In injection molding, a two-plate mold is the most fundamental and widely used mold design. It is constructed from two main sections, a cavity side (A-side) and a core side (B-side), which separate along a single plane known as the parting line. When the mold opens, the finished part and the plastic runner system used to fill it are ejected together.
The simplicity of the two-plate mold is its greatest strength, making it cost-effective and reliable. However, this same simplicity constrains where the plastic can be injected into the part, a critical trade-off that every designer must understand.
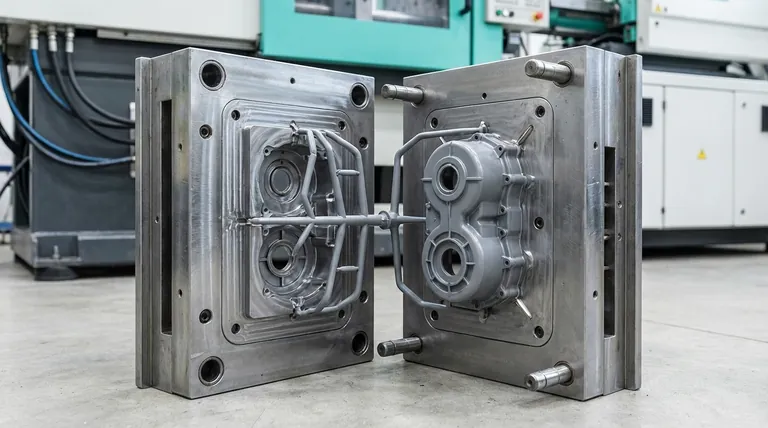
How a Two-Plate Mold Works: The Core Mechanics
A two-plate mold's operation is straightforward, built upon the interaction between its two primary halves.
The A-Side and B-Side
The mold is composed of two halves. The A-side, also known as the cavity plate, typically forms the exterior cosmetic surface of the part and is mounted on the stationary platen of the molding machine.
The B-side, or core plate, forms the internal geometry and houses the ejector system. It is mounted on the moving platen of the machine.
The Parting Line
The parting line is the single surface where the A-side and B-side meet when the mold is closed. The separation of the mold always occurs along this plane.
The Injection and Ejection Cycle
During operation, the two plates are clamped together. Molten plastic is injected through a sprue, flows through channels called runners, and enters the part cavity through a gate.
After the plastic cools and solidifies, the B-side pulls away from the A-side. Ejector pins within the B-side then push the finished part, with the runner system still attached, out of the mold.
The Role of the Runner and Gate
In a two-plate mold, the design of the runner and gate system is directly tied to the mold's fundamental structure.
Contained Within the Parting Line
The runner system must be carved into the surface of the parting line. This is a defining constraint of the two-plate design.
Because the runner is on the same plane as the part's edge, plastic must be injected from the side of the cavity.
Common Gating Options
This constraint leads to specific gate types, most commonly an edge gate. This type of gate feeds plastic into the side of the part, leaving a small blemish that must be trimmed after molding.
Manual Degating Requirement
Since the runner and the part are ejected as a single piece, they must be separated. This is often a manual secondary operation called degating, which adds to labor costs and cycle time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of a two-plate mold involves balancing cost, complexity, and part quality.
Advantage: Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
With fewer components and no complex mechanisms, two-plate molds are the least expensive to design and manufacture. This makes them ideal for lower-budget projects and simpler part geometries.
Advantage: Robustness and Reliability
Their simple construction means there are fewer things that can break. Two-plate molds are highly reliable, easy to maintain, and often allow for faster cycle times because of their direct, uncomplicated action.
Limitation: Restricted Gating Location
The inability to gate directly into the center of a part is the most significant drawback. This can affect how the plastic fills the mold, potentially causing cosmetic issues or structural weaknesses. It also means the gate mark is always on the part's perimeter.
Limitation: Runner Waste and Secondary Operations
The runner system is ejected with the part in every cycle, creating scrap material. While this plastic can sometimes be reground and reused, it represents a material cost. The required manual degating also adds a labor cost that can be significant in high-volume production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the correct mold type is a critical decision based on your specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing tool cost and complexity: The two-plate mold is the default and most effective choice, especially for parts where the gate mark location is not a cosmetic issue.
- If your primary focus is cosmetic appearance and flexible gate location: A two-plate mold is likely insufficient. You should investigate a three-plate or hot runner mold, which allows for gating directly onto the top of a part.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with minimal material waste: The runner scrap from a two-plate mold can add up, making a "runnerless" hot runner system more cost-effective over the life of the project.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs is the first step toward designing a mold that is perfectly aligned with your project's budget, quality, and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Simple, robust, and reliable | Restricted gating location (side-only) |
| Cost | Lower initial tooling cost | Runner waste and manual degating add cost |
| Application | Ideal for simpler parts and lower budgets | Not suitable for top-gated or high-cosmetic parts |
Ready to choose the right mold for your project? KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for your prototyping and production needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between two-plate, three-plate, and hot runner molds to ensure your project's success. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- Is it fitting the mould or mold? A Guide to Correct Spelling by Region
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture



















