An auger reactor is a processing vessel that uses a large, rotating screw—known as an auger—to continuously transport material through a heated, enclosed chamber. It is primarily used for thermochemical conversion processes like pyrolysis where precise control over the movement and heating of solid materials is essential.
The core value of an auger reactor is its mechanical ability to handle difficult or non-uniform solid feedstocks and control their processing time. This makes it highly effective for maximizing the production of solid outputs, such as biochar, but less suitable for producing liquid bio-oils.
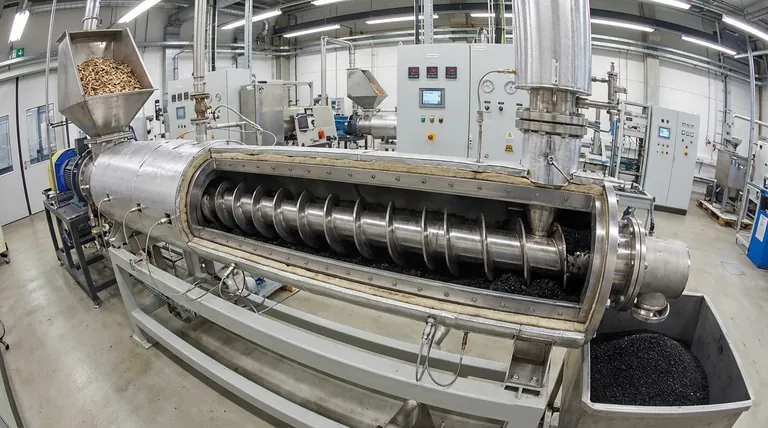

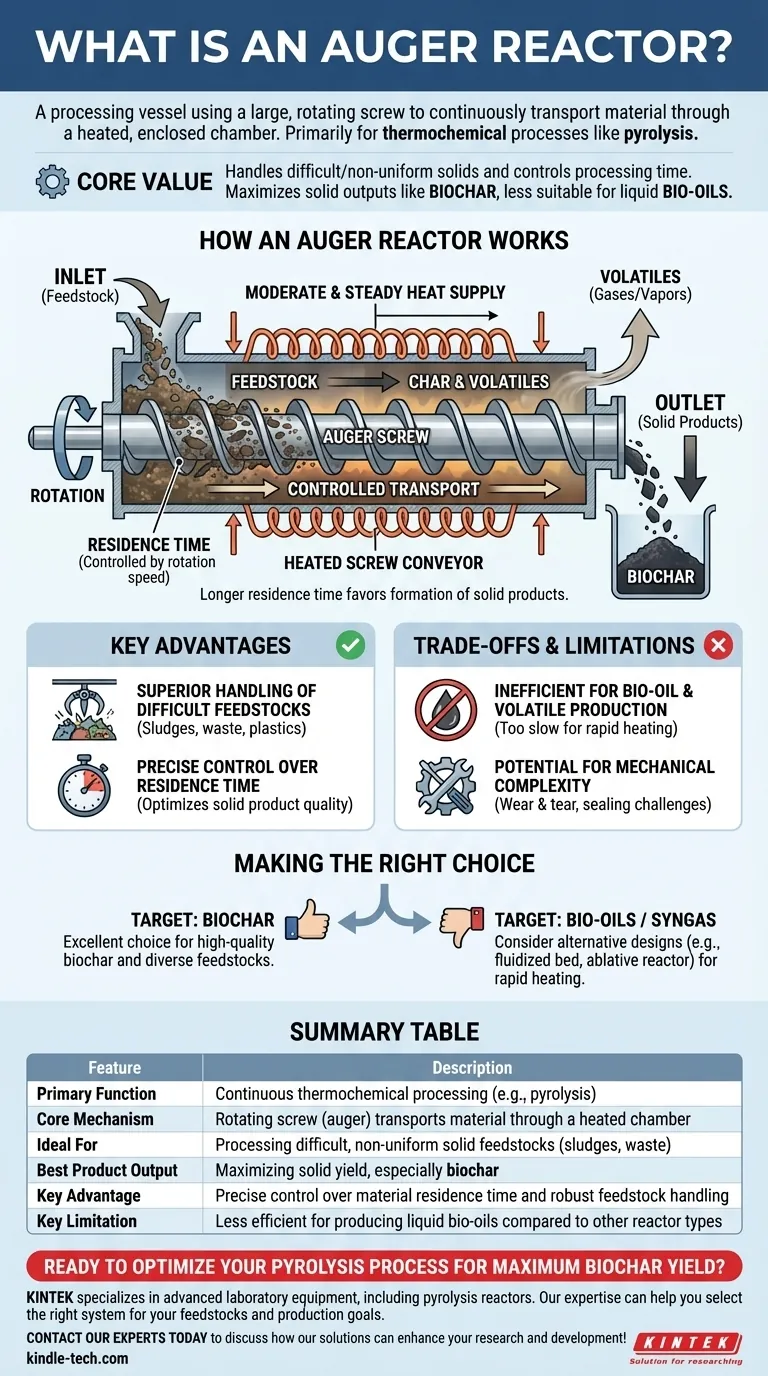
How an Auger Reactor Works
The Core Mechanism: A Heated Screw Conveyor
At its heart, an auger reactor operates on a simple, robust principle. Imagine a large meat grinder or a corkscrew inside a heated pipe.
The auger screw is the central component. As it rotates, its helical blades (or "flights") push the solid feedstock forward from the inlet to the outlet of the reactor.
The Process: Controlled Heating and Transport
The feedstock is fed into one end of the reactor. The screw conveys the material through the externally heated chamber at a consistent, predictable rate.
This design provides a moderate and steady heat supply directly to the material as it moves. The speed of the screw's rotation directly dictates the residence time—how long the material is exposed to the heat.
The Output: A Focus on Solid Products
Because the material is slowly and consistently heated while being transported, the process conditions typically favor the formation of solid products.
In pyrolysis, this longer residence time allows volatile gases to undergo secondary reactions, cracking and re-polymerizing into additional solid char, thus maximizing the biochar yield.
Key Advantages of the Auger Design
Superior Handling of Difficult Feedstocks
The mechanical force of the screw makes it exceptionally good at processing heterogeneous or difficult materials like sludges, agricultural waste, or plastics.
It can break up clumps and move irregularly shaped particles that would clog or fail to flow properly in other reactor types.
Precise Control Over Residence Time
The operator can precisely control the processing time by simply adjusting the rotational speed of the auger.
This level of control is critical for optimizing reactions where the solid product quality is the primary goal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Inefficient for Bio-oil and Volatile Production
The auger reactor's greatest strength is also its key limitation. Its moderate heating rate and longer residence time are not ideal for producing bio-oils.
Maximizing liquid yield requires extremely rapid heating (fast pyrolysis) to quickly vaporize the material and remove the volatiles before they can break down into char and non-condensable gases. The auger design is intentionally slow and methodical, making it poorly suited for this task.
Potential for Mechanical Complexity
As a system with large, moving parts operating at high temperatures, auger reactors can be subject to mechanical wear and require careful maintenance.
Ensuring a proper seal around the rotating screw to prevent air from entering the chamber—which would cause unwanted combustion—is a critical and often complex engineering challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an auger reactor must be driven by your desired final product.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: The auger reactor is an excellent choice due to its precise control over solids processing and its robust ability to handle diverse feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is producing bio-oils or syngas: You should consider alternative designs like a fluidized bed or ablative reactor, which are engineered for the rapid heating needed to maximize volatile yields.
Ultimately, the auger reactor excels as a purpose-built tool for the deliberate and controlled conversion of solid feedstocks into valuable solid products.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Continuous thermochemical processing (e.g., pyrolysis) |
| Core Mechanism | Rotating screw (auger) transports material through a heated chamber |
| Ideal For | Processing difficult, non-uniform solid feedstocks (sludges, waste) |
| Best Product Output | Maximizing solid yield, especially biochar |
| Key Advantage | Precise control over material residence time and robust feedstock handling |
| Key Limitation | Less efficient for producing liquid bio-oils compared to other reactor types |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum biochar yield?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis reactors. Our expertise can help you select the right system to handle your specific feedstocks and achieve your production goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is batch reactor pros and cons? Weighing Flexibility vs. Efficiency for Your Lab
- How is a high-pressure reactor used in the modification of photocatalytic membranes? Unlock Advanced In-Situ Synthesis
- Why is the use of zirconium or high-nickel alloys necessary for methanol carbonylation reactors? Ensure Process Safety
- What is the function of a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor? Optimize Fe3O4 Synthesis for Boron Adsorbents
- What is the significance of acid leaching reactors in graphite recycling? Ensure Battery-Grade Purity and Resilience
- How does residence time affect reaction rate? Maximize Conversion and Optimize Your Chemical Process
- What is the design pressure of SS reactor? A Guide to Defining Your Process-Specific Requirements
- How do thermocouples and data loggers monitor biomass degradation? Master Precision in High-Pressure Reactors













