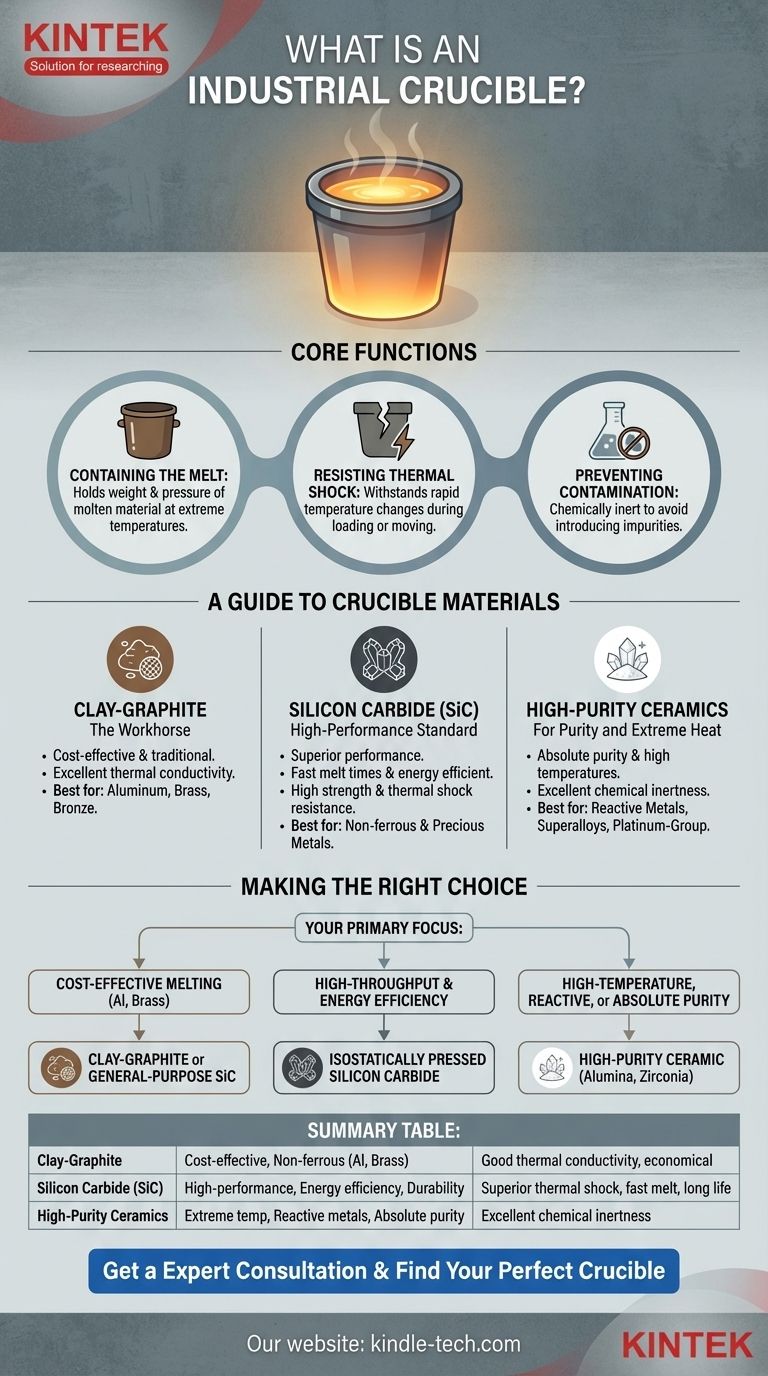
At its core, an industrial crucible is a high-performance container engineered to melt, hold, and process materials at extremely high temperatures. It is a fundamental component in foundries, metallurgy, and advanced materials manufacturing, serving as the vessel where solids are transformed into liquids under intense heat.
The critical insight is that a crucible is not merely a "pot for hot metal." It is a highly engineered tool where the choice of material is paramount, dictating the crucible's performance, lifespan, and the purity of the final product.

The Core Function: Surviving Extreme Environments
A crucible's job is to reliably contain a violent and reactive process. Its design and material science are focused on withstanding three primary challenges.
Containing the Melt
The most basic function is to act as a refractory vessel, holding the weight and pressure of molten material, which can range from hundreds to thousands of degrees Celsius.
The crucible must maintain its structural integrity at temperatures that would instantly destroy ordinary materials, preventing catastrophic failures.
Resisting Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the stress a material endures when its temperature changes rapidly. A crucible experiences this when cold metal is added to a hot vessel or when the crucible itself is moved into or out of a furnace.
A material's ability to resist cracking or shattering under this stress is a primary factor in its selection and is crucial for both safety and operational lifespan.
Preventing Contamination
The crucible material must be chemically inert, meaning it should not react with or dissolve into the molten substance it holds.
Any reaction can introduce impurities, altering the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the final alloy. This is especially critical when producing high-purity metals or specialized superalloys.
A Guide to Crucible Materials
The material is the most important feature of a crucible. The choice depends entirely on the application, balancing temperature requirements, chemical compatibility, and cost.
Clay-Graphite: The Workhorse
This composite material is a cost-effective and traditional choice, primarily used for melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze.
The graphite provides excellent thermal conductivity for efficient heat transfer, while the clay and other binders provide structural form and strength.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): The High-Performance Standard
Silicon carbide crucibles offer superior performance over clay-graphite. They have exceptional thermal conductivity, leading to faster melt times and better energy efficiency.
Their high mechanical strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical erosion make them a versatile and durable choice for a wide range of non-ferrous and precious metals.
High-Purity Ceramics: For Purity and Extreme Heat
When absolute purity is required or temperatures are exceptionally high, ceramics like Alumina (Al₂O₃), Zirconia (ZrO₂), and Magnesia (MgO) are used.
These materials are essential for melting reactive metals (like titanium), superalloys for aerospace, and platinum-group metals, where even minor contamination is unacceptable. They generally have lower thermal conductivity but superior chemical inertness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible is an exercise in engineering trade-offs. No single material is perfect for every task.
The Cost-Performance Equation
Clay-graphite crucibles have a low upfront cost but a shorter operational lifespan and lower temperature limits. Silicon carbide is more expensive but often provides a lower cost-per-melt due to its extended durability and efficiency. High-purity ceramics are the most expensive and are reserved for applications where their unique properties are essential.
Durability vs. Chemical Purity
Composite crucibles like SiC and clay-graphite are generally more robust and resistant to thermal shock. However, their binding agents can be a source of minor contamination. Monolithic ceramic crucibles offer the highest purity but can be more brittle and require more careful handling protocols.
Matching the Crucible to the Furnace
The heating method impacts the ideal crucible choice. In a fuel-fired furnace, high thermal conductivity (like SiC) is vital to transfer heat from the flame to the metal. In an induction furnace, the crucible's electrical properties matter; a conductive graphite crucible will heat up directly, while a non-conductive ceramic crucible allows the magnetic field to pass through and heat the metal itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal dictates the correct crucible. Consider the material you are melting, your budget, and your purity requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective melting of non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A clay-graphite or a general-purpose silicon carbide crucible is your most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production and energy efficiency: A high-quality, isostatically pressed silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of fast heat-up times and long service life.
- If your primary focus is melting high-temperature superalloys, reactive metals, or requires absolute purity: A high-purity ceramic crucible, such as alumina or zirconia, is non-negotiable to prevent contamination.
Understanding these principles transforms the crucible from a simple consumable into a strategic tool for controlling the outcome of your metallurgical process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Clay-Graphite | Cost-effective melting of non-ferrous metals (Al, Brass) | Good thermal conductivity, economical, traditional choice |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High-performance melting, energy efficiency, durability | Superior thermal shock resistance, fast melt times, long lifespan |
| High-Purity Ceramics | Extreme temperatures, reactive metals, absolute purity | Excellent chemical inertness (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia) |
Selecting the right crucible is critical to your process efficiency, product purity, and operational safety. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a comprehensive range of industrial crucibles tailored for your specific metallurgical needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between materials like silicon carbide and high-purity ceramics to find the perfect solution for your application. Contact us today to ensure your lab is equipped for success and discuss how our crucibles can enhance your results.
Get a Expert Consultation & Find Your Perfect Crucible
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use



















