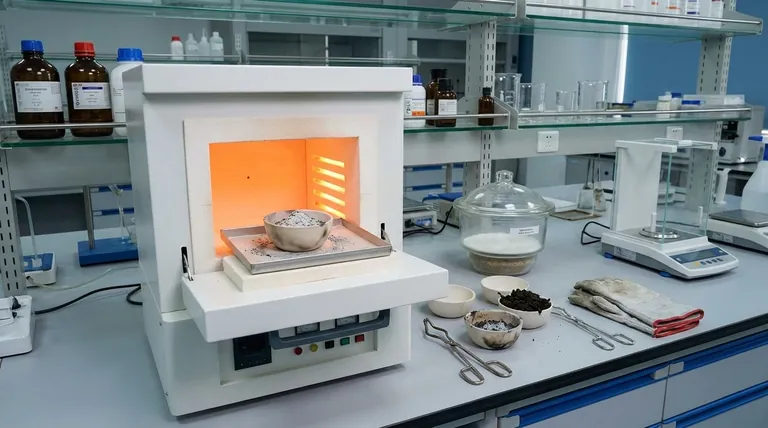
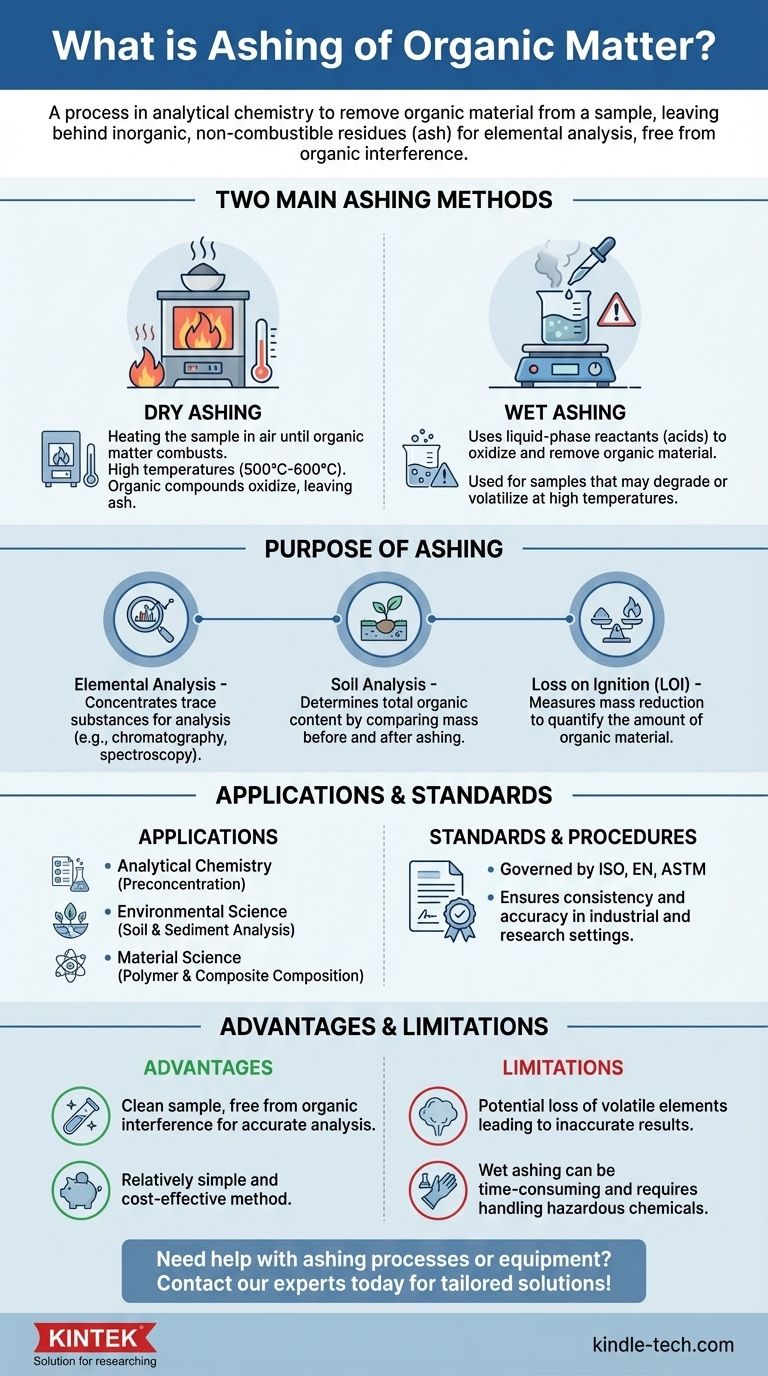
Ashing of organic matter is a process used in analytical chemistry to remove organic material from a sample, leaving behind inorganic, non-combustible residues known as ash. This process is essential for analyzing the elemental composition of a sample, as it eliminates unwanted organic compounds that could interfere with the analysis. Ashing can be performed through two main methods: dry ashing and wet ashing. Dry ashing involves heating the sample in air until the organic matter combusts, while wet ashing uses liquid-phase reactants, such as acids, to oxidize and remove organic material. The process is often governed by international standards and can include specific objectives like Loss on Ignition (LOI), where the mass reduction of the sample is measured before and after ashing. Ashing is widely used in various fields, including soil analysis, to determine the organic content of samples.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Ashing:
- Ashing is a process used to remove organic material from a sample, leaving behind inorganic residues (ash).
- This process is crucial for elemental composition analysis, as it eliminates organic compounds that could interfere with the results.
-
Types of Ashing:
-
Dry Ashing:
- Involves heating the sample in air until the organic matter combusts.
- The organic compounds react with oxygen, oxidizing and leaving behind inorganic ash.
- This method is often used for samples that can withstand high temperatures.
-
Wet Ashing:
- Uses liquid-phase reactants, such as combinations of acids, to oxidize and remove organic material.
- This method is typically used for samples that may degrade or volatilize at high temperatures.
-
Dry Ashing:
-
Purpose of Ashing:
-
Elemental Analysis:
- Ashing is used to concentrate trace substances in a sample, making it easier to perform chemical analyses such as chromatography or optical analyses like spectroscopy.
-
Soil Analysis:
- In soil science, ashing helps determine the total organic content by comparing the mass of the sample before and after ashing.
-
Loss on Ignition (LOI):
- A specific objective of ashing where the sample is weighed before and after the process to determine the mass reduction, which indicates the amount of organic material present.
-
Elemental Analysis:
-
Standards and Procedures:
- The ashing process is often governed by international standards such as ISO, EN, or ASTM.
- These standards ensure consistency and accuracy in the ashing process, particularly in industrial and research settings.
-
Applications of Ashing:
-
Analytical Chemistry:
- Ashing is a critical step in the preconcentration of trace elements for further analysis.
-
Environmental Science:
- Used in soil and sediment analysis to determine organic content and assess environmental contamination.
-
Material Science:
- Ashing can be used to analyze the composition of materials, such as polymers or composites, by removing organic binders or fillers.
-
Analytical Chemistry:
-
Process Details:
-
Sample Preparation:
- Samples must be prepared appropriately before ashing, which may include drying, grinding, or homogenizing.
-
Heating Process:
- In dry ashing, samples are heated in a furnace at high temperatures (typically between 500°C to 600°C) until all organic matter is combusted.
-
Residue Analysis:
- The remaining ash is then analyzed to determine the inorganic composition of the sample.
-
Sample Preparation:
-
Advantages and Limitations:
-
Advantages:
- Ashing provides a clean sample free from organic interference, which is essential for accurate elemental analysis.
- It is a relatively simple and cost-effective method for sample preparation.
-
Limitations:
- Some samples may lose volatile elements during the ashing process, leading to inaccurate results.
- Wet ashing, while effective, can be more time-consuming and requires careful handling of hazardous chemicals.
-
Advantages:
By understanding the ashing process, its methods, and applications, one can effectively utilize this technique in various scientific and industrial contexts to achieve accurate and reliable analytical results.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Removal of organic material, leaving inorganic ash for analysis. |
| Types | - Dry Ashing: Heating in air. - Wet Ashing: Using acids for oxidation. |
| Purpose | - Elemental analysis. - Soil analysis. - Loss on Ignition (LOI). |
| Standards | Governed by ISO, EN, ASTM for consistency and accuracy. |
| Applications | Analytical chemistry, environmental science, material science. |
| Advantages | Clean samples, cost-effective, simple. |
| Limitations | Potential loss of volatile elements, hazardous chemical handling. |
Need help with ashing processes or equipment? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature of a muffle furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Application
- How do you take care of a muffle furnace? Extend Equipment Life and Ensure Accurate Results
- How do you use a muffle furnace in a lab? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe & Precise Operation
- What is the muffle furnace analysis? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing for Your Materials
- What are the four steps to the heat treating process? Master the 3 Core Stages for Superior Results



















