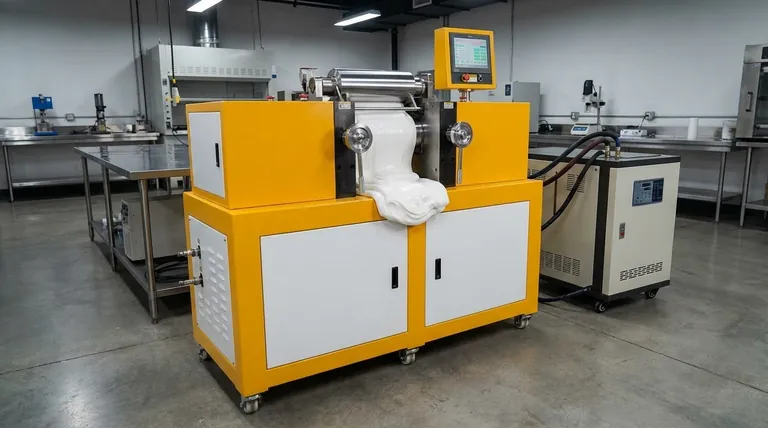
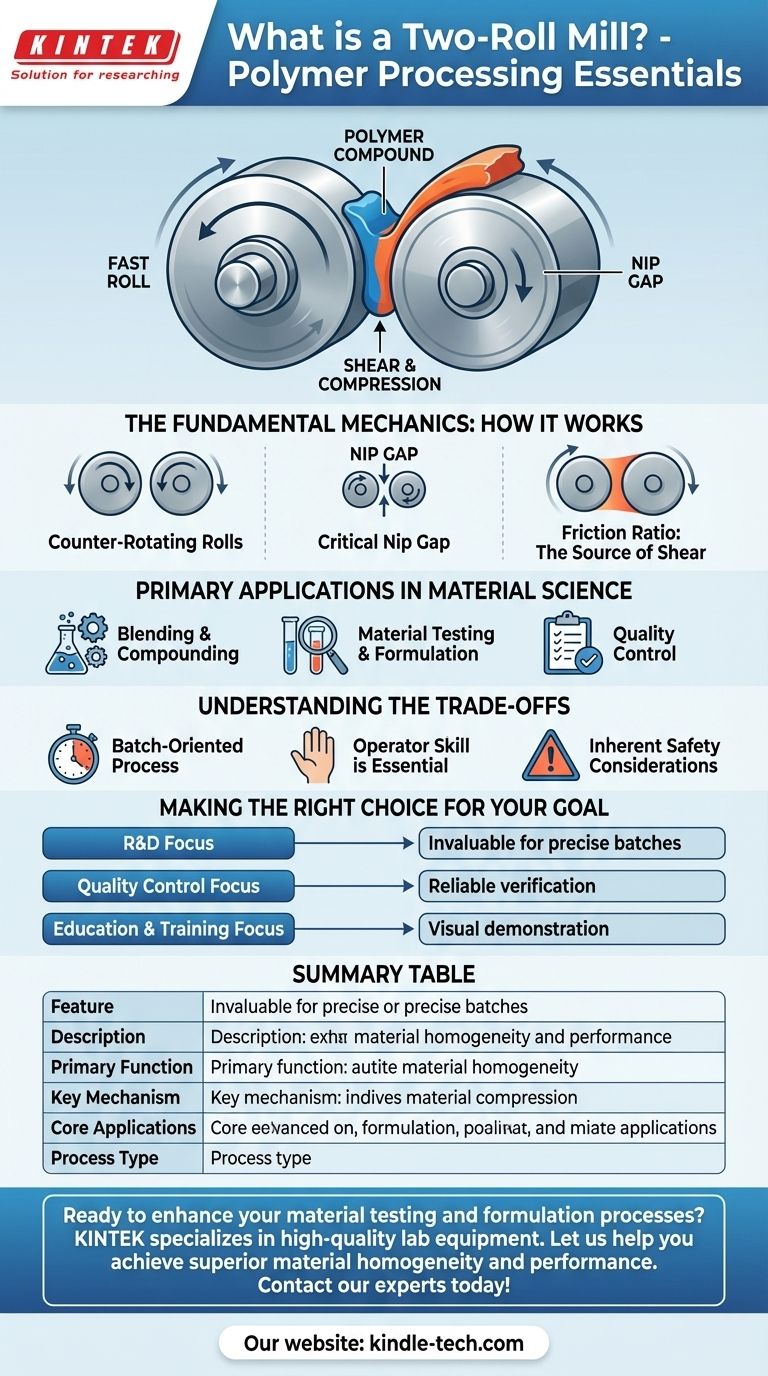
At its core, a two-roll mill is a fundamental piece of machinery used for the intensive mixing and shearing of polymers. It consists of two parallel, horizontal metal rolls that rotate towards each other at different speeds. The material, typically rubber or plastic, is repeatedly passed through the narrow, adjustable gap between these rolls, subjecting it to immense compression and shear forces that blend the components.
The two-roll mill is not just a simple mixer; it is a precision tool for manipulating the physical properties of materials. Its power lies in the controlled application of intense shear forces, generated by the differential speed of its rolls, to compound, refine, and test polymer-based formulations.

The Fundamental Mechanics: How It Works
A two-roll mill's operation is based on a few key mechanical principles that work in concert to process materials effectively. Understanding these principles is crucial to understanding its function.
The Counter-Rotating Rolls
The machine is built around two robust, hollow metal rolls positioned horizontally. They are designed to rotate inwards, pulling material down into the gap between them.
The Critical Nip Gap
The small space between the two rolls is known as the nip. This gap is adjustable, allowing an operator to control the amount of pressure and mechanical work applied to the material as it is forced through.
The Friction Ratio: The Source of Shear
The most critical element for mixing is the friction ratio. This refers to the speed difference between the two rolls. One roll turns faster than the other, which creates the intense shearing action necessary to blend polymers with additives, break down material structures, and ensure a homogenous mixture.
Primary Applications in Material Science
The two-roll mill is a versatile tool used across research, quality control, and small-scale production, primarily within the polymer industry.
Blending and Compounding
This is the mill's most common application. It is used to mix a base polymer, like rubber or PVC, with a variety of additives. These can include pigments for color sampling, fillers for strength, plasticizers for flexibility, and other agents to achieve desired properties.
Material Testing and Formulation
In laboratory settings, two-roll mills are indispensable for material development. Engineers can create and evaluate small batches of new plastic or rubber formulations before committing to expensive, large-scale production.
Quality Control
Manufacturers use these mills to test incoming raw materials or samples from a production run. This ensures the compound meets specific processing and performance standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the two-roll mill has specific characteristics that make it suitable for some tasks but less ideal for others.
A Batch-Oriented Process
The two-roll mill is fundamentally a batch processing machine. An operator works with a finite amount of material for a set period. This makes it perfect for labs and custom compounding but less efficient for high-volume, continuous manufacturing.
Operator Skill is Essential
Effective operation is highly dependent on the skill of the technician. The process of "cutting" the material off one roll and folding it back into the nip to ensure proper mixing is a manual art that requires significant training and experience.
Inherent Safety Considerations
The high-powered nip point where the rolls meet presents a significant safety hazard. Modern mills are equipped with extensive safety features, but operator awareness and adherence to procedure are paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a two-roll mill is the appropriate tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A two-roll mill is an invaluable and flexible tool for creating and testing small, precise batches of new material formulations.
- If your primary focus is quality control: It provides a reliable, hands-on method for sampling and verifying the physical properties of raw materials or finished compounds.
- If your primary focus is education or training: The mill offers a clear, visual demonstration of how shear, pressure, and temperature affect polymer behavior.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay of nip gap and friction ratio is the key to leveraging this foundational equipment for material innovation and control.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Intensive mixing and shearing of polymers (e.g., rubber, plastic) |
| Key Mechanism | Counter-rotating rolls with a differential speed (friction ratio) |
| Core Applications | R&D, material testing, quality control, and small-batch production |
| Process Type | Batch processing |
Ready to enhance your material testing and formulation processes?
A two-roll mill is essential for precise R&D, quality control, and small-batch compounding. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including reliable two-roll mills, to meet the exacting needs of your laboratory.
Let us help you achieve superior material homogeneity and performance.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your polymer processing challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Open Type Two Roll Mixing Mill Machine for Rubber Crusher
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Jar Mill with Agate Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the screw extrusion process? A Guide to Continuous Plastic Profiling
- What is the process of pyrolysis of rubber? A Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Waste into Fuel
- How does extrusion work step by step? A Guide to the Continuous Manufacturing Process
- Why is calendering important? Achieve Superior Fabric Finishing for Your Textiles
- What are the advantages of coextrusion? Achieve Multi-Material Efficiency and Superior Performance
- What are the advantages of twin screw extruder? Superior Mixing, Flexibility & Efficiency
- How does a vulcanizing machine work? Mastering the Art of Rubber Transformation
- What is the difference between two-high and three high rolling mills? Boost Your Metal Rolling Efficiency



















