lies in one fundamental action: movement. This movement fundamentally changes how heat is transferred to the coldest point of the product.
The Basic Mechanism
A rotary retort is typically a horizontal, pressurized vessel. Inside, a large, cage-like drum holds the containers—whether they are cans, jars, or pouches. This entire inner drum rotates along the retort's long axis, driven by an external motor, tumbling the containers end-over-end.
Forcing Convection
In a static retort, heat moves from the outside of the container inward primarily through slow conduction (for solids) or natural convection (for liquids). For thick products like condensed soup or pet food, this is a very slow process.
Rotation changes everything. As the container tumbles, the headspace bubble (the small pocket of air or gas at the top) is forced to travel through the product. This bubble acts like a built-in mixing paddle, creating forced convection that aggressively stirs the contents.
The Impact on Heat Transfer
This constant mixing ensures that the product is heated evenly and much more rapidly. It prevents scorching or overcooking of the product near the container walls while ensuring the geometric center—the "cold spot"—reaches the target sterilization temperature much faster.
The Primary Advantage: Faster, Better Processing
The simple act of rotation delivers significant benefits in both product quality and operational efficiency, especially for foods that are difficult to process statically.
Overcoming Slow Heat Transfer
For viscous products like sauces, purees, or foods with particulates like chunky soups, the difference is night and day. Forced convection can reduce processing times by as much as 50-90% compared to a static process.
Preserving Product Quality
Shorter exposure to high temperatures is the key to quality preservation. By reducing the cook time, a rotary retort helps maintain better texture, color, flavor, and nutrient retention. The result is a final product that is far superior to one that has been held at high temperatures for an extended period.
Increasing Throughput
Faster cycle times directly translate to higher plant throughput. More batches can be processed in the same amount of time using the same equipment footprint, improving overall operational efficiency and lowering the per-unit cost of production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a rotary retort is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is highly dependent on the product, and its complexity introduces unique considerations.
Product Suitability is Critical
The primary limitation is the product itself. Delicate products that can be damaged by mechanical agitation, such as soft fruits, layered desserts, or whole fish fillets, are poor candidates for rotary processing. The agitation would destroy the product's structure.
Container Integrity Requirements
The containers must be robust enough to withstand the continuous tumbling and mechanical stress of the process. While modern pouches and cans are designed for this, it is a critical factor in packaging selection and process validation.
Mechanical Complexity and Cost
Rotary retorts are mechanically more complex than their static counterparts. They have motors, drive systems, and large rotating seals that require more maintenance and a higher initial capital investment. The added complexity introduces more potential points of failure that must be managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Ultimately, the decision to use a rotary retort must be driven by the specific characteristics of your product and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is on low-viscosity liquids (like broths) or solid-packed products (like tuna in brine): A simpler, more cost-effective static retort is often the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is preserving the quality of viscous, heat-sensitive, or particulate-heavy foods (like premium soups or sauces): A rotary retort is the superior technology for achieving uniform heating and shorter, quality-preserving cycle times.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput for a suitable product: The significant reduction in cycle time offered by a rotary retort can provide a compelling return on the higher initial investment.
Understanding the principle of forced convection is the key to deciding when a rotary retort is not just an option, but a necessity for superior product quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rotary Retort | Static Retort |
|---|---|---|
| Agitation | Yes (Tumbling/Rotation) | No |
| Heat Transfer | Forced Convection | Conduction/Natural Convection |
| Ideal For | Viscous, particulate-heavy foods (sauces, soups) | Liquids, solid-packed foods (broths, tuna) |
| Processing Time | Significantly Faster (up to 50-90% reduction) | Slower |
| Product Quality | Superior (better texture, color, nutrient retention) | Standard |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to enhance your thermal processing efficiency and product quality?
If you process viscous, particulate-heavy, or heat-sensitive foods like sauces, soups, or pet food, a rotary retort from KINTEK is the key to achieving faster cycle times and superior product quality. Our expertise in lab and pilot-scale equipment can help you validate this technology for your specific needs.
Contact our sterilization experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary retort can optimize your production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory autoclave play in the separation of lignin? High-Purity Extraction for Biomass Research
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding



















