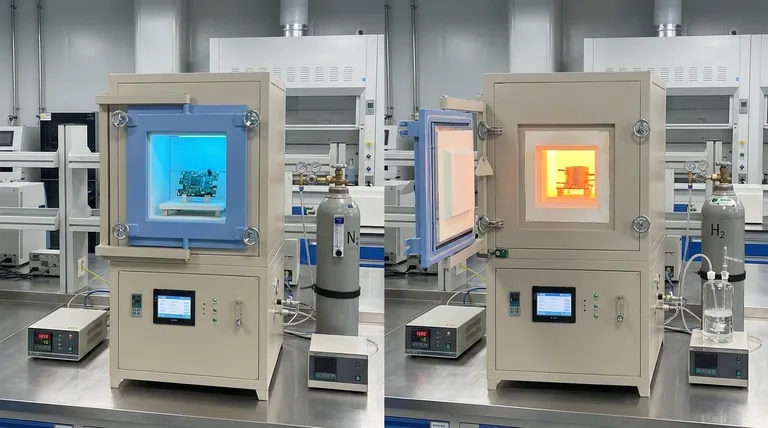
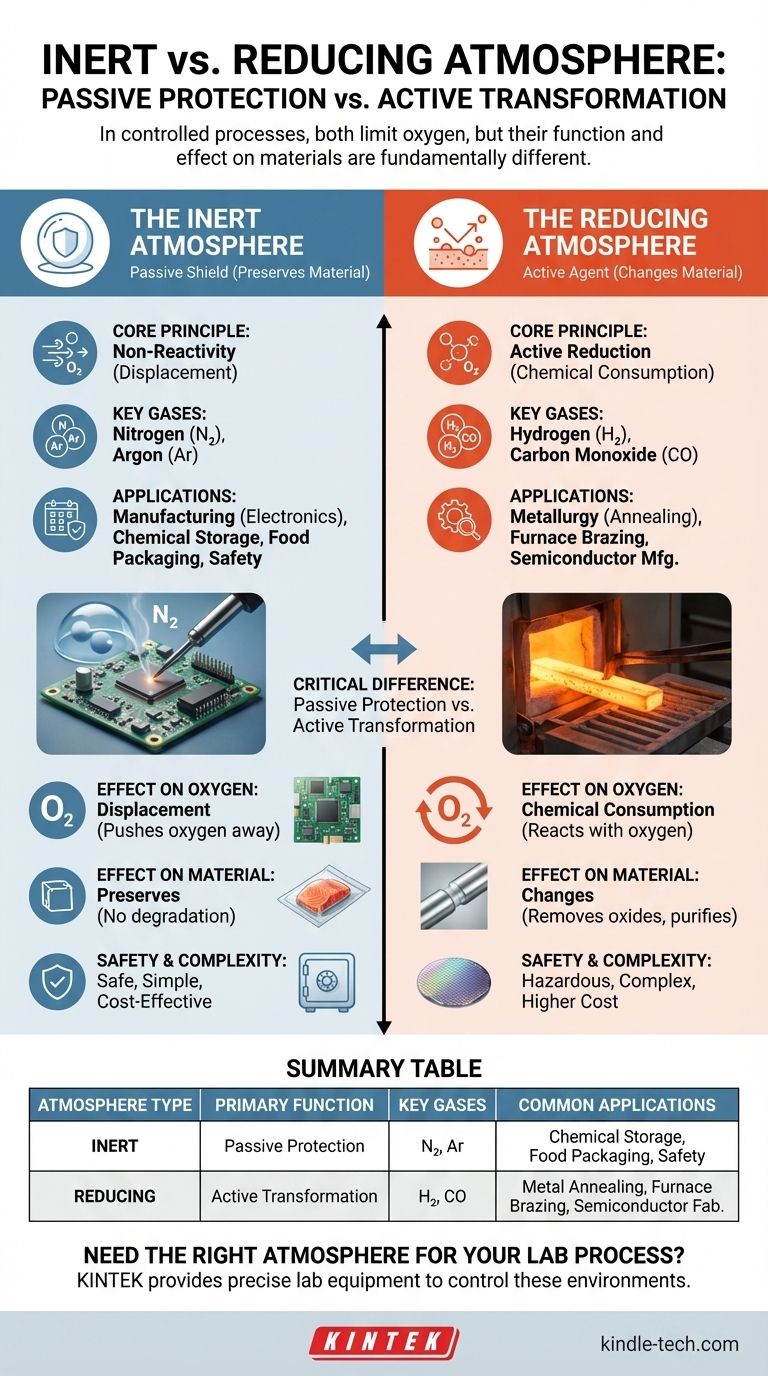
In controlled chemical and industrial processes, an inert atmosphere and a reducing atmosphere are both environments designed to limit the effects of oxygen. An inert atmosphere is chemically non-reactive, acting as a passive shield to prevent unwanted reactions like oxidation. A reducing atmosphere goes a step further; it is an active environment that not only lacks oxygen but also contains gases that can chemically reverse oxidation on a material's surface.
The critical difference lies in their function: an inert atmosphere is passive, simply preventing reactions by replacing oxygen. A reducing atmosphere is active, containing gases that not only prevent oxidation but can also chemically strip oxygen from materials.

The Inert Atmosphere: A Protective Shield
An inert atmosphere is the most common type of controlled environment used to prevent unwanted chemical changes. Its purpose is to protect a material or process from the highly reactive gases present in ambient air, primarily oxygen and water vapor.
The Core Principle: Non-Reactivity
The fundamental goal is to displace the reactive air with a gas that will not participate in chemical reactions. By flooding a chamber or container with a gas like nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar), you create a stable environment.
This acts as a protective bubble, effectively stopping oxidation, corrosion, and other forms of degradation before they can start. The material inside is simply preserved in its current state.
Common Applications
Inert atmospheres are critical where preservation is the goal. This includes:
- Manufacturing: Protecting sensitive electronic components from oxidation during soldering.
- Chemical Storage: Preventing the degradation of air-sensitive reagents.
- Food Packaging: Using nitrogen to displace oxygen and extend the shelf life of products like potato chips or coffee.
- Safety: Preventing fires or explosions by removing the oxygen component of the fire triangle in vessels containing flammable substances.
The Reducing Atmosphere: An Active Agent
A reducing atmosphere is a more specialized and chemically active environment. It is used when simply preventing oxidation is not enough—you must also reverse it.
The Core Principle: Driving Reduction
This atmosphere actively promotes reduction reactions, which involve an atom gaining electrons. In many industrial processes, this means chemically stripping oxygen atoms from a compound.
To achieve this, the environment is filled with reductant gases like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), or dissociated ammonia. These gases have a high affinity for oxygen and will react with any oxides present on a material's surface, effectively cleaning or purifying it.
Common Applications
Reducing atmospheres are essential in processes where the material's surface chemistry must be actively changed:
- Metallurgy: During the heat treatment (annealing) of steel, a reducing atmosphere removes surface oxides, resulting in a bright, clean finish.
- Furnace Brazing: Ensuring a strong, pure metal-to-metal bond by removing any oxides that would interfere with the process.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Creating ultra-pure surfaces required for fabricating integrated circuits.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
Choosing the right atmosphere requires understanding the trade-offs between passive protection and active treatment. The incorrect choice can lead to process failure or damaged materials.
Effect on Oxygen
An inert atmosphere works by displacement. It simply pushes the oxygen out of the way. If a small leak occurs, oxygen can enter and cause localized oxidation.
A reducing atmosphere works by chemical consumption. The active gases will seek out and react with any trace oxygen, effectively "scrubbing" it from the environment and from the material's surface.
Effect on the Material
An inert atmosphere preserves a material. It ensures the product you put in is the same product you take out, just without any air-induced degradation.
A reducing atmosphere changes a material. It chemically alters the surface by removing oxides, which can be a critical step in preparing it for subsequent processes.
Safety and Complexity
Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are relatively safe and easy to handle.
Reducing gases are often hazardous. Hydrogen is highly flammable, and carbon monoxide is toxic, requiring more complex equipment, rigorous safety protocols, and higher operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice depends entirely on whether your goal is to simply protect a material or to actively transform its surface chemistry.
- If your primary focus is preservation or safety: Use an inert atmosphere. It is the standard for preventing degradation, combustion, or oxidation without altering the material itself.
- If your primary focus is purification or surface cleaning: Use a reducing atmosphere. It is necessary when you must actively remove existing oxides, such as in metal heat treatment or furnace brazing.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and simplicity: An inert atmosphere is almost always the less complex and more affordable solution for general-purpose protection.
Understanding this distinction between passive protection and active chemical change empowers you to select the precise atmospheric control your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Primary Function | Key Gases Used | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Passive Protection (Prevents oxidation) | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Chemical storage, food packaging, safety |
| Reducing | Active Transformation (Removes oxides) | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Metal annealing, furnace brazing, semiconductor fabrication |
Need the Right Atmosphere for Your Lab Process?
Choosing between an inert atmosphere for protection and a reducing atmosphere for purification is critical for your results. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables to create and control these environments, ensuring your materials are processed correctly—whether you need simple preservation or active surface cleaning.
Let our experts help you select the ideal solution for your application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments
- What is the role of nitrogen in annealing process? Creating a Controlled, Protective Atmosphere
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment



















