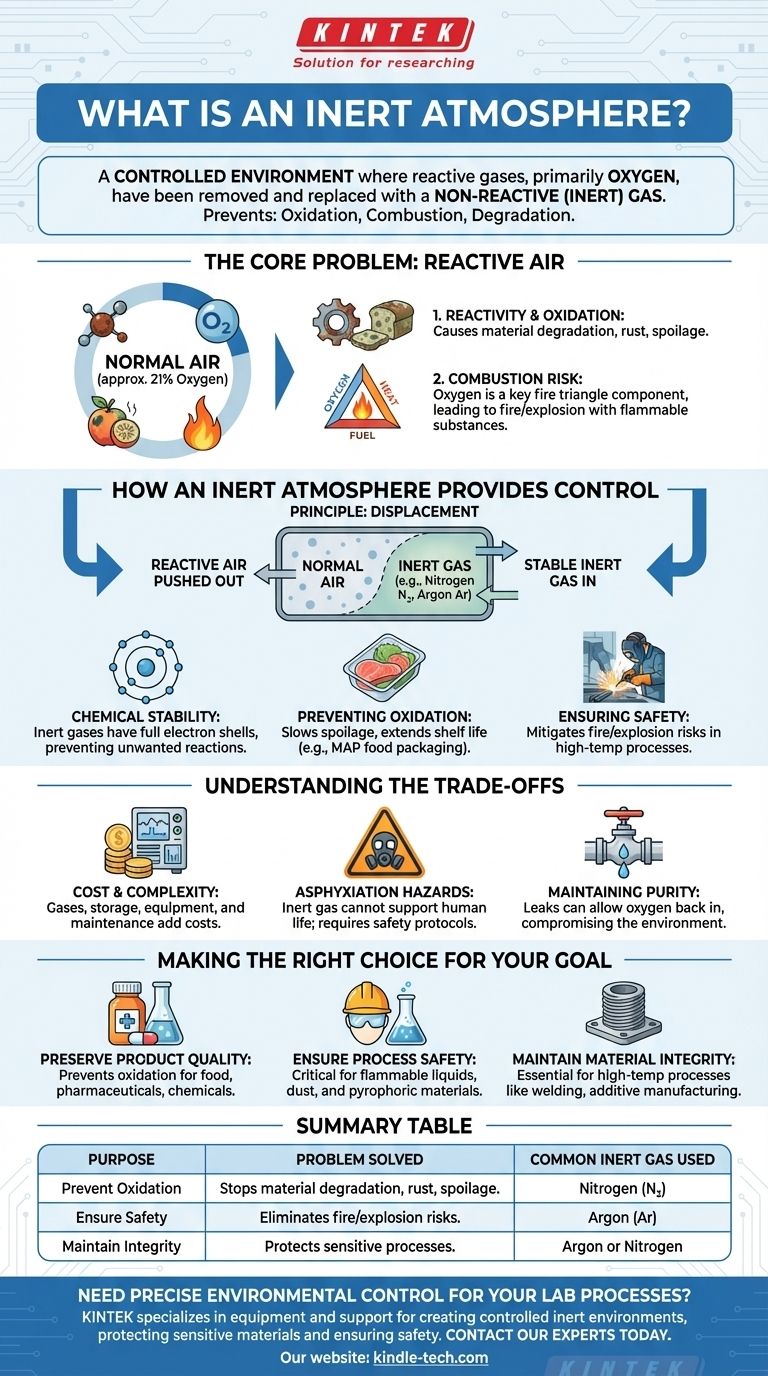
An inert atmosphere is a controlled environment from which reactive gases, primarily oxygen, have been removed and replaced with a non-reactive (inert) gas. This is done to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, combustion, or degradation of sensitive materials. It is a fundamental technique used across scientific research, industrial manufacturing, and food preservation.
The core purpose of an inert atmosphere is to gain control over a chemical environment. By replacing reactive air with a stable gas, you can intentionally stop or slow down natural processes like decay, rust, and fire, ensuring product quality, process safety, and material integrity.

The Core Problem: Why Normal Air Is Often an Issue
To understand the need for an inert atmosphere, we must first recognize the problems that normal air, and specifically its components, can cause in sensitive processes.
The Reactivity of Oxygen
The air we breathe is approximately 21% oxygen, which is a highly reactive element. This reactivity is responsible for countless chemical processes.
While essential for life, this tendency to react causes oxidation, a process that degrades materials. This includes the spoiling of food, the rusting of metals, and the breakdown of sensitive chemicals.
The Risk of Combustion
Oxygen is a critical component of the "fire triangle" along with heat and fuel. In many industrial processes that involve flammable substances or fine powders, the presence of oxygen creates a constant risk of fire or explosion.
Removing oxygen from the environment effectively breaks the fire triangle, making the process significantly safer.
How an Inert Atmosphere Provides Control
Creating an inert atmosphere is a solution based on a simple principle: displacement. By flooding a sealed space with a non-reactive gas, the reactive air is pushed out.
The Principle of Chemical Stability
The science behind this relies on the stability of inert gases. Gases like nitrogen and argon have full outer electron shells, making them chemically non-reactive under most conditions.
They do not readily bond with other elements, so they can exist in an environment without interfering with the materials or chemicals present. This stability prevents the unwanted reactions that oxygen would otherwise cause.
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
In food packaging, replacing air with nitrogen—a process called Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)—dramatically slows down spoilage and extends shelf life.
Similarly, in electronics manufacturing or chemical synthesis, an inert atmosphere protects sensitive components and reagents from degrading due to exposure to oxygen or moisture.
Ensuring Safety and Stability
In fields like chemical manufacturing or 3D metal printing, processes often involve high temperatures and flammable materials.
Operating within an inert atmosphere mitigates the risk of fire and explosions, allowing these processes to be performed safely and with predictable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, implementing an inert atmosphere is a deliberate engineering choice with specific considerations. It is not a universally necessary solution.
Cost and Complexity
The gases used, such as high-purity nitrogen or argon, have associated costs for purchase, storage, and handling. The equipment required to create and maintain the sealed, inert environment also adds mechanical complexity and cost to any operation.
Asphyxiation Hazards
The most critical safety concern is the risk of asphyxiation. An atmosphere that cannot support combustion or oxidation also cannot support human life. Strict safety protocols, including oxygen monitoring and ventilation, are essential in any area where inert gases are used.
Maintaining Purity
Achieving and maintaining a truly inert atmosphere can be challenging. Leaks in the container or system can allow oxygen to seep back in, compromising the integrity of the process and potentially negating the benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying an inert atmosphere is about matching the solution to a specific problem. Your primary objective will determine its value.
- If your primary focus is preserving product quality: An inert atmosphere is one of the most effective ways to prevent oxidation, extending the shelf life of food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
- If your primary focus is process safety: It is a non-negotiable safety measure when working with flammable liquids, combustible dusts, or pyrophoric materials.
- If your primary focus is material integrity: It is essential for high-temperature processes like welding or additive manufacturing, where it prevents the formation of oxides that weaken the final product.
Ultimately, creating an inert atmosphere is a fundamental tool for achieving precision and control, transforming an unpredictable environment into a stable and safe one.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Problem Solved | Common Inert Gas Used |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Oxidation | Stops material degradation, rust, and spoilage. | Nitrogen (N₂) |
| Ensure Safety | Eliminates fire/explosion risks from flammable materials. | Argon (Ar) |
| Maintain Integrity | Protects sensitive processes in manufacturing and R&D. | Argon or Nitrogen |
Need precise environmental control for your lab processes?
An inert atmosphere is key to ensuring safety, preventing contamination, and achieving reliable results in chemical synthesis, material processing, and sample preparation.
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and expert support to create and maintain these controlled environments. Our solutions help you protect sensitive materials and operate safely.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum or atmosphere control affect Beryllium during thermal deformation? Unlock Superior Material Integrity
- What is the typical composition of protective gas mixtures used in industrial heat treating? Master Atmosphere Control
- What is the primary role of a high-temperature atmosphere furnace in the production of activated carbon xerogels?
- How does a tube atmosphere furnace optimize niobium-promoted catalysts? Unlock SMSI for Fischer-Tropsch Excellence
- What are the hazards of inert gases? Understanding the Silent Threat of Asphyxiation
- How does a tube atmosphere furnace provide the necessary sintering environment for converting lignin foam? Expert Guide
- What are inert atmosphere conditions? Control Chemical Reactions and Ensure Safety
- What is a controlled atmosphere heat treatment furnace? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Results



















