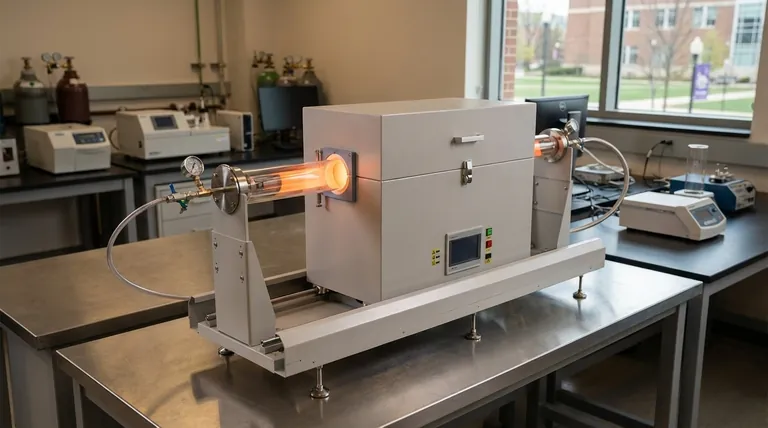
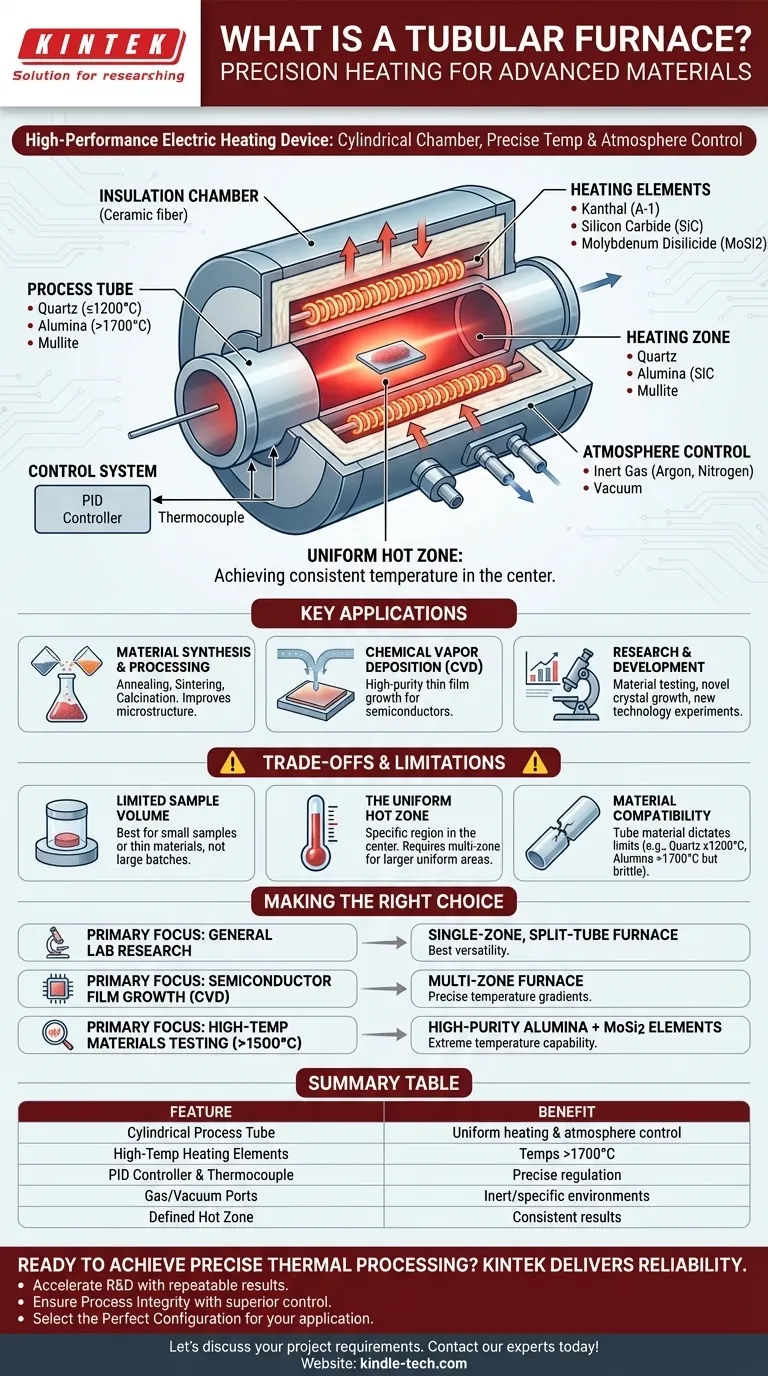
In essence, a tubular furnace is a high-performance electric heating device distinguished by its cylindrical chamber, often called a process tube. It is engineered to heat small samples or substrates to precise and often very high temperatures within a tightly controlled atmospheric environment. This makes it a cornerstone piece of equipment for materials science, research, and specialized manufacturing processes.
The defining feature of a tubular furnace is its cylindrical process tube, which enables exceptional temperature uniformity and atmosphere management. This precise control makes it an indispensable tool for developing and processing advanced materials in laboratory and industrial settings.

How a Tubular Furnace Works: The Core Components
A tubular furnace's design is straightforward but highly effective. It integrates several key components to create a stable, high-temperature processing environment.
The Process Tube
This is the central chamber where the material sample is placed. Tubes are typically made from materials like quartz, alumina, or mullite, chosen based on the required maximum temperature and chemical resistance.
The Heating Elements
Resistive heating elements, such as Kanthal (A-1), silicon carbide (SiC), or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), surround the process tube. When electricity passes through them, they generate the intense, uniform heat needed for processing.
The Insulation Chamber
To achieve high temperatures efficiently and ensure operator safety, the heating elements are encased in high-grade ceramic fiber insulation. This minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment, reducing energy consumption and keeping the furnace's external shell cool.
The Control System
A thermocouple is placed near the heating elements to measure the temperature accurately. This reading is fed into a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which modulates the power to the elements to maintain the desired temperature setpoint with extreme precision.
Atmosphere Control
Many applications require processing materials in the absence of oxygen or within a specific gas environment. Tube furnaces are easily sealed with end flanges that include ports for introducing inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or for creating a vacuum.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The ability to control both temperature and atmosphere with high precision makes tubular furnaces vital for a range of sophisticated applications.
Material Synthesis and Processing
They are commonly used for processes like annealing, which alters a material's microstructure to improve ductility, and sintering, which fuses powders into a solid mass. Calcination, a process of heating materials to drive off impurities, is another key use.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
In CVD, a substrate is heated inside the tube furnace while specific gases are introduced. The gases react and decompose on the hot substrate, depositing a high-purity thin film—a fundamental process in the semiconductor and coatings industries.
Research and Development
In university and corporate R&D labs, tube furnaces are essential workhorses. They are used to test the thermal properties of new materials, grow novel crystals, and conduct experiments that form the basis of new technologies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a tubular furnace is a specialized tool with specific constraints that are important to understand.
Limited Sample Volume
By their nature, tube furnaces are designed for smaller samples or for continuous processing of thin materials like wires or fibers. They are not suitable for large-batch heat treatment, where a box furnace would be more appropriate.
The Uniform Hot Zone
Perfectly uniform temperature is typically only achieved in a specific region in the center of the tube, known as the "hot zone." The length of this zone is a critical specification. For applications needing a longer uniform zone or a specific temperature gradient, more complex and expensive multi-zone furnaces are required.
Material Compatibility
The process tube material dictates the furnace's operational limits. Quartz is cost-effective and excellent for viewing the sample but is generally limited to ~1200°C. High-purity alumina tubes can reach temperatures above 1700°C but are opaque and more brittle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct configuration depends entirely on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is general lab research: A single-zone, split-tube furnace offers the best versatility for testing a wide variety of materials and processes.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor film growth (CVD): A multi-zone furnace is non-negotiable for the precise temperature gradient control this process demands.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials testing (>1500°C): You must select a furnace with high-purity alumina components and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements.
Ultimately, understanding the design and capabilities of a tubular furnace empowers you to precisely control the thermal processing environment for your specific material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Process Tube | Enables uniform heating and excellent atmosphere control |
| High-Temperature Heating Elements | Capable of reaching temperatures exceeding 1700°C |
| PID Controller & Thermocouple | Delivers precise and stable temperature regulation |
| Gas/Vacuum Ports | Allows processing in inert or specific gas environments |
| Defined Hot Zone | Ensures consistent results within a uniform temperature area |
Ready to Achieve Precise Thermal Processing?
KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment for your specific needs. Whether you are developing new materials, conducting CVD, or performing high-temperature research, our tubular furnaces are engineered for reliability and precision.
We help you:
- Accelerate R&D with consistent, repeatable results.
- Ensure Process Integrity with superior temperature and atmosphere control.
- Select the Perfect Configuration for your application, from single-zone to multi-zone systems.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the ideal tubular furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature of alumina tube? Achieve Safe & Reliable High-Temp Processing
- What are the functions of a high-pressure horizontal tube furnace in 650 °C CO2 oxidation experiments?
- Why is a vacuum tube furnace required for HEA powder drying? Ensure Purity and Stress Relief in Alloy Production
- How is a laboratory tube furnace used to evaluate the resistance of rare earth catalysts to flue gas impurities?
- What are the advantages of a quartz tube micro-reactor for CO oxidation? Unlock Real-Time In-Situ Analysis
- What functions does a tube furnace perform for NASICON electrolyte pre-treatment? Ensure High-Phase Material Purity
- What can you use glass tubes for? Essential Applications in Labs, Industry, and Design
- What is the principle of a tube furnace? Master Controlled Heating for Precise Lab Results



















