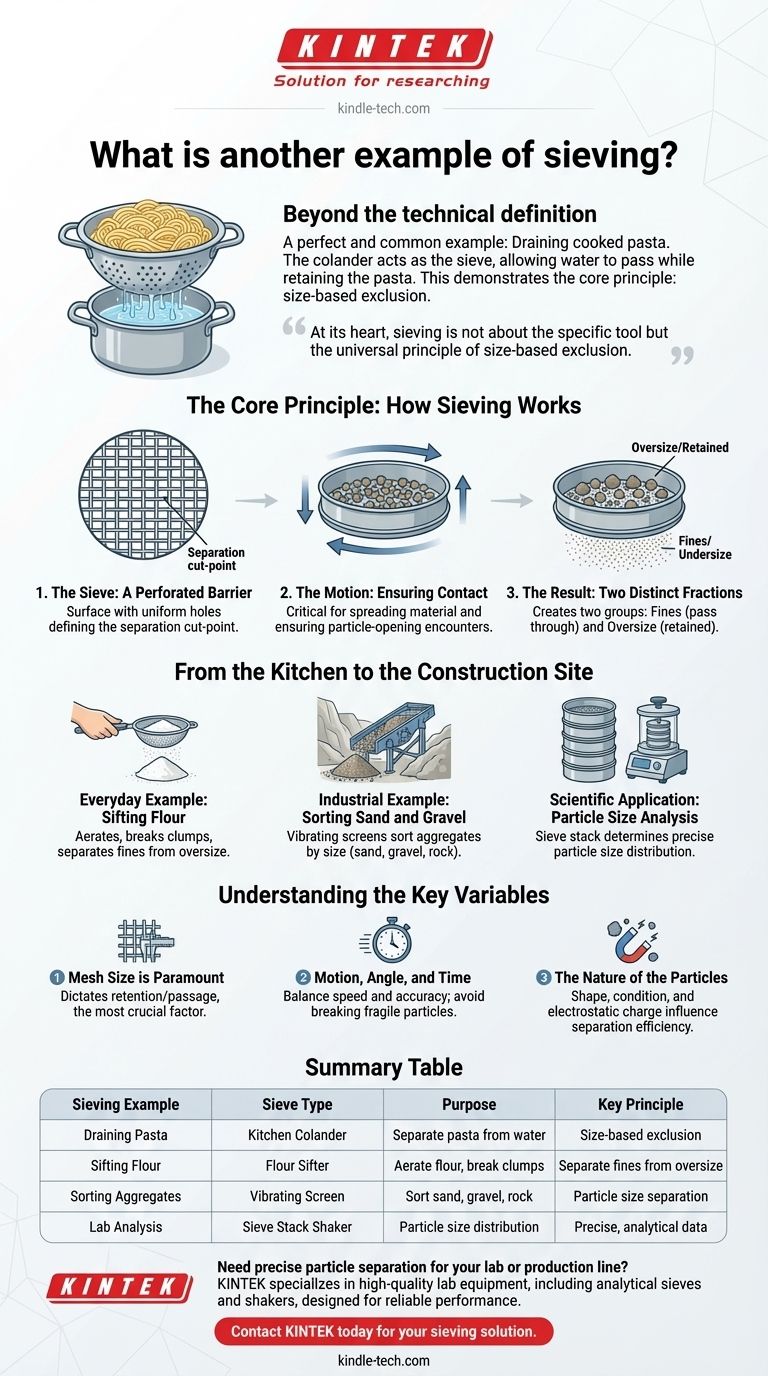
Beyond the technical definition, a perfect and common example of sieving is using a colander to drain cooked pasta. The colander acts as the sieve, its holes allowing the water to pass through freely while its solid surface retains the much larger pasta. This simple kitchen task demonstrates the core principle of sieving: using a perforated barrier to physically separate components of a mixture based on their size.
At its heart, sieving is not about the specific tool but the universal principle of size-based exclusion. It is a fundamental method of physical separation that relies on a barrier with specific-sized openings to sort a mixture into two groups: those that can pass through and those that cannot.

The Core Principle: How Sieving Works
Sieving is an intuitive process, but its effectiveness in technical applications relies on a few key factors that work in concert. Understanding these clarifies how a simple concept becomes a powerful analytical and industrial tool.
The Sieve: A Perforated Barrier
The essential component of any sieving operation is the sieve itself. This is simply a surface—often a wire mesh or a perforated plate—containing holes of a uniform size and shape.
These openings define the separation cut-point. Anything smaller than the openings can potentially pass through, while anything larger is retained.
The Motion: Ensuring Contact
A sample simply resting on a sieve will not separate efficiently. As the references note, vertical or horizontal motion is critical to the process.
Shaking, vibrating, or tumbling the sieve serves two purposes. First, it spreads the material across the entire surface, maximizing the use of the available area. Second, and more importantly, it ensures that each particle has multiple opportunities to encounter an opening and pass through if it is small enough.
The Result: Two Distinct Fractions
The outcome of any sieving process is the creation of two separate material groups, known as fractions.
The material that passes through the mesh is called the "fines" or "undersize". The material that remains on top of the sieve surface is called the "oversize" or "retained" fraction.
From the Kitchen to the Construction Site
The principle of sieving is applied across countless industries at vastly different scales. The underlying concept remains identical.
Everyday Example: Sifting Flour
When baking, a cook sifts flour to break up clumps and aerate it. The sifter's mesh screen holds back the larger, compacted clumps of flour while allowing the fine, individual particles to pass through, resulting in a lighter final product.
Industrial Example: Sorting Sand and Gravel
At a quarry or construction site, large vibrating screens are used to sort aggregates. A mixture of rock, gravel, and sand is loaded onto a screen. The fine sand falls through, while larger rocks and gravel are retained and can be sorted further with different mesh sizes.
Scientific Application: Particle Size Analysis
In laboratories, scientists use a stack of analytical sieves, each with a progressively smaller mesh size, to determine the particle size distribution of a sample.
The sample is placed on the top sieve (the one with the largest holes), and the entire stack is shaken. Particles are sorted down through the stack until they reach a sieve they cannot pass. By weighing the material retained on each sieve, a precise profile of the sample's composition can be created.
Understanding the Key Variables
Optimizing a sieving process means controlling the factors that influence its efficiency and accuracy. The goal is not always perfect separation but achieving the right separation for a specific purpose.
Mesh Size is Paramount
The size of the openings in the sieve mesh is the single most important variable. It directly dictates which particles are retained and which pass through. Choosing the correct mesh size is the first step in any sieving application.
Motion, Angle, and Time
The type and intensity of motion matter. Aggressive shaking can speed up separation but may also cause fragile particles to break, which would skew an analytical result by creating more "fines." The angle of the sieve and the duration of the process are also adjusted to balance speed with accuracy.
The Nature of the Particles
The shape and condition of the particles themselves play a significant role. Long, needle-shaped particles may pass through a mesh end-on even if their volume is technically too large. Likewise, wet, sticky, or electrostatically charged materials can clump together and clog the sieve openings, preventing proper separation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" sieving method depends entirely on what you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is a quick, rough separation: A single sieve with an appropriate mesh size and manual agitation is sufficient for tasks like gardening or basic food preparation.
- If your primary focus is precise, analytical data: A standardized stack of calibrated sieves operated by a mechanical shaker for a set duration is necessary for quality control or scientific research.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of sieving empowers you to control the physical properties of materials, a foundational capability in science and industry alike.
Summary Table:
| Sieving Example | Sieve Type | Purpose | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Draining Pasta | Kitchen Colander | Separate pasta from water | Size-based exclusion |
| Sifting Flour | Flour Sifter | Aerate flour, break clumps | Separate fines from oversize |
| Sorting Aggregates | Vibrating Screen | Sort sand, gravel, rock | Particle size separation |
| Lab Analysis | Sieve Stack Shaker | Particle size distribution | Precise, analytical data |
Need precise particle separation for your lab or production line? The right sieving equipment is critical for accurate results, from quality control to R&D. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including analytical sieves and shakers, designed to deliver reliable performance for your specific application. Let our experts help you select the ideal sieving solution. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision



















